
a.
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
a.
Answer to Problem 37E
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Alternate hypothesis:
Explanation of Solution
It is given that among a sample of 500 chips produced by less expensive machine, 70 chips were defective and among a sample of 400 chips produced by more expensive machine, 20 chips were defective. The manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
Hypothesis:
Hypothesis is an assumption about the parameter of the population, and the assumption may or may not be true.
Let
Claim:
Here, the claim is that the manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Null hypothesis is a statement which is tested for statistical significance in the test. The decision criterion indicates whether the null hypothesis will be rejected or not in the favor of alternate hypothesis.
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is less than or equal to 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Alternate hypothesis:
Alternate hypothesis is contradictory statement of the null hypothesis
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
b.
Find the value of test statistic.
b.
Answer to Problem 37E
The value of test statistic is 4.4776.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is less than or equal to 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
Point estimates:
The total number of chips produced by less expensive machine is
The point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the less expensive machine is obtained as follows:
Thus, the point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the less expensive machine is 0.14.
The total number of chips produced by more expensive machine is
The point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the more expensive machine is obtained as follows:
Thus, the point estimate for the proportion of defectives produced by the more expensive machine is 0.05.
Estimate of pooled proportion:
The estimate of pooled proportion is obtained as follows:
Thus, the estimate of pooled proportion is 0.1.
Test statistic:
The test statistic for testing the difference between two proportions is,
Under the null hypothesis,
The test statistic is obtained as follows,
Thus, the test statistic is 4.4776.
c.
Check whether the null hypothesis is rejected at
c.
Answer to Problem 37E
The null hypothesis is rejected at
Explanation of Solution
P-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P-value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot.
- Choose View Probability > OK.
- Under Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter 0 as mean and 1 as standard deviation.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Under Define shaded area by choose X value and Right Tail.
- In X-value enter 4.4776.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
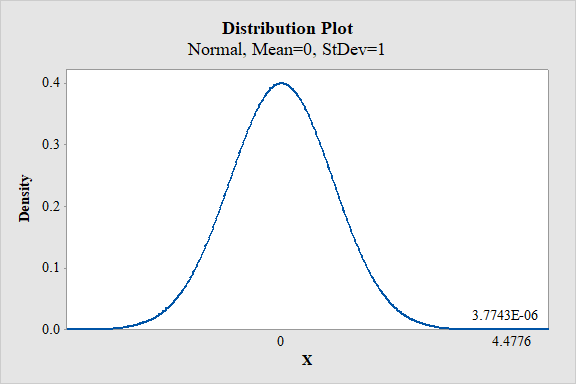
From the MINITAB output, the P-value is
Thus, the P-value is
Decision rule based on P-value:
If
If
Here, the level of significance is
Conclusion based on P-value approach:
The P-value is
Here, P-value is less than the
That is,
By the rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
d.
Find the machine that has to be bought by manufacturer.
d.
Answer to Problem 37E
The manufacturer has to by the more expensive machine.
Explanation of Solution
From part (c), it is known that the null hypothesis is rejected.
That is, the proportion of defectives produced by less expensive machine is more than 5% more than the proportion of defectives produced by more expensive machine.
The claim was that, the manufacturer wants to buy more expensive machine if the proportion of defectives is more than 5% less than on the less expensive machine.
Since, the claim of the manufacturer is satisfied. The manufacturer has to buy the more expensive machine.
Thus, the manufacturer has to buy more expensive machine.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- A survey of 250 young professionals found that two-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is [ ], [ ] As 0.72 is ▼ above the upper limit within the limits below the lower limit of the confidence interval, we ▼ can cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forward
- From a sample of 26 graduate students, the mean number of months of work experience prior to entering an MBA program was 34.67. The national standard deviation is known to be18 months. What is a 90% confidence interval for the population mean? Question content area bottom Part 1 A 9090% confidence interval for the population mean is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracketenter your response here,enter your response here. (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA test consists of 10 questions made of 5 answers with only one correct answer. To pass the test, a student must answer at least 8 questions correctly. (a) If a student guesses on each question, what is the probability that the student passes the test? (b) Find the mean and standard deviation of the number of correct answers. (c) Is it unusual for a student to pass the test by guessing? Explain.arrow_forwardIn a group of 40 people, 35% have never been abroad. Two people are selected at random without replacement and are asked about their past travel experience. a. Is this a binomial experiment? Why or why not? What is the probability that in a random sample of 2, no one has been abroad? b. What is the probability that in a random sample of 2, at least one has been abroad?arrow_forward
- Questions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardTo help consumers in purchasing a laptop computer, Consumer Reports calculates an overall test score for each computer tested based upon rating factors such as ergonomics, portability, performance, display, and battery life. Higher overall scores indicate better test results. The following data show the average retail price and the overall score for ten 13-inch models (Consumer Reports website, October 25, 2012). Brand & Model Price ($) Overall Score Samsung Ultrabook NP900X3C-A01US 1250 83 Apple MacBook Air MC965LL/A 1300 83 Apple MacBook Air MD231LL/A 1200 82 HP ENVY 13-2050nr Spectre XT 950 79 Sony VAIO SVS13112FXB 800 77 Acer Aspire S5-391-9880 Ultrabook 1200 74 Apple MacBook Pro MD101LL/A 1200 74 Apple MacBook Pro MD313LL/A 1000 73 Dell Inspiron I13Z-6591SLV 700 67 Samsung NP535U3C-A01US 600 63 a. Select a scatter diagram with price as the independent variable. b. What does the scatter diagram developed in part (a) indicate about the relationship…arrow_forwardTo the Internal Revenue Service, the reasonableness of total itemized deductions depends on the taxpayer’s adjusted gross income. Large deductions, which include charity and medical deductions, are more reasonable for taxpayers with large adjusted gross incomes. If a taxpayer claims larger than average itemized deductions for a given level of income, the chances of an IRS audit are increased. Data (in thousands of dollars) on adjusted gross income and the average or reasonable amount of itemized deductions follow. Adjusted Gross Income ($1000s) Reasonable Amount ofItemized Deductions ($1000s) 22 9.6 27 9.6 32 10.1 48 11.1 65 13.5 85 17.7 120 25.5 Compute b1 and b0 (to 4 decimals).b1 b0 Complete the estimated regression equation (to 2 decimals). = + x Predict a reasonable level of total itemized deductions for a taxpayer with an adjusted gross income of $52.5 thousand (to 2 decimals). thousand dollarsWhat is the value, in dollars, of…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





