
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided, and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry, where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
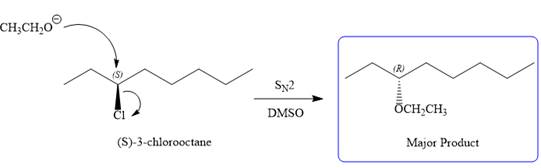
E2 pathway:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
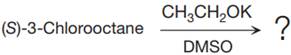
The structure of
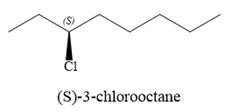
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination as chlorine is a moderately good leaving group. The chlorine atom is attached to an
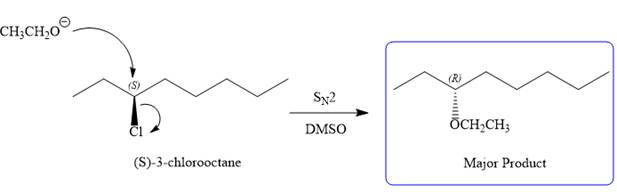
the corresponding ions:
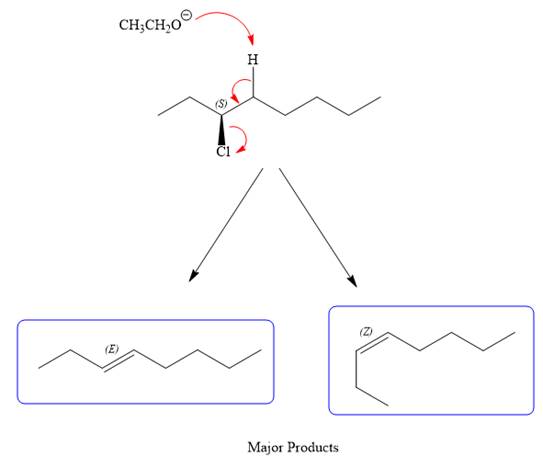
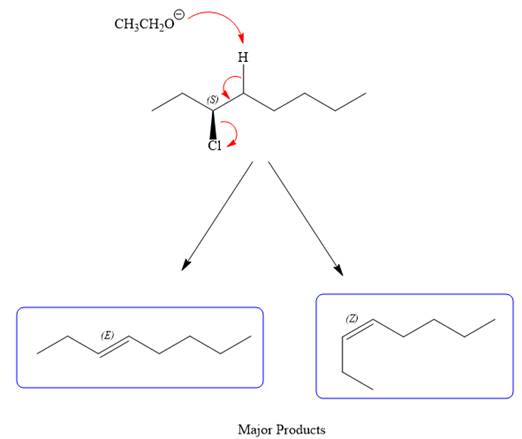
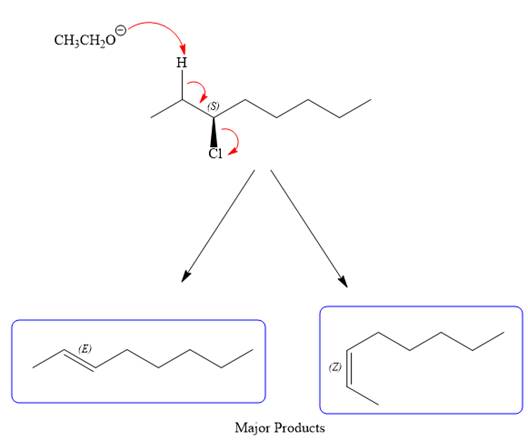
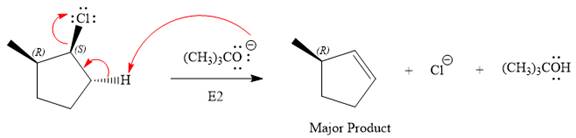
For the E2 product, the base abstracts the alpha hydrogen atom, which results in the formation of a mixture of products. The substrate has two types of alpha hydrogen atoms attached at C2 and C4 carbon atoms. Thus, in all four different products (alkenes) are possible for the
Note the stereochemistry, which is governed by the attack of the nucleophile from the side opposite the leaving group to yield major product in case of
As for the E2 reaction, as there are two different hydrogen atoms attached on either sides of the carbon atom with the leaving group, there could be four stereoisomers for the reaction. All four will be the major products.
