
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977121
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.1, Problem 9.2P
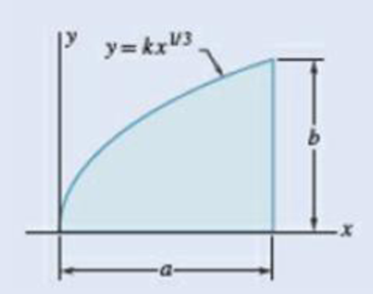
9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration the moment of inertia of the shaded area with respect to y axis.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2. Solve the following linear time invariant differential equations using Laplace transforms subject to
different initial conditions
(a) y-y=t
for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 1
(b) ÿ+4y+ 4y = u(t)
for y(0) = 0 and y(0) = 1
(c) y-y-2y=0
for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 0
3. For the mechanical systems shown below, the springs are undeflected when x₁ = x2 = x3 = 0 and
the input is given as fa(t). Draw the free-body diagrams and write the modeling equations governing
each of the systems.
K₁
000
K₂
000
M₁
M2
-fa(t)
B₂
B₁
(a)
fa(t)
M2
K₂
000
B
K₁
x1
000
M₁
(b)
This question i m uploading second time . before you provide me incorrect answer. read the question carefully and solve accordily.
Chapter 9 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.9 through 9.11 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.9 through 9.11 Determine by direct integration...
Ch. 9.1 - 9.9 through 9.11 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.12 through 9.14 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.13PCh. 9.1 - 9.12 through 9.14 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.15 and 9.16 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.16PCh. 9.1 - 9.17 and 9.18 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.18PCh. 9.1 - Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.20PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.21PCh. 9.1 - Determine the polar moment of inertia and the...Ch. 9.1 - 9.23 and 9.24 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.1 - 9.23 and 9.24 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.1 - (a) Determine by direct integration the polar...Ch. 9.1 - (a) Show that the polar radius of gyration kQ of...Ch. 9.1 - Determine the polar moment of inertia and the...Ch. 9.1 - Determine the polar moment of inertia and the...Ch. 9.1 - Using the polar moment of inertia of the isosceles...Ch. 9.1 - Prove that the centroidal polar moment of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - 9.31 and 9.32 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.2 - 9.31 and 9.32 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.2 - 9.33 and 9.34 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.2 - 9.33 and 9.34 Determine the moment of inertia and...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.35PCh. 9.2 - Determine the moments of inertia of the shaded...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.37PCh. 9.2 - Fig. P9.37 and P9.38 9.38 Knowing that the shaded...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.39PCh. 9.2 - Fig. P9.39 and P9.40 9.40 The polar moments of...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.41PCh. 9.2 - 9.41 through 9.44 Determine the moments of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - 9.41 through 9.44 Determine the moments of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - 9.41 through 9.44 Determine the moments of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - 9.45 and 9.46 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.2 - 9.45 and 9.46 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.47PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.48PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.49PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.50PCh. 9.2 - Four L3 3 14 - in. angles are welded to a rolled...Ch. 9.2 - Two 20-mm steel plates are welded to a rolled S...Ch. 9.2 - A channel and a plate are welded together as shown...Ch. 9.2 - The strength of the rolled W section shown is...Ch. 9.2 - Two L76 76 6.4-mm angles are welded to a C250 ...Ch. 9.2 - Two steel plates are welded to a rolled W section...Ch. 9.2 - 9.57 and 9.58 The panel shown forms the end of a...Ch. 9.2 - 9.57 and 9.58 The panel shown forms the end of a...Ch. 9.2 - 9.59 and 9.60 The panel shown forms the end of a...Ch. 9.2 - 9.59 and 9.60 The panel shown forms the end of a...Ch. 9.2 - A vertical trapezoidal gate that is used as an...Ch. 9.2 - The cover for a 0.5-m-diameter access hole in a...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the x coordinate of the centroid of the...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the x coordinate of the centroid of the...Ch. 9.2 - Show that the system of hydrostatic forces acting...Ch. 9.2 - Show that the resultant of the hydrostatic forces...Ch. 9.3 - 9.67 through 9.70 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.3 - 9.67 through 9.70 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.3 - 9.67 through 9.70 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.70PCh. 9.3 - 9.71 through 9.74 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.71 through 9.74 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.71 through 9.74 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.74PCh. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.78PCh. 9.3 - Determine for the quarter ellipse of Prob. 9.67...