
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
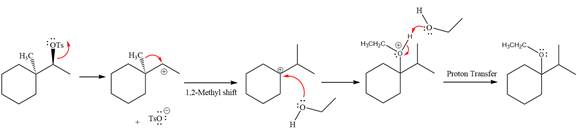
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
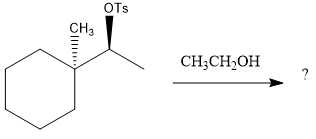
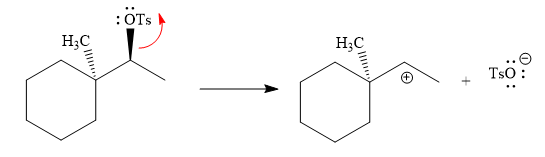
The absolute configuration of the substrate is S. This is solvolysis reaction because ethanol acts as a nucleophile and a solvent. The leaving group,
The attacking species
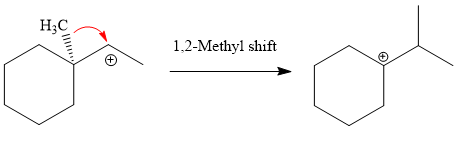
The loss of the leaving group,
A tertiary carbocation is highest stability than a secondary and primary carbocation. Next,
Now, the weak nucleophile,
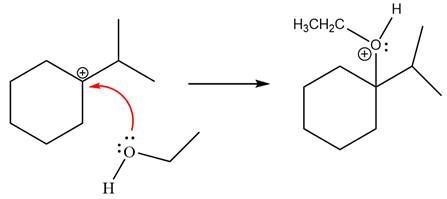
Finally, deprotonation of the
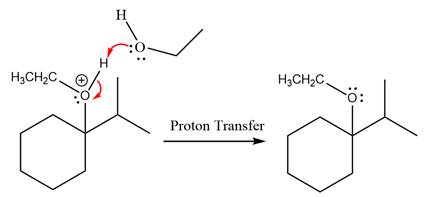
The detailed, complete mechanism is as follows:
The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
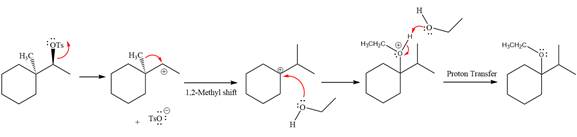
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
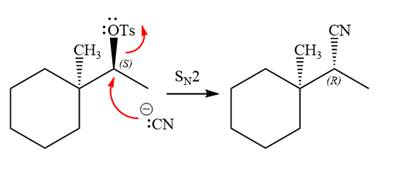
The stereochemistry of the product is R configuration.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
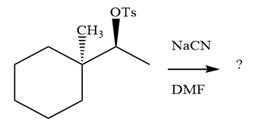
The absolute configuration of the substrate is S. The leaving group,
The attacking species
The carbon atom attached to the leaving group is a chiral center.
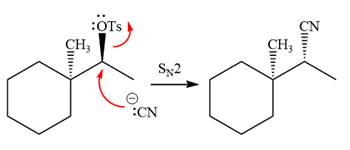
The stereochemistry of the product is R configuration.
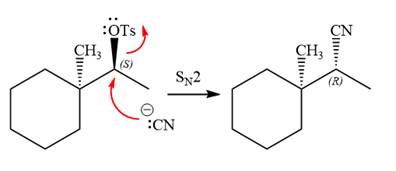
The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
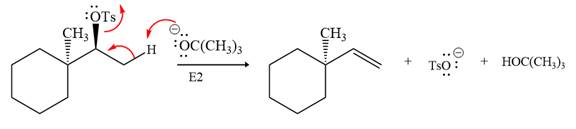
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
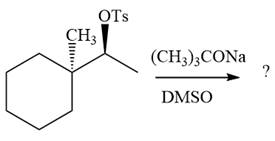
The absolute configuration of the substrate is S. The leaving group,
The attacking species
In the substrate, the alpha C atom has one H atom attached to it. Since

The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
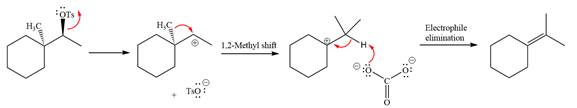
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
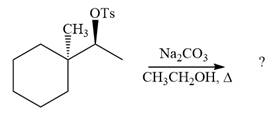
The absolute configuration of the substrate is S. The leaving group,
The attacking species
The loss of the leaving group,
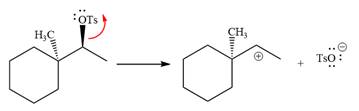
A tertiary carbocation is greatest stability than a secondary and primary carbocation. Next,
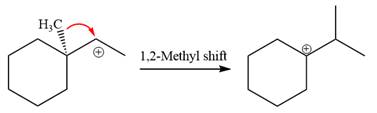
Now, the weak nucleophile
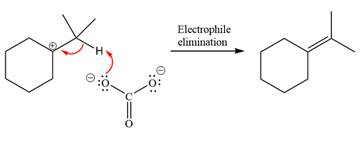
The detailed, complete mechanism is as follows:
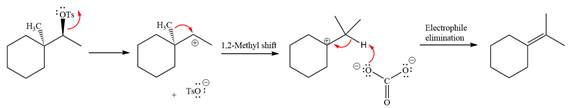
The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
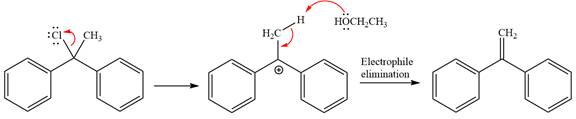
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
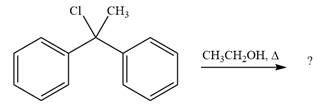
This is a solvolysis reaction because ethanol acts as a nucleophile and the solvent. The leaving group,
The attacking species
The loss of the leaving group,
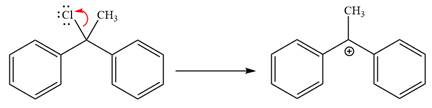
Now, the weak nucleophile
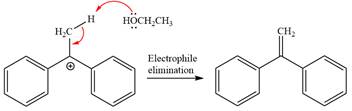
The detailed, complete mechanism is as follows:
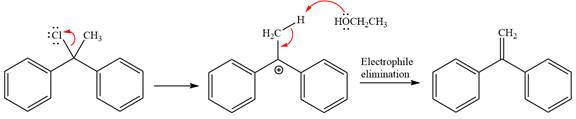
