
The exergy destruction associated with each process of the Brayton cycle and the exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator.
Answer to Problem 150P
The exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with regeneration process for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 5-3 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 6-1 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator is
Explanation of Solution
Draw
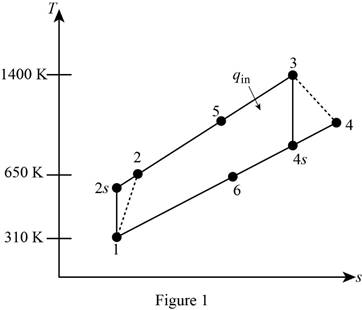
Write the expression of pressure ratio for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, pressure at state 2 is
Write the pressure ratio and pressure relation for the process 3-4.
Here, pressure at state 3 is
Write the expression of efficiency of the turbine
Here, enthalpy at state 3 is
Write the expression of heat added due to regeneration
Here, the effectiveness of the regenerator is
Write the expression of net work output of the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the work output by the turbine is
Write the expression of heat input to the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression of heat rejected by the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression of specific enthalpy at state 6
Write the specific enthalpy relation for the regenerator.
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 1-2 for Brayton cycle
Here, the gas constant of air is R, entropy of air at state 2 as a function of temperature only is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 3-4
Here, entropy of air at state 3 as a function of temperature is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for Brayton cycle
Here, entropy of air at state 5 as a function of temperature alone is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 5-3
Here, the temperature of the heat source is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 6-1
Here, the temperature of the sink is
Write the expression of stream exergy at the exit of the regenerator (state 6)
Here, the specific enthalpy of the surroundings is
Write the expression of change entropy for the exit of the regenerator
Here, entropy of air at the surroundings as a function of temperature alone is
Conclusion:
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 310 K
Substitute 900 kPa for
Substitute
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 50.06
Substitute
Substitute 0.80 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute 310.24
Substitute 659.84
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 310 K
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with regeneration process for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 5-3 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 6-1 for Brayton cycle is
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 300 K
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Air enters the compressor of a regenerative gas turbine engine at 310 K and 100 kPa, where it is compressed to 900 kPa and 650 K. The regenerator has an effectiveness of 75%, and the air enters the turbine at 1400 K. Assume variable specific heats for air. For a turbine efficiency of 90 percent, determine the amount of heat transfer in the regenerator. The amount of heat transfer in the regenerator is kJ/kg.arrow_forwardAir enters the compressor of a regenerative gas turbine engine at 310 K and 100 kPa, where it is compressed to 900 kPa and 650 K. The regenerator has an effectiveness of 79 percent, and the air enters the turbine at 1400 K. Assume constant specific heats for air at room temperature. The properties of air at room temperature are cp = 1.005 kJ/kg·K and k = 1.4. For a turbine efficiency of 90 percent, determine the amount of heat transfer in the regenerator. The amount of heat transfer in the regenerator is kJ/kg.arrow_forwardHints: Find the closed loop transfer function and then plot the step response for diFerentvalues of K in MATLAB. Show step response plot for different values of K. Auto Controls Show solutions and provide matlab code NO COPIED ANSWERS OR WILL REPORT!!!! Use own solutionarrow_forward
- what is shear stress and normal? how to tell them while calculating?arrow_forward12 mm 45 mm 20 kN 20 kN 12 mm 45 mm PROBLEM 1.61 For the assembly and loading of Problem 1.60, determine (a) the average shearing stress in the pin at C, (b) the average bearing stress at C in member BC, (c) the average bearing stress at B in member BC. PROBLEM 1.60 Two horizontal 20-kN forces are applied to pin B of the assembly shown. Knowing that a pin of 20-mm diameter is used at each connection, determine the maximum value of the average normal stress (a) in link AB, (b) in link BC.arrow_forwardHow do you find these answers?arrow_forward
- 250 mm 400 mm A B C E F 250 mm PROBLEM 1.52 Each of the two vertical links CF connecting the two horizontal members AD and EG has a 10 × 40-mm uniform rectangular cross section and is made of a steel with an ultimate strength in tension of 400 MPa, while each of the pins at C and F has a 20-mm diameter and are made of a steel with an ultimate strength in shear of 150 MPa. Determine the overall factor of safety for the links CF and the pins connecting them to the horizontal members. 24 kNarrow_forward50 mm 12 mm B O C OA 300 mm 450 mm E PROBLEM 1.51 Each of the steel links AB and CD is connected to a support and to member BCE by 25-mm-diameter steel pins acting in single shear. Knowing that the ultimate shearing stress is 210 MPa for the steel used in the pins and that the ultimate normal stress is 490 MPa for the steel used in the links, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired. (Note that the links are not reinforced around the pin holes.)arrow_forward3. A 15% magnesium chloride solution is flowing through a 5-nom sch 40 commercial steel pipe at a rate of 325,000 lbm/h. The average temperature of the magnesium chloride solution as it flows through the pipe is 10°F. Determine the convective heat transfer coefficient inside the pipe.arrow_forward
- 2. Jojoba oil is flowing through a ¾-nom stainless steel pipe at a flow rate of 1,850 lbm/h. After the velocity profile in the pipe is fully developed, the oil enters a heater, as shown in Figure P5.7. The length of the heater section is 5 ft. The properties of the jojoba oil at the average temperature in the heater section are given in Table P5.7. Determine the convective heat transfer coefficient inside the heater section of the pipe. ¾ nom stainless steel pipe Heater section L=5ft Fig. P5.7 TABLE P5.7 Thermophysical Properties of Jojoba Oil at the Average Temperature in the Heater P (lbm/ft³) 68.671 (Btu/lbm-R) 0.30339 μ (lbm/ft-s) 0.012095 k (Btu/h-ft-°F) 0.077424arrow_forward1. Water is flowing inside of a 3-std type K copper tube at a flow rate of 1.2 kg/s. The average temperature of the water is 50°C. Cold, dry air at a temperature of 5°C and atmospheric pressure flows outside of the tube in cross flow with a velocity of 85 m/s. Determine the UA product for this tube under clean conditions.arrow_forwardHints: Find the closed loop transfer function and then plot the step response for diFerentvalues of K in MATLAB. Show step response plot for different values of K. Auto Controls Show solutions and provide matlab code NO COPIED ANSWERS OR WILL REPORT!!!!arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