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.85PCh. 9.3 - 9.86 through 9.88 For the area indicated,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.86 through 9.88 For the area indicated,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.86 through 9.88 For the area indicated,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.89 and 9.90 For the angle cross section...Ch. 9.3 - 9.89 and 9.90 For the angle cross section...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine for the quarter...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - For the quarter ellipse of Prob. 9.67, use Mohrs...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.98PCh. 9.4 - 9.98 though 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - 9.98 though 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - 9.98 through 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - 9.98 through 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.103PCh. 9.4 - 9.104 and 9.105 Using Mohrs circle, determine the...Ch. 9.4 - 9.104 and 9.105 Using Mohrs circle, determine the...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.106PCh. 9.4 - it is known that for a given area Iy = 48 106 mm4...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.108PCh. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, prove that the expression...Ch. 9.4 - Using the invariance property established in the...Ch. 9.5 - A thin plate with a mass m is cut in the shape of...Ch. 9.5 - A ring with a mass m is cut from a thin uniform...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.113PCh. 9.5 - The parabolic spandrel shown was cut from a thin,...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.115PCh. 9.5 - Fig. P9.115 and P9.116 9.116 A piece of thin,...Ch. 9.5 - A thin plate of mass m is cut in the shape of an...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.118PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.119PCh. 9.5 - The area shown is revolved about the x axis to...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.121PCh. 9.5 - Determine by direct integration the mass moment of...Ch. 9.5 - Fig. P9.122 and P9.123 9.123 Determine by direct...Ch. 9.5 - Determine by direct integration the mass moment of...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.125PCh. 9.5 - A thin steel wire is bent into the shape shown....Ch. 9.5 - Shown is the cross section of an idler roller....Ch. 9.5 - Shown is the cross section of a molded flat-belt...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.129PCh. 9.5 - Knowing that the thin cylindrical shell shown has...Ch. 9.5 - A circular hole of radius r is to be drilled...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.132PCh. 9.5 - After a period of use, one of the blades of a...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the 0.9-lb...Ch. 9.5 - 9.135 and 9.136 A 2-mm thick piece of sheet steel...Ch. 9.5 - 9.135 and 9.136 A 2 -mm thick piece of sheet steel...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.137PCh. 9.5 - A section of sheet steel 0.03 in. thick is cut and...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.139PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.140PCh. 9.5 - The machine element shown is fabricated from...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moments of inertia and the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.5 - Fig. P9.143 and P9.144 9.144 Determine the mass...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.5 - Aluminum wire with a weight per unit length of...Ch. 9.5 - The figure shown is formed of 18-in.-diameter...Ch. 9.5 - A homogeneous wire with a mass per unit length of...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.153PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.154PCh. 9.6 - 9.153 through 9.156 A section of sheet steel 2 mm...Ch. 9.6 - 9.153 through 9.156 A section of sheet steel 2 mm...Ch. 9.6 - The figure shown is formed of 1.5-mm-diameter...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.158PCh. 9.6 - 9.159 and 9.160 Brass wire with a weight per unit...Ch. 9.6 - Fig. P9.160 9.159 and 9.160 Brass wire with a...Ch. 9.6 - Complete the derivation of Eqs. (9.47) that...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.162PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.163PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.164PCh. 9.6 - Shown is the machine element of Prob. 9.141....Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.6 - The thin, bent plate shown is of uniform density...Ch. 9.6 - A piece of sheet steel with thickness t and...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the...Ch. 9.6 - 9.170 through 9.172 For the wire figure of the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.171PCh. 9.6 - 9.172 Prob. 9.146 9.146 Aluminum wire with a...Ch. 9.6 - For the homogeneous circular cylinder shown with...Ch. 9.6 - For the rectangular prism shown, determine the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.175PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.176PCh. 9.6 - Consider a cube with mass m and side a. (a) Show...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.178PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.179PCh. 9.6 - 9.180 through 9.184 For the component described in...Ch. 9.6 - 9.180 through 9.184 For the component described in...