
Derivatives; interest rate swap; fixed-rate debt; fair value change unrelated to hedged
(Note: This is a variation of Exercise A–5, modified to consider fair value change unrelated to hedged risk.)
On January 1, 2018, LLB Industries borrowed $200,000 from Trust Bank by issuing a two-year, 10% note, with interest payable quarterly. LLB entered into a two-year interest rate swap agreement on January 1, 2018, and designated the swap as a fair value hedge. Its intent was to hedge the risk that general interest rates will decline, causing the fair value of its debt to increase. The agreement called for the company to receive payment based on a 10% fixed interest rate on a notional amount of $200,000 and to pay interest based on a floating interest rate. The contract called for cash settlement of the net interest amount quarterly.
Floating (LIBOR) settlement rates were 10% at January 1, 8% at March 31, and 6% June 30, 2018. The fair values of the swap are quotes obtained from a derivatives dealer. Those quotes and the fair values of the note are as indicated below. The additional rise in the fair value of the note (higher than that of the swap) on June 30 was due to investors’ perceptions that the creditworthiness of LLB was improving.
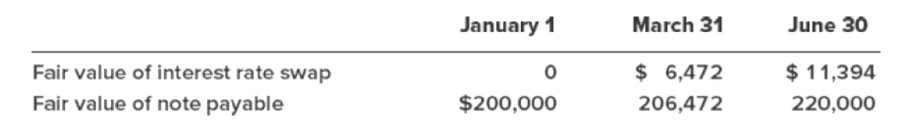
Required:
- 1. Calculate the net cash settlement at June 30, 2018.
- 2. Prepare the
journal entries on June 30, 2018, to record the interest and necessary adjustments for changes in fair value. Use the extended method demonstrated in Illustration A–3.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter A Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- I need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning


