
(a)
Interpretation:
The probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus A in the bonding and also in the antibonding orbitals is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Electronic configuration tells about the arrangement of the electrons in each subshell and each orbital of an atom. The distribution of the electrons in the molecules is described by the molecular orbital theory. The unoccupied molecular orbital having lowest energy is known as the LUMO and the occupied molecular orbital having highest energy is known as the HOMO.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9B.2P
The probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus A in the bonding orbital is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that a small-electron probe having volume
The value of R is
The value of
The value of
The expression that is used represent probability of finding an electron is given below.
Where,
The distance between A and B is
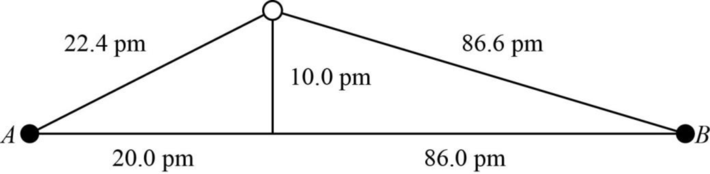
Figure 1
The value of
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus A in the bonding orbital is
(b)
Interpretation:
The probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus B in the bonding and also in the antibonding orbitals is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 9B.2P
The probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus B in the bonding orbital is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that a small-electron probe having volume
The value of R is
The value of
The value of
The expression that is used represent probability of finding an electron is given below.
Where,
The distance between A and B is
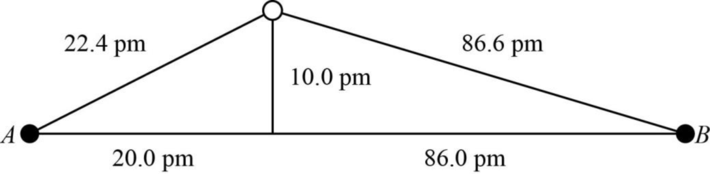
Figure 1
The value of
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the probability of the presence of an electron at nucleus B in the bonding orbital is
(c)
Interpretation:
The probability of the presence of an electron at half way between A and B in the bonding and also in the antibonding orbitals is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem 9B.2P
The probability of the presence of an electron at half way between A and B in the bonding orbital is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that a small-electron probe having volume
The value of R is
The value of
The value of
The expression that is used represent probability of finding an electron is given below.
Where,
The distance between A and B is
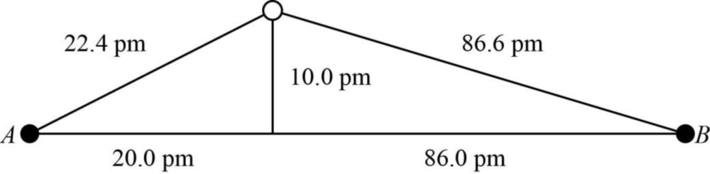
Figure 1
The value of
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the probability of the presence of an electron at half way between A and B in the bonding orbital is
(d)
Interpretation:
The probability of the presence of an electron at a point
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem 9B.2P
The probability of the presence of an electron at a point
Explanation of Solution
It is given that a small-electron probe having volume
The value of R is
The value of
The value of
The expression that is used represent probability of finding an electron is given below.
Where,
The distance between A and B is
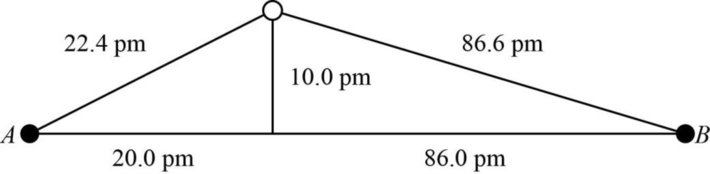
Figure 1
The value of
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the probability of the presence of an electron at a point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. VOL.1+2 (LL)(11TH)
- (c) (4pts) Mechanism: heat (E1) CH3OH + 1.5pts each _E1 _ (1pt) Br CH3OH (d) (4pts) Mechanism: SN1 (1pt) (e) (3pts) 1111 I H 10 Ill!! H LDA THF (solvent) Mechanism: E2 (1pt) NC (f) Bri!!!!! CH3 NaCN (3pts) acetone Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) (SN1) -OCH3 OCH3 1.5pts each 2pts for either product 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H Br (g) “,、 (3pts) H CH3OH +21 Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) H CH3 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistryarrow_forwardA mixture of butyl acrylate and 4'-chloropropiophenone has been taken for proton NMR analysis. Based on this proton NMR, determine the relative percentage of each compound in the mixturearrow_forwardQ5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





