
State the P–value for each test by performing a test of the null hypothesis that the group means or group proportions are equal versus the alternative that they are not equal.
Answer to Problem 1CS
The P–value for the each test is as follows:
| Characteristic | P–value |
| Age | 0.057 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.000 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.037 |
| Treatment for hypertension | 0.819 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.337 |
| Diabetes | 0.875 |
| Cigarette smoking | 0.343 |
| Coronary bypass surgery | 0.762 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The data represents the means and standard deviations corresponding to three characteristics of standard treatment and new treatment.
Furthermore, the data corresponding to the percentage with the characteristics for the 5 characteristics for standard treatment and new treatment is given.
Here, it is given that the
Let
Hypothesis test for the variable “Age”:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the mean age of new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the mean age of new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populations means using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the sample size as 731, sample mean as 64 and sample standard deviation as 11.
- In second sample, enter the sample size as 1,089, sample mean as 65 and sample standard deviation as 11.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
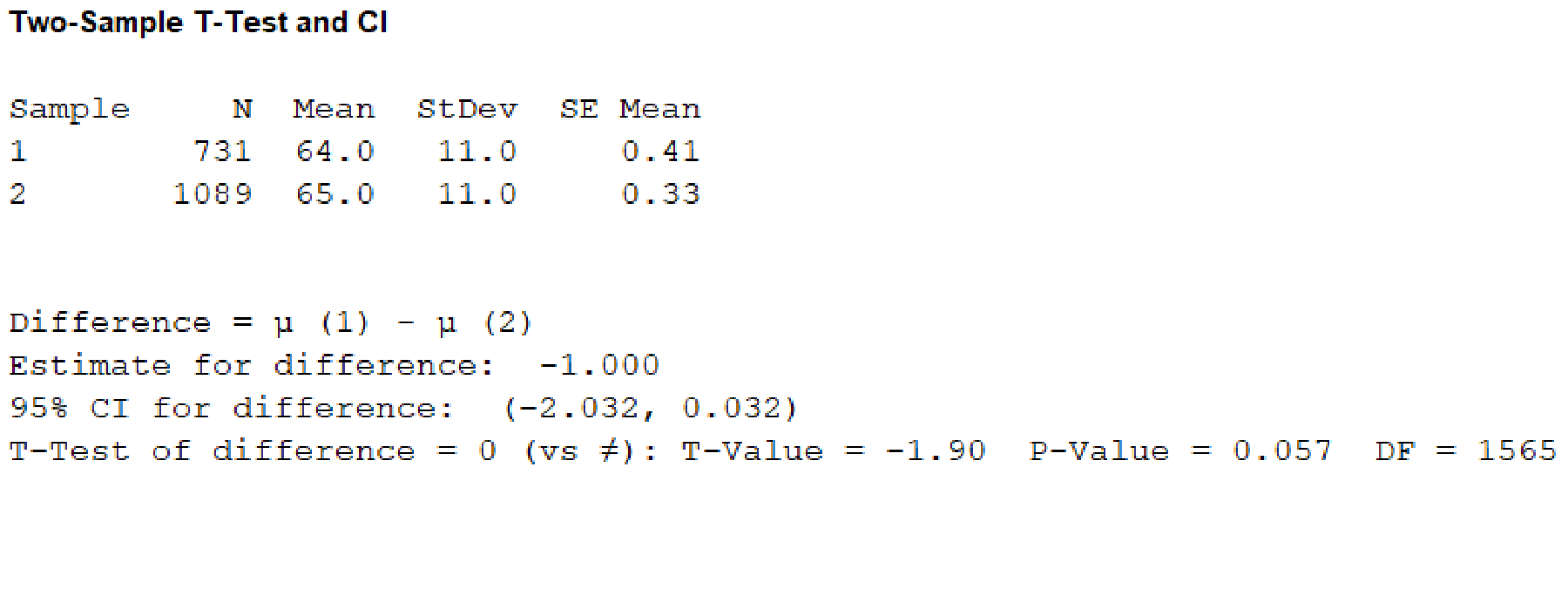
From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Age” is 0.057.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Systolic blood pressure”:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the mean systolic blood pressure of new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the mean systolic blood pressure of new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two population means using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the sample size as 731, sample mean as 121 and sample standard deviation as 18.