The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is to be provided. The stereochemistry of the products is to be predicted where appropriate. If the reaction yields exclusively one product or a mixture of products, then the major product is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
For the prediction of the outcome of the
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The complete, detailed mechanism for the reaction is shown below:
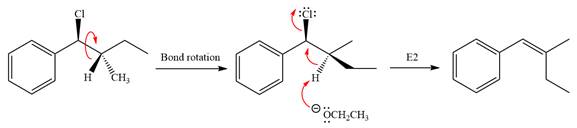
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
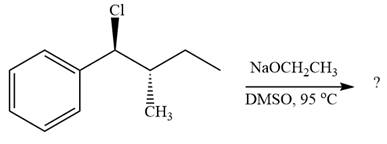
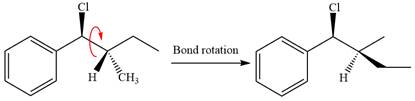
The leaving group,
The attacking species
In the substrate, only one H atom can be eliminated. The leaving group and H atom are on same side.
The base deprotonates a hydrogen atom from the substrate and to yield the most substituted alkene as the product.
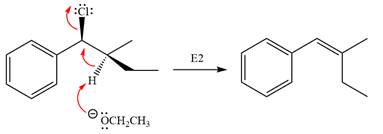
The detailed, complete mechanism is as follows:
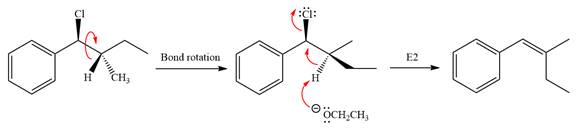
The outcome of the given reaction is predicted by considering factors like the nature of the leaving group, substrate, the strength of the reagent used, solvent, and temperature.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- CUE COLUMN NOTES (A. Determine Stereoisomers it has ⑤ Identify any meso B compounds cl Br cl -c-c-c-c-¿- 1 CI C- | 2,4-Dichloro-3-bromopentanearrow_forwardThe acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forwardWhat does the phrase 'fit for purpose' mean in relation to analytical chemistry? Please provide examples too.arrow_forward
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density × NO2 ○ donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O electron-rich electron-deficient no inductive effects O no resonance effects O similar to benzene E [ CI O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Explanation Check ○ donating withdrawing no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardUnderstanding how substituents activate Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation HN NH2 Check X (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Aarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects on benzene For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density Molecule CF3 O donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene CH3 O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects O donating O withdrawing Ono resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Explanation Check Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- * Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules. Follow Up Questions for Part B 12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts) a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts) b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts) ofarrow_forwardDraw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers Draw 1 chemical reaction of an etherarrow_forwardPlease help me with the following questions for chemistry.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

