
EP BIOLOGY:SCIENCE F/LIFE...-MOD.ACCESS
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134839530
Author: BELK
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9LTB
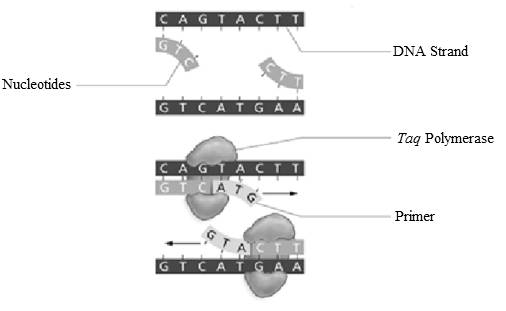
Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates the components in the PCR reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
This is what the LAB FLOW would look like:
CULTURE BACTERIA
EXTRACT RNA
RANDOM HEXAMER REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION OF RNA
PCR OF lacZ GENE
ELECTROPHORESIS
If you wanted to prepare only one PCR reaction, how much of each reagent would you add to the PCR tube?
What would be the final primer concentration if 0.5 μl of 10 μM primers were added to a PCR reaction with a final volume of 20 μl?
After running a qPCR experiment, we will have graphs showing the amount of fluorescence detected by the digital camera compared to the number of PCR cycles run. Suppose
you see the following graph output by the qPCR machine:
Relative Fluoresence
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
0
10
20
30
40
50
Cycles
Which curve (blue, red, or green) represents a sample with the smallest amount of mRNA present? Why? Be sure to discuss Ct values in your answer.
The process of PCR essentially revolves around three phases. Briefly describe these phases and the events that occur in them. Take note the temperature on which these phases take place.
Chapter 9 Solutions
EP BIOLOGY:SCIENCE F/LIFE...-MOD.ACCESS
Ch. 9 - Is a round yellow pea seed (genotype Rr Y y) an...Ch. 9 - What factors cause quantitative variation in a...Ch. 9 - The DNA profile below is from a mother, a father,...Ch. 9 - Prob. 4LTBCh. 9 - Prob. 5LTBCh. 9 - Prob. 6LTBCh. 9 - Prob. 7LTBCh. 9 - Prob. 8LTBCh. 9 - Add labels to the figure that follows, which...Ch. 9 - Prob. 10LTB
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following best describes the process of DNA sequencing? a. DNA is separated on a gel, and the different bands are labeled with fluorescent nucleotides and scanned with a laser. b. A laser is used to fluorescently label the nucleotides present within the DNA, the DNA is run on a gel, and then the DNA is broken into fragments. c. Nucleotides are scanned with a laser and incorporated into the DNA that has been separated on a gel, and then the DNA is amplified with PCR. d. Fragments of DNA are produced in a reaction that labels them with any of four different fluorescent dyes, and the fragments then are run on a gel and scanned with a laser. e. DNA is broken down into its constituent nucleotides, and the nucleotides are then run on a gel and purified with a laser.arrow_forwardBOTTOM The sequence depicted on the gel is 5'-GTGATGTAG-3' The sequence depicted on the gel is 3'- GTGATGTAG -5' The sequence shown on the gel is the sequence of the template strand of the reaction The sequence shown on the gel is complementary to the template strand of the reaction The template strand of the reaction is antiparallel to the sequence shown on the gel The largest fragment shown on the gel is closest to the top The largest fragment shown on the gel is closest to the bottom Each of the fragments shown on the gel have a primer incorporated at their 5' end Each of the fragments shown on the gel have a primer incorporated at their 3' end The number of nucleotides in the shortest band on the gel is 21 The number of nucleotides in the longest band on the gel is 21 ick Save and Submit to save and submit. Cick Save All Answers to save all answers.arrow_forwardA typical polymerase cycle reaction (PCR) program (Figure 3) followed as: HOLD 1 HOLD 3 HOLD 2 (30CYCLES) 95° C 94°C 72C 72° C 04:00 1:00 1:00 10:00 52.0° C 1:00 04° C 00 Figure 3 (i) Why is polymerase cycle reaction (PCR) repeated 30 times (Figure 3)? What are the differences between primers for PCR program, and primers for DNA replication process during S-phase? (ii) (iii) What are the FIVE (5) basic reagents used in PCR?arrow_forward
- please solve this with step-by-step calculations and explanations.arrow_forwardExplain how the percentage efficiency of a real-time PCR reaction is determined using a theoretical experiment and why this is essential in any real-time PCR analysis.arrow_forwardPlease fill in the blank and explain answerarrow_forward
- Make the PCR Cocktail I field out my work.. but I don't know which one is incoeert.. This table lists the ingredients, stock reagent concentrations, and concentrations in the PCR reaction. Prepare a "PCR cocktail" to be added to your samples to achieve these concentrations. Make enough cocktail to run nine samples. [Four student samples + three positive controls + one negative control + one extra.] {Hint: Remember that the concentration in the reaction is not the same as the concentration in the cocktail!] Component Stock Concentration Concentration in the PCR reaction Volume per reaction Volume to make cocktail Sterile water - - 0µl 0µl PCR buffer w/ MgCl2 10x 1x 4µl 36µl Nucleotide mix 10 mM 0.2 mM 0.8µl 7.2µl Primer 1 (Forward) 10 µM 1.0 µM 4µl 36µl Primer 2 (Reverse) 10 µM 1.0 µM 4µl 36µl Taq DNA polymerase 5 U/µl 1.0 U 8µl 72µl DNA template (sample) - ~1 ng 20 µl 180µl Total - - 40 µl 360 µlarrow_forwardThe image below shows the general structure of a gene on a chromosome. The arrows above and below the chromosome indicate the binding positions of potential forward (F) and reverse (R) PCR primers. Select two primers from the list below that would exclusively amplify exon 3 in a PCR reaction. ut of Intron 1 Intron 2 +1 Poly-A signal ATG TAG F1 Exon 1 F4 Exon 2 F6 Exon 3 R6 R4 R3 R2 R1 Promoter Select all that apply: cross out Da. F1 cross out Ob. F2 cross out Oc. F3 cross out O d. F4 cross out O e. F5 cross out f. F6 cross out g. R1 cross out Oh. R2 cross out OL R3 cross out O. R4 cross out k. R5 cross out R6 TIarrow_forwardFrom a single DNA molecule, calculate how many copies would be produced in 12 cycles of pcrarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Molecular Techniques: Basic Concepts; Author: Dr. A's Clinical Lab Videos;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7HFHZy8h6z0;License: Standard Youtube License