- In second sample, enter the sample size as 1,089, sample mean as 124 and sample standard deviation as 17.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Systolic blood pressure” is 0.000.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Diastolic blood pressure”:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the mean diastolic blood pressure of new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the mean diastolic blood pressure of new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populations means using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the sample size as 731, sample mean as 71 and sample standard deviation as 10.
- In second sample, enter the sample size as 1,089, sample mean as 72 and sample standard deviation as 10.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
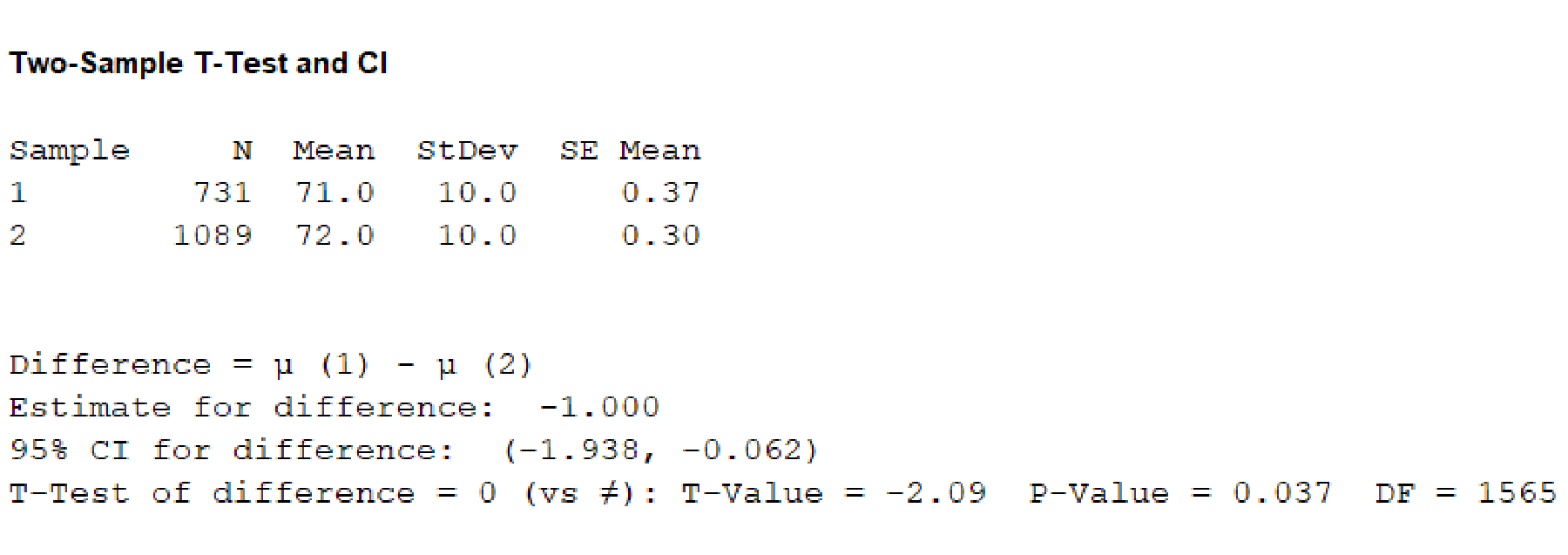
From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Diastolic blood pressure” is 0.037.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Treatment for hypertension”:
The sample size of standard treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of treatment for hypertension under new treatment is
The sample size of new treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of treatment for hypertension under new treatment is
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the proportion of treatment for hypertension under new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the proportion of treatment for hypertension under new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two population proportions using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Proportions.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the number of trials as 731 and number of events as 462.