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.182PCh. 9.6 - 9.180 through 9.184 For the component described in...Ch. 9.6 - 9.180 through 9.184 For the component described in...Ch. 9 - Determine by direct integration the moments of...Ch. 9 - Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of...Ch. 9 - Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of...Ch. 9 - Determine the moments of inertia Ix and Iy of the...Ch. 9 - Determine the polar moment of inertia of the area...Ch. 9 - Two L4 4 12-in. angles are welded to a steel...Ch. 9 - Using the parallel-axis theorem, determine the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.192RPCh. 9 - Fig. P9.193 and P9.194 9.193 A thin plate with a...Ch. 9 - Fig. P9.193 and P9.194 9.194 A thin plate with...Ch. 9 - A 2-mm-thick piece of sheet steel is cut and bent...Ch. 9 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Create a table comparing five different analogous variables for translational, rotational, electrical and fluid systems. Include the standard symbols for each variable in their respective systems.arrow_forward2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities v₁ and v₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 m2 βarrow_forward4. Find the equivalent spring constant and equivalent viscous-friction coefficient for the systems shown below. @ B₁ B₂ H B3 (b)arrow_forward
- 5. The cart shown below is inclined 30 degrees with respect to the horizontal. At t=0s, the cart is released from rest (i.e. with no initial velocity). If the air resistance is proportional to the velocity squared. Analytically determine the initial acceleration and final or steady-state velocity of the cart. Take M= 900 kg and b 44.145 Ns²/m². Mg -bx 2 отarrow_forward9₁ A Insulated boundary Insulated boundary dx Let's begin with the strong form for a steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction problem, without convection. d dT + Q = dx dx According to Fourier's law of heat conduction, the heat flux q(x), is dT q(x)=-k dx. x Q is the internal heat source, which heat is generated per unit time per unit volume. q(x) and q(x + dx) are the heat flux conducted into the control volume at x and x + dx, respectively. k is thermal conductivity along the x direction, A is the cross-section area perpendicular to heat flux q(x). T is the temperature, and is the temperature gradient. dT dx 1. Derive the weak form using w(x) as the weight function. 2. Consider the following scenario: a 1D block is 3 m long (L = 3 m), with constant cross-section area A = 1 m². The left free surface of the block (x = 0) is maintained at a constant temperature of 200 °C, and the right surface (x = L = 3m) is insulated. Recall that Neumann boundary conditions are naturally satisfied…arrow_forward1 - Clearly identify the system and its mass and energy exchanges between each system and its surroundings by drawing a box to represent the system boundary, and showing the exchanges by input and output arrows. You may want to search and check the systems on the Internet in case you are not familiar with their operations. A pot with boiling water on a gas stove A domestic electric water heater A motor cycle driven on the roadfrom thermodynamics You just need to draw and put arrows on the first part a b and carrow_forward
- 7. A distributed load w(x) = 4x1/3 acts on the beam AB shown in Figure 7, where x is measured in meters and w is in kN/m. The length of the beam is L = 4 m. Find the moment of the resultant force about the point B. w(x) per unit length L Figure 7 Barrow_forward4. The press in Figure 4 is used to crush a small rock at E. The press comprises three links ABC, CDE and BG, pinned to each other at B and C, and to the ground at D and G. Sketch free-body diagrams of each component and hence determine the force exerted on the rock when a vertical force F = 400 N is applied at A. 210 80 80 C F 200 B 80 E 60% -O-D G All dimensions in mm. Figure 4arrow_forward2. Figure 2 shows a device for lifting bricks and concrete blocks. It comprises two compo- nents ABC and BD, with a frictionless pin at B. Determine the minimum coefficient of friction required at A and D if the device is to work satisfactorily. W all dimensions in inches Figure 2 Darrow_forward
- 1. The shaft AD in Figure 1 supports two pulleys at B and C of radius 200 mm and 250 mm respectively. The shaft is supported in frictionless bearings at A and D and is rotating clockwise (when viewed from the right) at a constant speed of 300 rpm. Only bearing A can support thrust. The tensions T₁ = 200 N, T₂ = 400 N, and T3 = 300 N. The distances AB = 120 mm, BC = 150 mm, and CD120 mm. Find the tension 74 and the reaction forces at the bearings. A T fo Figure 1arrow_forward5. Figure 5 shows a two-dimensional idealization of the front suspension system for a car. During cornering, the road exerts a vertical force of 5 kN and a leftward horizontal force of 1.2 kN on the tire, which is of 510 mm diameter. Draw free-body diagrams of each component and determine the forces transmitted between them. 250 A -320 B 170 D 170 -220-220- all dimensions in mm. Figure 5arrow_forward8. The force F in Figure 8 is 120 lb and the angle 0 = 25°. Find the axial force N, the shear force V and the bending moment M at the point K which is midway between B and C and illustrate their directions on a sketch of the segment KCD. E -0 B K అ D H 7 A- all dimensions in inches Figure 8 Ꮎ G Farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License