
Interpretation:
The reaction through which, the given substrate more likely to participate has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
The compound that is been attacked by nucleophile is known as electrophile. Usually electrophile is referred as substrates. Valency of carbon atom is four. Therefore, carbon atom has four bonds. Hence, apart from the bond that is with the leaving group, the carbon atom contains three other bonds also.
Out of the three bonds that are present apart from the leaving group, if one is an alkyl group, then the substrate is known as “primary”. If there are two alkyl groups, then the substrate is known as “secondary”. If there are three alkyl groups, then the substrate is known as “tertiary”. This is represented as shown below,
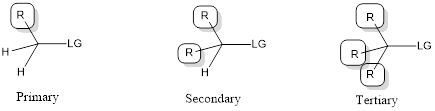
In
In
In simple words, we can say that, if the substrate is a primary or secondary one, then the reaction will proceed through
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (1 SEM.)
- Provide the unknown for the given data.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structures of two methanol (CH3OH) molecules and depict hydrogenbonding between them with dashed lines. Show all lone pairs. Provide a thorough analysis to apply concept idea into other problems.arrow_forwardSteps and explanation please.arrow_forward
- How could you distinguish between each pair of compounds below using IR? For each pair citeone bond and it’s frequency that you could use to distinguish between them. Please provide thorough analysis to apply into further problems.arrow_forwardSteps and explanation please.arrow_forwardSteps and explanation on how to solve.arrow_forward
- Provide the unknown for the given data.arrow_forwardElectron Arrangement A. Fill in the following chart relating to levels, sublevels and orbitals. Levels (n) 1 Sublevels # of Orbitals per sublevel 2 3 4 # of Electrons per sublevel Total Electrons per level Complete: B. Answer the following questions related to levels, sublevels, orbitals and electrons. 1. How many sublevels are in energy level 2? 2. How many orbitals are in a 4f sublevel? 3. How many electrons can level 3 hold? 4. How many orbitals are in level 4? 5. How many electrons can sublevel 2p hold? 11arrow_forwardProvide the unknown for the given details.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