- In second sample, enter the number of trials as 1,089 and number of events as 694.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
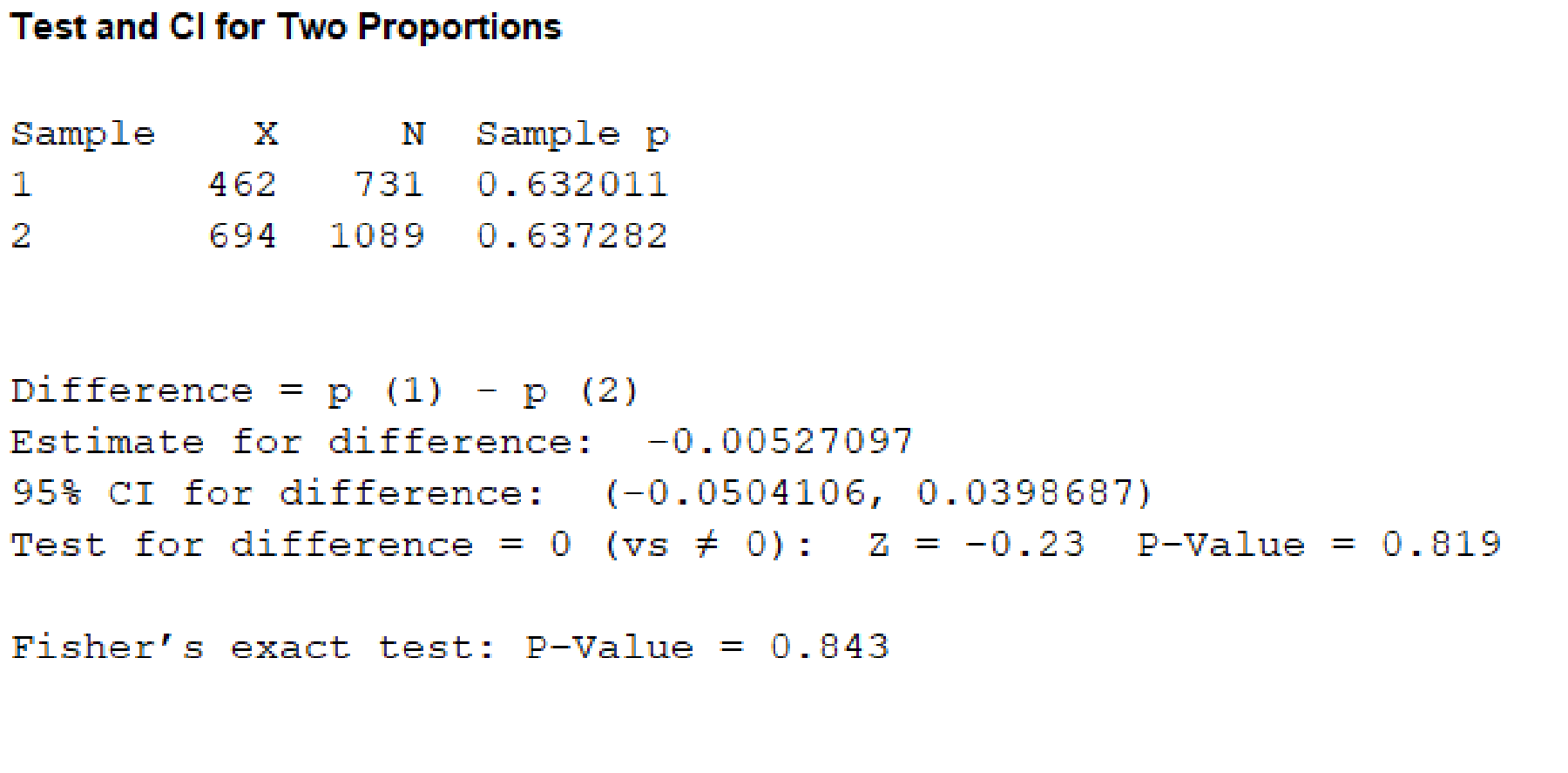
From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Treatment for hyper tension” is 0.819.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Atrial fibrillation”:
The sample size of standard treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of treatment for Atrial fibrillation under standard treatment is
The sample size of new treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of Atrial fibrillation under new treatment is
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the proportion of Atrial fibrillation under new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the proportion of Atrial fibrillation under new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populationproportions using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Proportions.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the number of trials as 731 and number of events as 92.
