
Derivatives; interest rate swap
On January 1, 2018, Labtech Circuits borrowed $100,000 from First Bank by issuing a three-year, 8% note, payable on December 31, 2020. Labtech wanted to hedge the risk that general interest rates will decline, causing the fair value of its debt to increase. Therefore, Labtech entered into a three-year interest rate swap agreement on January 1, 2018, and designated the swap as a fair value hedge. The agreement called for the company to receive payment based on an 8% fixed interest rate on a notional amount of $100,000 and to pay interest based on a floating interest rate tied to LIBOR. The contract called for cash settlement of the net interest amount on December 31 of each year.
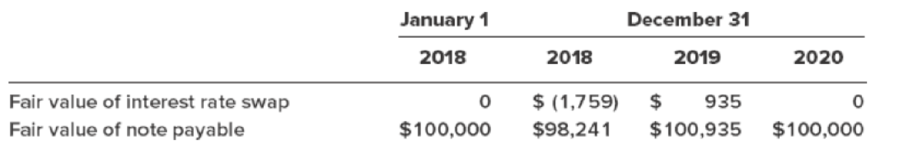
Floating (LIBOR) settlement rates were 8% at inception and 9%, 7%, and 7% at the end of 2018, 2019, and 2020, respectively. The fair values of the swap are quotes obtained from a derivatives dealer. These quotes and the fair values of the note are as follows:
Required:
- 1. Calculate the net cash settlement at the end of 2018, 2019, and 2020.
- 2. Prepare the
journal entries during 2018 to record the issuance of the note, interest, and necessary adjustments for changes in fair value. - 3. Prepare the journal entries during 2019 to record interest, net cash interest settlement for the interest rate swap, and necessary adjustments for changes in fair value.
- 4. Prepare the journal entries during 2020 to record interest, net cash interest settlement for the interest rate swap, necessary adjustments for changes in fair value, and repayment of the debt.
- 5. Calculate the book values of both the swap account and the note in each of the three years.
- 6. Calculate the net effect on earnings of the hedging arrangement in each of the three years. (Ignore income taxes.)
- 7. Suppose the fair value of the note at December 31, 2018, had been $97,000 rather than $98,241, with the additional decline in fair value due to investors’ perceptions that the creditworthiness of Labtech was worsening. How would that affect your entries to record changes in the fair values?
(1)
Derivatives: Derivatives are some financial instruments which are meant for managing risk and safeguard the risk created by other financial instruments. These financial instruments derive the values from the future value of underlying security or index. Some examples of derivatives are forward contracts, interest rate swaps, futures, and options.
Interest rate swap: This is a type of derivative used by two parties under a contract to exchange the consequences (net cash difference between interest payments) of fixed interest rate for floating interest rate, or vice versa, without exchanging the principal or notional amounts.
To determine: The net cash settlement as at December 31, 2018, 2019, and 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the net cash settlement as at December 31, 2018.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Fixed interest payments | $8,000 |
| Floating interest payments | (9,000) |
| Net interest receipts (payments) | $(1,000) |
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Compute fixed interest receipts.
| Computation of Fixed Interest Receipts | ||||||
| Notional Amount ($) | Fixed Interest Rate | Time Period | = | Fixed Interest Receipts (S) | ||
| $100,000 | 8% | 1 year | = | $8,000 | ||
Table (2)
Compute floating interest payments.
| Computation of Floating Interest Payments | ||||||
| Notional Amount ($) | Floating Interest Rate | Time Period | = | Floating Interest Payments (S) | ||
| $100,000 | 9% | 1 year | = | $9,000 | ||
Table (3)
Determine the net cash settlement as at December 31, 2019.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Fixed interest payments | $8,000 |
| Floating interest payments | (7,000) |
| Net interest receipts (payments) | $1,000 |
Table (4)
Working Notes:
Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Compute floating interest payments.
| Computation of Floating Interest Payments | ||||||
| Notional Amount ($) | Floating Interest Rate | Time Period | = | Floating Interest Payments (S) | ||
| $100,000 | 7% | 1 year | = | $7,000 | ||
Table (5)
Determine the net cash settlement as at December 31, 2020.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Fixed interest payments | $8,000 |
| Floating interest payments | (7,000) |
| Net interest receipts (payments) | $1,000 |
Table (6)
Working Notes:
Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Compute floating interest payments.
| Computation of Floating Interest Payments | ||||||
| Notional Amount ($) | Floating Interest Rate | Time Period | = | Floating Interest Payments (S) | ||
| $100,000 | 7% | 1 year | = | $7,000 | ||
Table (7)
(2)
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
To journalize: The entries of issue of note, interest payments, and adjustment entries to reflect fair value during 2018
Explanation of Solution
Entry for issuance of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| January | 1 | Cash | 100,000 | ||
| Notes Payable | 100,000 | ||||
| (To record issuance of note) | |||||
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since obligation to pay the note increased, liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Entry for interest expense payment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 8,000 | ||||
| (To record interest expense payment) | |||||
Table (9)
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Note: Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Entry for net cash settlement:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 1,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,000 | ||||
| (To record net cash settlement which is the difference between fixed interest and variable interest) | |||||
Table (10)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for net cash settlement value.
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since fixed interest payment is paid as per the agreement, the expense value increased, and an increase in expense is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of interest swap:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap | 1,759 | ||
| Interest Rate Swap | 1,759 | ||||
| (To record decrease in fair value from $0 to $(1,759)) | |||||
Table (11)
- Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap is a loss account. Since interest rate increased causing holding loss increase, which decrease equity, so equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Interest Rate Swap is a liability account because the fair value has decreased from $0 to $(1,759), and a decrease in asset is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Notes Payable | 1,759 | ||
| Holding Gain–Hedged Note | 1,759 | ||||
| (To record decrease in fair value from $100,000 to $98,241) | |||||
Table (12)
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since fair value of the note decreased, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Holding Gain–Hedged Note is a revenue account. The fair value of hedged liability has decreased causing a holding gain. Since holding gains increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
(3)
To journalize: The entries of issue of note, interest payments, and adjustment entries to reflect fair value during 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Entry for interest expense payment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 8,000 | ||||
| (To record interest expense payment) | |||||
Table (13)
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Note: Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Entry for net cash settlement:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | |||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 1,000 | ||
| Interest Expense | 1,000 | ||||
| (To record net cash settlement which is the difference between fixed interest and variable interest) | |||||
Table (14)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for net cash settlement value.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since fixed interest payment is received as per the agreement, the expense value decreased, and a decrease in expense is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of interest swap:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Rate Swap | 2,694 | ||
| Holding Gain–Interest Rate Swap | 2,694 | ||||
| (To record increase in fair value from $(1,759) to $935) | |||||
Table (15)
- Interest Rate Swap is an asset account because the fair value has increased from $(1,759) to $935 causing an increase of $2,694, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Holding Gain–Interest Rate Swap is a revenue account. Since holding gains increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | |||||
| December | 31 | Holding Loss–Hedged Note | 2,694 | ||
| Note Payable | 2,694 | ||||
| (To record increase in fair value from $98,241 to $100,935) | |||||
Table (16)
- Holding Loss–Hedged Note is a loss account. The fair value of hedged liability has increased causing a holding loss. Since holding losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since fair value of the note increased, liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
(4)
To journalize: The entries of issue of note, interest payments, and adjustment entries to reflect fair value during 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Entry for interest expense payment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2020 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 8,000 | ||||
| (To record interest expense payment) | |||||
Table (17)
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Note: Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Entry for net cash settlement:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2020 | |||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 1,000 | ||
| Interest Expense | 1,000 | ||||
| (To record net cash settlement which is the difference between fixed interest and variable interest) | |||||
Table (18)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for net cash settlement value.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since fixed interest payment is received as per the agreement, the expense value decreased, and a decrease in expense is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of interest swap:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2020 | |||||
| December | 31 | Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap | 935 | ||
| Interest Rate Swap | 935 | ||||
| (To record change in fair value from $935 to $0) | |||||
Table (19)
- Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap is a loss account. Since holding losses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Interest Rate Swap is a liability account because the fair value has increased causing an increase in the obligation, and an increase in liability is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2020 | |||||
| December | 31 | Notes Payable | 935 | ||
| Holding Gain–Hedged Note | 935 | ||||
| (To record decrease in fair value of note from $100,935 to $100,000) | |||||
Table (20)
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since fair value of the note decreased, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Holding Gain–Hedged Note is a revenue account. The fair value of hedged liability has decreased causing a holding gain. Since holding gains increase equity, so equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Entry for repayment of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2020 | |||||
| December | 31 | Notes Payable | 100,000 | ||
| Cash | 100,000 | ||||
| (To record note being paid) | |||||
Table (21)
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since obligation to pay the note is decreased, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
(5)
Explanation of Solution
Determine the book value of swap in the years 2018, 2019, and 2020.
| Interest Rate Swap | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | 2018 | |||||
| January 1 | December 31 | Holding loss | 1,759 | |||
| Total | $0 | Total | $1,759 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $1,759 | ||||
| 2019 | 2019 | |||||
| December 31 | Holding gain | 2,694 | January 1 | Balance | $1,759 | |
| Total | 2,694 | Total | $1,759 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $935 | ||||
| 2020 | 2020 | |||||
| January 1 | Balance | 935 | December 31 | Holding loss | 935 | |
| Total | 935 | Total | 935 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $0 | ||||
Table (22)
Note: Refer to Requirements 2, 3, and 4 for values and computation of all values.
Determine the book value of note in the years 2018, 2019, and 2020.
| Note Payable | ||||||
| Date | Details | Debit ($) | Date | Details | Credit ($) | |
| 2016 | 2016 | |||||
| December 31 | Holding gain | 1,759 | January 1 | Cash | 100,000 | |
| Total | $0 | Total | 100,000 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $98,241 | ||||
| 2017 | 2017 | |||||
| December 31 | January 1 | Balance | $98,241 | |||
| Holding loss | 2,694 | |||||
| Total | 0 | Total | $100,935 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $100,935 | ||||
| 2018 | 2018 | |||||
| December 31 | Holding gain | 935 | January 1 | Balance | 100,935 | |
| Cash | 100,000 | |||||
| Total | 100,935 | Total | 100,935 | |||
| December 31 | Balance | $0 | ||||
Table (23)
Note: Refer to Requirements 2, 3, and 4 for values and computation of all values.
(6)
Explanation of Solution
Determine the net effect of fair value hedge on earnings for the years 2018, 2019, and 2020.
| L Circuits | |||
| Income Statement | |||
| For the Years Ended December 31, 2018, 2019, and 2020 | |||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| Interest expense (Fixed receipts) | (8,000) | (8,000) | (8,00) |
| Interest expense (Net cash settlement) | (1,000) | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| Holding gain (loss)–Interest rate swap | (1,759) | 2,694 | (935) |
| Holding gain (loss)–Hedged note | 1,759 | (2,694) | 935 |
| Net effect on earnings (Floating interest payment on swap) | (9,000) | (7,000) | (7,000) |
Table (24)
Note: Refer to requirements 1, 2, 3, and 4 for values and computation of all values.
(7)
To journalize: The entries of issue of note, interest payments, and adjustment entries to reflect fair value during 2018, if fair value would have been $97,000 rather than $98,241.
Explanation of Solution
The additional decline in fair value from $98,241 to $97,000 would not make any difference in the entries because the reason for decline is not related to interest rate.
Entry for interest expense payment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 8,000 | ||||
| (To record interest expense payment) | |||||
Table (25)
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Note: Refer to Table (2) for value and computation of fixed interest payments.
Entry for net cash settlement:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Interest Expense | 1,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,000 | ||||
| (To record net cash settlement which is the difference between fixed interest and variable interest) | |||||
Table (26)
Note: Refer to Table (1) for net cash settlement value.
- Interest Expense is an expense account. Since fixed interest payment is paid as per the agreement, the expense value increased, and an increase in expense is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of interest swap:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap | 1,759 | ||
| Interest Rate Swap | 1,759 | ||||
| (To record decrease in fair value from $0 to $(1,759)) | |||||
Table (27)
- Holding Loss–Interest Rate Swap is a loss account. Since interest rate increased causing holding loss increase, which decrease equity, so equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Interest Rate Swap is a liability account because the fair value has decreased from $0 to $(1,759), and a decrease in asset is credited.
Entry for changes in fair value of note:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2018 | |||||
| December | 31 | Notes Payable | 1,759 | ||
| Holding Gain–Hedged Note | 1,759 | ||||
| (To record decrease in fair value from $100,000 to $98,241) | |||||
Table (28)
- Notes Payable is a liability account. Since fair value of the note decreased, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Holding Gain–Hedged Note is a revenue account. The fair value of hedged liability has decreased causing a holding gain. Since holding gains increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- I need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