The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
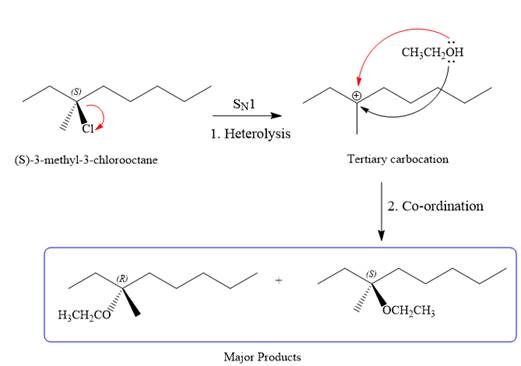
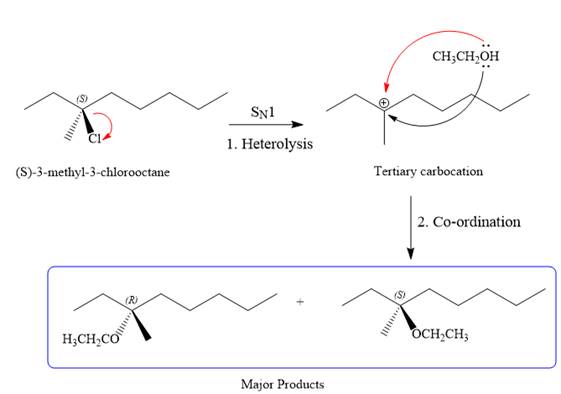
SN1 pathway:
E1 pathway:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is

The structure of
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination as chlorine is a moderately good leaving group. The chlorine atom is attached to an
As the leaving group is attached to a tertiary carbon atom,
First step in the
Step two is the attack of the nucleophile on the carbocation from both the sides to generate mixture of stereoisomers if the substrate has a chiral center and the reaction occurs at the chiral center. The C3 carbon atom where the reaction occurs is a chiral carbon atom. Thus, a mixture of stereoisomers is produced as the racemic mixture; thus, two produces are formed as major products in the
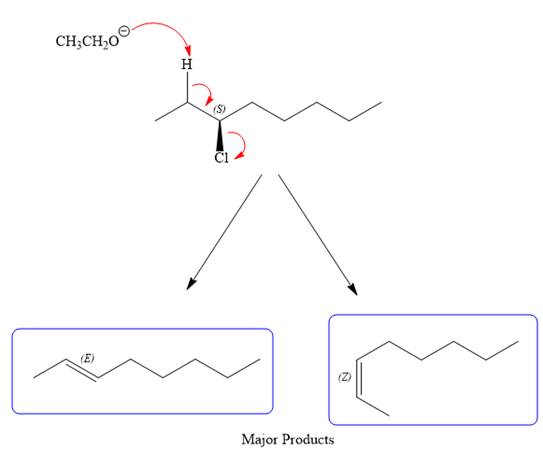
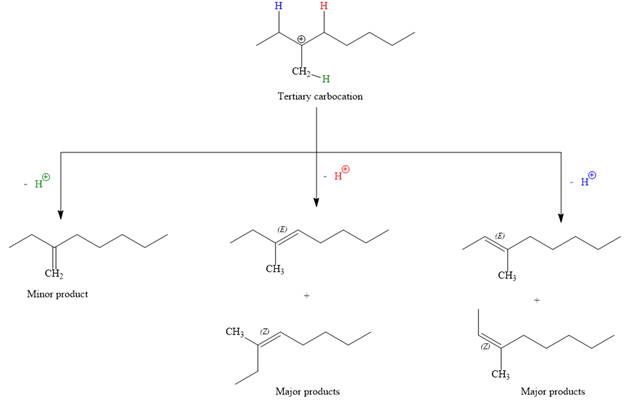
For the E1 product, the first step is common, that is, formation of a tertiary carbocation.