- In second sample, enter the number of trials as 1,089 and number of events as 121.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Atrial fibrillation” is 0.337.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Diabetes”:
The sample size of standard treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of diabetes under standard treatment is
The sample size of new treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of diabetes under new treatment is
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the proportion of Diabetes under new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the proportion of Diabetes under new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populationproportions using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Proportions.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the number of trials as 731 and number of events as 221.
- In second sample, enter the number of trials as 1,089 and number of events as 333.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Diabetes” is 0.875.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Cigarette smoking”:
The sample size of standard treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of cigarette smoking under standard treatment is
The sample size of new treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of cigarette smoking under new treatment is
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the proportion of Cigarette smoking under new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the proportion of Cigarette smoking under new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populationsproportions using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Proportions.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the number of trials as 731 and number of events as 94.
- In second sample, enter the number of trials as 1,089 and number of events as 124.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
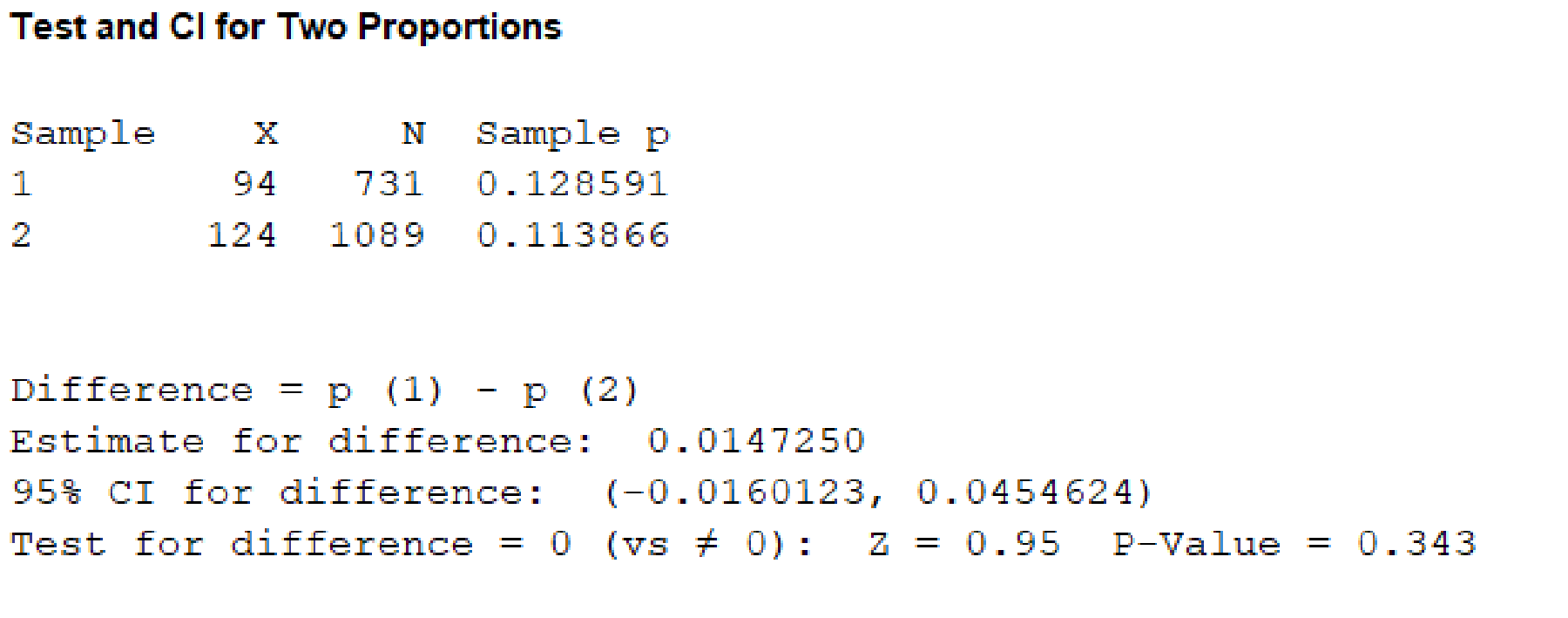
From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Cigarette smoking” is 0.343.
