
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
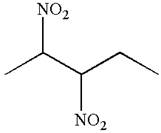
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentane. The parent chain has two identical substituents; thus the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
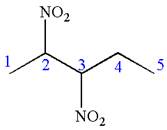
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
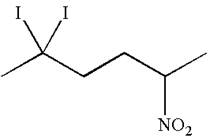
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is hexane. The parent chain has three substituents; thus the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
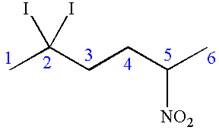
The substituents are arranged in an alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
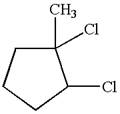
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The ring has three substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
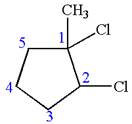
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
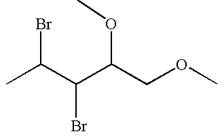
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The parent chain has four substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
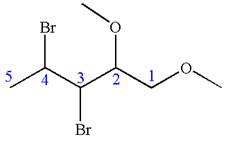
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
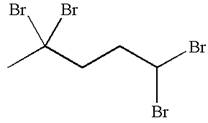
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The parent chain has four identical substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
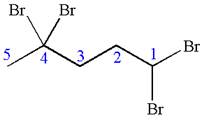
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents in a way to provide the lowest set of locants.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
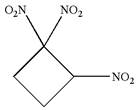
In this molecule, the four carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclobutane. The ring has three identical substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
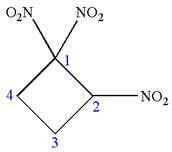
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(g)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
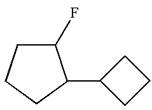
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The ring has two substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
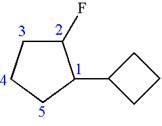
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(h)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
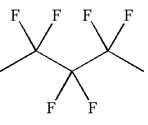
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentane. The parent chain has six identical substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
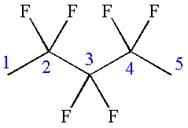
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(i)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
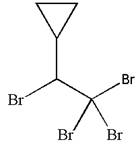
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has two carbon atoms. Hence, the root is ethane. The parent chain has five substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
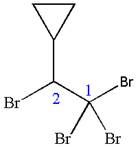
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(j)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
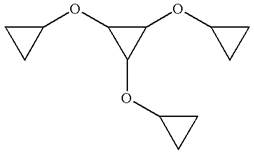
In this molecule, the middle ring of three carbons is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopropane. The ring has three identical substituents.
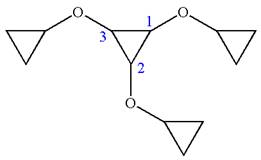
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Tarrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Indicate which of the following mechanisms is in operation: SN1, SN2, E1, or E2.arrow_forward(c) (4pts) Mechanism: heat (E1) CH3OH + 1.5pts each _E1 _ (1pt) Br CH3OH (d) (4pts) Mechanism: SN1 (1pt) (e) (3pts) 1111 I H 10 Ill!! H LDA THF (solvent) Mechanism: E2 (1pt) NC (f) Bri!!!!! CH3 NaCN (3pts) acetone Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) (SN1) -OCH3 OCH3 1.5pts each 2pts for either product 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H Br (g) “,、 (3pts) H CH3OH +21 Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) H CH3 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistryarrow_forward
- A mixture of butyl acrylate and 4'-chloropropiophenone has been taken for proton NMR analysis. Based on this proton NMR, determine the relative percentage of each compound in the mixturearrow_forwardQ5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forwardCalculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structurearrow_forward

 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax