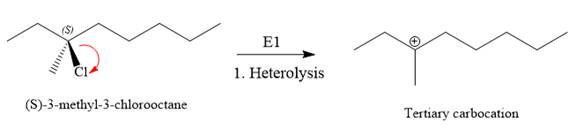
In the second step, the hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom of the carbocation is abstracted, resulting into an alkene. The tertiary carbocation formed above has three different adjacent hydrogen atoms.
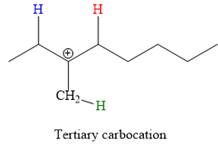
Elimination usually occurs so as to produce the most stable (the most substituted) alkene as the major product. Thus, abstraction of the green hydrogen atom by the base would result in the least substituted alkene, and therefore, it will be the minor product.
Abstraction of red and blue protons would result in four possible products, all of which are major products.
The complete, detailed mechanism for the E1 reaction is given below:
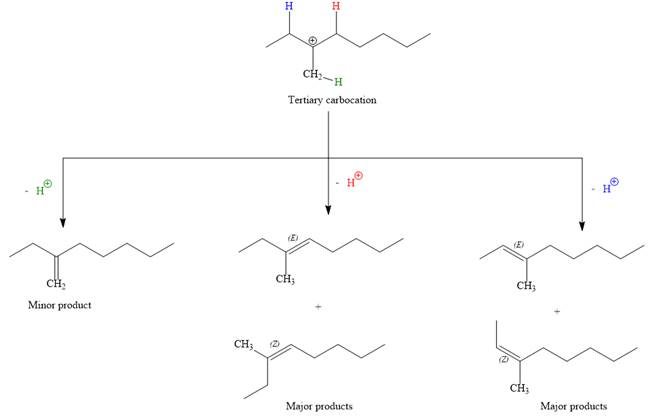
Note the stereochemistry, there are four major products (trisubstituted alkenes), and one minor product (disubstituted alkene) formed in the above mechanism.
The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
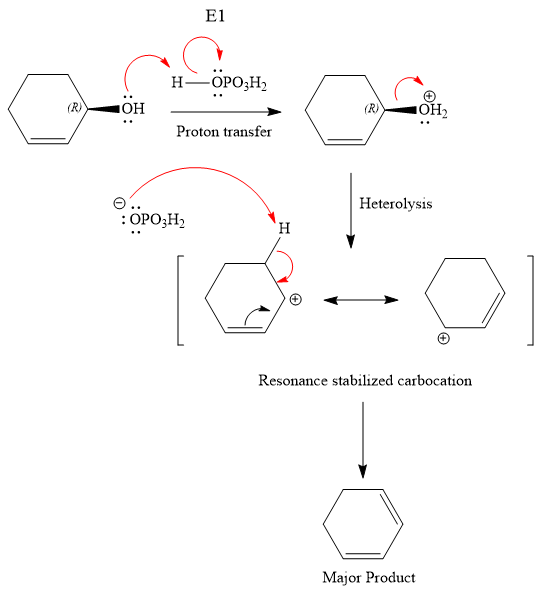
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
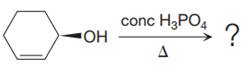
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination; however hydroxyl group is not a good leaving group. The chlorine atom is attached to an
The reagent used is a phosphoric acid, which is a strong acid. It will protonate the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group and convert it into a good leaving group. Elimination reactions are generally favored if the reaction conditions includes heat. This rules out both the substitution reactions. And as the hydroxyl group will be protonated by the strong acid, in the next step, it will be removed to generate a resonance stabilized secondary carbocation. Thus, the E1 reaction is highly favored. In the next step, the hydrogen atom adjacent to the carbocation is removed to form an
The complete, detailed mechanism is shown below:
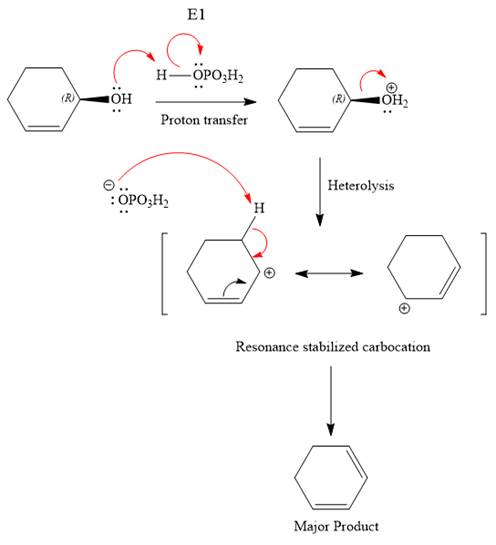
The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
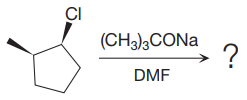
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination as chlorine is a moderately good leaving group. The chlorine atom is attached to an
