
a)
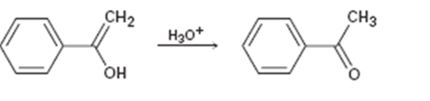
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation ion then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
b)
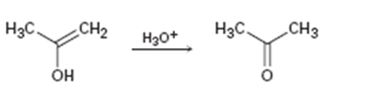
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
c)
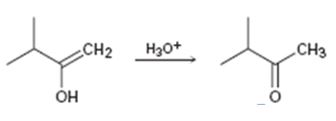
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Show that a molecule with configuration π4 has a cylindrically symmetric electron distribution. Hint: Let the π orbitals be equal to xf and yf, where f is a function that depends only on the distance from the internuclear axis.arrow_forward(a) Verify that the lattice energies of the alkali metal iodides are inversely proportional to the distances between the ions in MI (M = alkali metal) by plotting the lattice energies given below against the internuclear distances dMI. Is the correlation good? Would a better fit be obtained by plotting the lattice energies as a function of (1 — d*/d)/d, as theoretically suggested, with d* = 34.5 pm? You must use a standard graphing program to plot the graph. It generates an equation for the line and calculates a correlation coefficient. (b) From the graph obtained in (a), estimate the lattice energy of silver iodide. (c) Compare the results of (b) with the experimental value of 886 kJ/mol. If they do not agree, explain the deviation.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with #3 & 4? Thanks you so much!arrow_forward
- A solution consisting of 0.200 mol methylbenzene, C,H,CH,, in 500. g of nitrobenzene, CH,NO₂, freezes at 3.2°C. Pure nitrobenzene freezes at 6.0°C. The molal freezing point constant of nitrobenzene is _ °C/m. a) 2.8 b) 3.2 c) 5.6 d) 7.0 e) 14.0arrow_forwardBelow is the SN1 reaction of (S)-3-chlorocyclohexene and hydroxide ("OH). Draw the missing curved arrows, lone pairs of electrons, and nonzero formal charges. In the third box, draw the two enantiomeric products that will be produced. 2nd attempt Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. 0 D Draw the missing curved arrow notation. Add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges. + 노 V 1st attempt Feedback Please draw all four bonds at chiral centers. See Periodic Table See Hint F P 41 H Br See Periodic Table See Hint H Larrow_forwardHow close are the Mulliken and Pauling electronegativity scales? (a) Now that the ionization energies and electron affinities have been defined, calculate the Mulliken and Pauling electronegativities for C, N, O and F. Compare them. (Make the necessary adjustments to the values, such as dividing the ionization energies and electron affinities by 230kj/mol) (b) Plot both sets of electronegativities against atomic number (use the same graph). (c) Which scale depends most consistently on position in the Periodic Table?arrow_forward
- Below is the SN2 reaction between 2-bromopropane and iodide (I). Draw the mechanism arrows in the first box to reflect electron movements. In both boxes, add lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges. 4th attempt Feedback 3rd attempt Feedback 1 -Br H :Bri :Br: ili See Periodic Table See Hint ini See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardWhen 4-chloro-1-butanol is placed in sodium hydride, a cyclization reaction occurs. 3rd attempt 2 HO NaH CI D Draw the curved arrow notation to form the intermediate. 4 2 H₂ See Periodic Table See Hint =arrow_forwardSketch, qualitatively, the potential energy curves of the N-N bond of N2H4, N2 and N3- graph. Explain why the energy at the minimum of each curve is not the same.arrow_forward
- (a) Show that the lattice energies are inversely proportional to the distance between ions in MX (M = alkali metal, X = halide ions) by plotting the lattice energies of KF, KCl, and KI against the internuclear distances, dMX. The lattice energies of KF, KCl, and KI are 826, 717, and 645 kJ/mol, respectively. Does the correlation obtained correlate well? You will need to use a standard graphing program to construct the graph (such as a spreadsheet program). It will generate an equation for the line and calculate a correlation coefficient. (b) Estimate the lattice energy of KBr from your graph. (c) Find an experimental value for the lattice energy of KBr in the literature, and compare this value with the one calculated in (b). Do they agree?arrow_forwardShow the curved arrow mechanism and both products for the reaction between methyl iodide and propoxide. 1st attempt NV H 10: H H 1 Add the missing curved arrow notation. H + See Periodic Tablearrow_forwardFirst I wanted to see if you would mind checking my graphs behind me. (They haven't been coming out right)? Second, could you help me explain if the rate of reaction is proportional to iodide and persulfate of each graph. I highlighted my answer and understanding but I'm not sure if I'm on the right track. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