Hypothesis test for the variable “Coronary bypass surgery”:
The sample size of standard treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of Coronary bypass surgery under standard treatment is
The sample size of new treatment is
Hence, the specified characteristics of coronary bypass surgery under new treatment is
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the proportion of Coronary bypass surgery under new treatment and standard treatment.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the proportion of Coronary bypass surgery under new treatment and standard treatment.
P-value:
Software Procedure:
Step by step procedure to perform hypothesis test for the difference between the two populationproportions using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Proportions.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first sample, enter the number of trials as 1,089 and number of events as 317.
- In second sample, enter the number of trials as 731 and number of events as 208.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Enter 0 in Hypothesized value.
- In Alternative, select not equal to
- Click OK in all the dialogue boxes.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From, the MINITAB output the P-value corresponding to the variable “Coronary bypass surgery” is 0.762.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- We consider a (European) call option on a stock with expiration in 3 months and strike price $10. The annual interest rate on the market is r = 4%. The current price of the stock is $10 and we assume that the stock follows a geometric Brownian motion (Black-Scholes) model with parameters = 6% and σ = 0.2. (a) Determine the price Fo of this option at time t = : 0 (today). (b) Using the formulas provided in the lecture videos, calculate the value of each of the Greeks for this option. Namely, calculate A, T, v, О, p. (c) Find a formula for the change of the option price with respect to a change in the af (St, t) Әк strike price. In other words, determine (d) For each of the suggested modifications below, use an approximation to determine the change in the price of the option above without actually recalculating the price. For each one, provide an intuitive argument to explain why the price increases or decreases. (i) The rate of return μ decreases to 5%. (ii) The interest rate r…arrow_forwardA box containing 24 seemly identical resistors has just been received. However,unbeknownst, 4 of these resistors are defective. a. Five resistors are randomly selected from this box without replacement (oncemoved from the box it is not returned to the box), what is the probability that oneor more of the defective resistors is among those selected? b. Five resistors are randomly selected from this box with replacement (after theresistor is removed and checked, it is returned to the box prior to the nextselection (hence the same resistor can be selected more than once)), what is theprobability that one or more of the defective resistors is among those selected?arrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forward
- Triola statistics Readers who prefer printed books Readers who prefer e-booksarrow_forwardThe following is a list of data on the duration of a sample of 200 outbreaks, in hours. 