the corresponding ions:
Here,
For the E2 product, the base abstracts the alpha hydrogen atom which would result in the formation of a mixture of products. But since the base is a bulky base, the proton, which is least sterically hindered, will be abstracted to form the major product.
The complete, detailed mechanisms is shown below:

The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
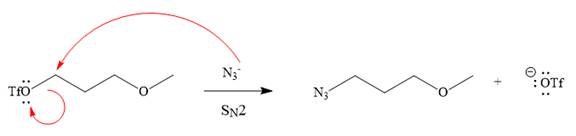
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
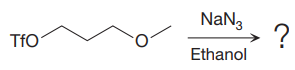
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination as the
The
The complete, detailed mechanism is shown below:

As the reaction yields a single product, it is the major product.
The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided and the products are to be predicted including stereochemistry where appropriate. It is be determined whether the reaction will yield exclusively one product or a mixture of products. If the reaction will yield a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In order to predict the outcome of the given reaction, four factors are considered.
First is to determine if the substrate molecule has a suitable leaving group. If the leaving group is suitable, then evaluate the type of carbon bonded to the leaving group. For an
Answer to Problem 9.63P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction and the products (major) including the stereochemistry are given below:
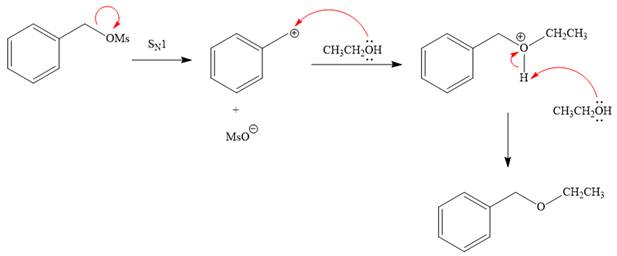
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
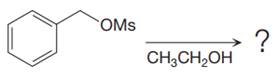
The substrate has one site for substitution or elimination, which is the
The attacking species and the solvent for the reaction is the same, that is, ethanol, which serves as a weak nucleophile and a polar protic solvent. This strongly favors
The first step in the
The complete, detailed mechanism is shown below:
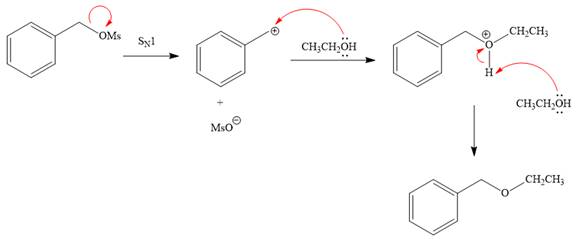
The outcome of any given reaction can be predicted by considering the factors like nature of the leaving group, substrate, strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

