
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles in ethanol is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In a charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom. Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
Negatively charged nucleophiles are stronger than corresponding uncharged nucleophiles. Of the two nucleophiles, the second
Therefore,
Negatively charged species are stronger nucleophiles than uncharged ones.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles, in ethanol, is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In the charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom. Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
Both are uncharged species, and the donor atoms in the two are from the same period. In this case, the strength of the nucleophile will depend on the electronegativity of the donor atom. The less electronegative nitrogen atom is better able to donate its lone pair than the more electronegative oxygen atom.
Therefore, the stronger electrophile is
The strength of a nucleophile increases with decreasing electronegativity of the donor atom.
(c)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles in ethanol is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In the charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
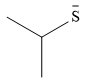
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
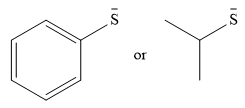
Both species are negatively charged, so the solvation effect of the protic solvent ethanol is expected to be similar.
The donor atom is also the same in both species. The strength as a nucleophile will then depend on the stability of the charge.
In the first species, the charge is resonance stabilized over a total of four atoms.
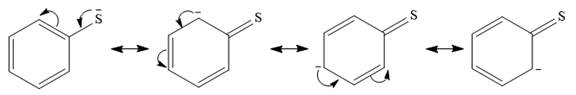
There is no such stabilization in the second species.
Therefore, the stronger nucleophile is the second species.

Resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a negatively charged nucleophile.
(d)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles in ethanol is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In the charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom. Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
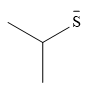
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
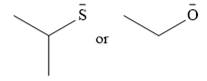
Both are negatively charged nucleophiles with the charge on atoms, S and O, that are from the same group. The sulfur atom is considerably larger than the oxygen atom, and normally would be expected to stabilize the charge better. This would mean that the second nucleophile, with less charge stabilization would be the stronger nucleophile.
However, the solvent in this case, ethanol is protic. It will solvate the smaller oxygen atom much better than the sulfur atom. This solvation will stabilize the second species more than the first one.
Therefore, the stronger nucleophile of the two in ethanol would be

Solvation of negatively charged species by protic solvents can reverse the usual order for nucleophiles containing donor atoms from the same group of the periodic table.
(e)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles in ethanol is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In the charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom. Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
Both are negatively charged species, with donor atoms that carry the charge from the same group. Usually this would mean the species with the smaller donor atom would be the stronger nucleophile. However, the solvent in this case is a protic solvent, ethanol. The smaller sulfur atom will be more strongly solvated than the larger selenium atom. This will reduce the strength of the sulfur containing nucleophile much more than that of the selenium containing nucleophile, thus reversing the usual order.
Therefore, the stronger nucleophile in ethanol is
Solvation of negatively charged species by protic solvents can reverse the usual order for nucleophiles containing donor atoms from the same group of the periodic table.
(f)
Interpretation:
The stronger of the given pair of nucleophiles in ethanol is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The strength of a nucleophile depends on several factors. Generally, a negatively charged species is a stronger nucleophile than an uncharged species. In the charged nucleophile, the less stable the charge, the higher the strength as a nucleophile. A negative charge is less stable on a relatively less electronegative atom. Therefore, when comparing atoms from the same period, the less electronegative atom (with a negative charge) is a stronger nucleophile. For atoms from the same group, stability of the charge depends on the size of the atom. If the atom bearing the charge is small, the stability is less and strength as a nucleophile is higher. Resonance can stabilize a charge through delocalization over more than one atom, so resonance stabilization of the charge reduces the strength of a nucleophile. The strength also depends, to some extent, on the inductive effect of the groups attached to the carbon that is bonded to the nucleophilic atom. Inductively electron donating groups destabilize the charge and increase the strength of the nucleophile. On the other hand, inductively electron withdrawing groups decrease the strength of a nucleophile.
Protic solvents strongly solvate and stabilize negatively charged species, and therefore, reduce the strength of negatively charged nucleophiles. If the atoms carrying the charge are from the same group, the order of strength is reversed in a protic solvent because the solvation is greater for smaller atoms.
Answer to Problem 9.57P
The stronger nucleophile of the two is
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of nucleophiles is
Both are negatively charged species, with the charge on atoms that are from the same period. The sizes of the two atoms are nearly the same, so solvation by the protic solvent is not expected to differ significantly. The strength will depend mostly on the electronegativity of the atom. The less electronegative Se will not stabilize the charge as strongly as the more electronegative Br.
Therefore, the stronger nucleophile of the two is
For nucleophiles containing donor atoms from the same period, lower the electronegativity of the donor atom, stronger is the nucleophile.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Using a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forwardCan you help me understand the CBC method on metal bridging by looking at this problem?arrow_forward
- A partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forwardProblem 38 can u explain and solve thanks april 24arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