107 73 68 97 76 79 94 59 98 57 54 65 71 70 84 88 62 82 61 79 98 66 62 79 86 68 74 61 62 116 65 88 64 79 78 74 92 75 5289 85 28 73 80 68 78 89 72 78 88 77 103 88 63 68 90 62 89 71 71 74 222 R 82 79 70 ST☑ 65 98 77 86 58 69 88 81 74 70 65 81 75 81 78 90 78 96 75 KRRE F S 62 94 62 79 83 93 135 71 85 84 83 63 61 65 83 70 70 81 77 72 84 33 62 92 65 67 59 58 66 66 94 77 63 71 101 78 43 78 66 75 68 76 59 67 61 71 64 76 72 77 74 65 82 86 66 86 68 85 27% 96 72 77 60 67 87 83 68 72 74 91 76 83 งงง 8 སྐྱ ཐྭ ༄ ཏྱཾ 89 81 71 85 99 59 92 87 84 75 77 51 45 80 84 93 69 76 89 75 67 92 89 82 96 77 102 66 68 61 73 72 76 73 77 79 94 63 59 62 71 81 65 73 63 63 89 82 64 85 92 64 73 a. What is the variable? What type? b. Construct an interval-frequency table, with columns containing: class mark, absolute frequency, relative frequency, cumulative frequency, cumulative relative frequency, and percentage frequency.arrow_forwardThis is the information about the actors who won the Best Actor Oscar: Best actors 44 41 62 52 41 34 34 52 41 37 38 34 32 40 43 56 41 39 49 57 35 30 39 41 44 41 38 42 52 51 49 35 47 31 47 37 57 42 45 42 44 62 43 42 48 49 56 38 60 30 40 42 36 76 39 53 45 36 62 43 51 32 42 54 52 37 38 32 45 60 46 40 36 47 29 43 a. What is the variable? What type? b. Construct an interval-frequency table, with columns containing: class mark, absolute frequency, relative frequency, cumulative frequency, cumulative relative frequency, and percentage frequency.arrow_forward
- ans c plsarrow_forwardCritically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES SCOTCEN POLL OF POLLS SHOULD SCOTLAND BE INDEPENDENT? NO 52% YES 58% LIVE CAW NAS & 28.30 HAS KILLED MORE THAN 2,600 IN WEST AFRICA, WORLD HEALTH ORG. BROOKEBCNNarrow_forwardCritically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES PRESIDENTIAL PREFERENCES RODOLFO CARTER 3% (+2pts) EVELYN MATTHEI 22% (+6pts) With the exception of President Boric, could you tell me who you would like to be the next president of Chile? CAMILA VALLEJO 4% (+2pts) JOSÉ ANTONIO KAST 19% (+5pts) MICHELLE BACHELET 6% (+1pts)arrow_forward
- Critically analyze the following graph and, based on statistical information, indicate the type of error it presents IN NO MORE THAN 3 LINES 13% APPROVE 4% DOESN'T KNOW DOESN'T RESPOND 5% NEITHER APPROVES NOR DISAPPROVES 78% DISAPPROVES SURVEY PRESIDENTIAL APPROVAL DROPS TO 13%arrow_forwardPlease help with this following question I'm not too sure if question (a) and (b) are correct and not sure how to calculate (c) The csv data is below "","New","Current" "1","67",66 "2","77",73 "3","76",73 "4","76",76 "5","77",79 "6","84",76 "7","71",78 "8","84",72 "9","73",76 "10","71",73 "11","72",77 "12","70",72 "13","75",72 "14","84",71 "15","77",73 "16","65",72 "17","69",73 "18","71",73 "19","79",71 "20","75",78 "21","76",69 "22","73",74 "23","76",71 "24","64",74 "25","81",78 "26","79",76 "27","70",77 "28","79",71 "29","84",73 "30","79",69 "31","69",72 "32","81",76 "33","77",70 "34","77",71 "35","71",69 "36","67",72 "37","70",76 "38","77",73 "39","82",73 "40","72",73arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following question(c) A previous study found that 15% of nurses reported participating in mental health support programs.From the 96% found in (b) , can you conclude that proportion of nurses reported participating in mental health support programs p(current), has changed from the previous study?(Yes/No) because the confidence interval in (b) (captures/does not capture) 15%.(d) Refer to your answer in (b) : The Alberta Nurses Association expects that not more than 23 % of nurses will participate in the survey on mental health support programs. Given the result in part (b) can we conclude that this expectation is reasonable?(Yes/No) because the (upper bound/lower bound) of the 96% confidence interval is (less than/not less than/greater than) 23%. The Alberta Nursing Association conducts an annual survey to estimate the proportion of nurses who participate in mental health support programs. The most recent application of this survey involved a random sample of…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





