
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.40SP
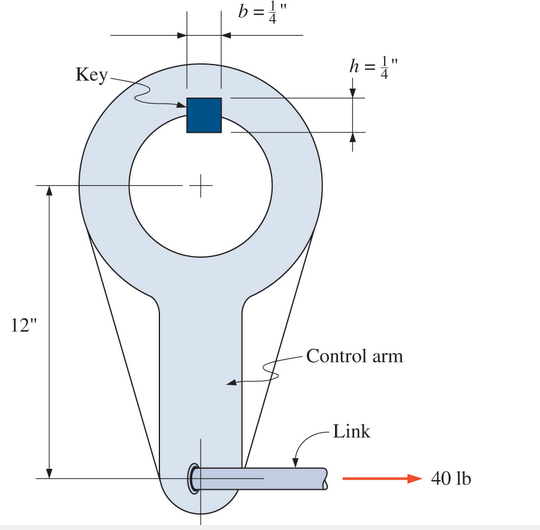
A control arm is keyed to a 1-in. -diameter shaft and a link transmits a 40 lb force to the end of the arm, as shown. The key is

Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule01:56
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve this and show all of the work
Solve this and show all of the work
Solve this and show all of the work
Chapter 9 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 9 - Write the direct stress formula in its three forms...Ch. 9 - A 6-in-diameter concrete test cylinder is loaded...Ch. 9 - Determine the tensile stress in each segment of...Ch. 9 - Calculate the stress developed in the following...Ch. 9 - The following members are subjected to axial...Ch. 9 - Determine the stresses in the two segments of the...Ch. 9 - A bin weighing 8 tons is supported by three steel...Ch. 9 - Diameters of small commercially available steel...Ch. 9 - A No. 32 (metric designation) reinforcing bar for...Ch. 9 - In the bolted connection of Figure 9.12 , assume...
Ch. 9 - Compute the force required to punch a...Ch. 9 - The 34 — in. — diameter bolt shown is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Why is strain unitless (or dimensionless)?Ch. 9 - (a) Given =1.2in. and L=100ft calculate (b) Given...Ch. 9 - A short compression member 2 in. by 2 in. in cross...Ch. 9 - A 100-ft-long rod is suspended from one end. The...Ch. 9 - Compute the total elongation of a steel bar,...Ch. 9 - A steel rod 34 in. in diameter and 25 ft long is...Ch. 9 - An aluminum rod 25mm in diameter and 4m long is...Ch. 9 - A steel rod 10 ft long is made up of two 5 ft...Ch. 9 - A titanium alloy bar elongates 0.500 in. when...Ch. 9 - Write a program that will calculate the allowable...Ch. 9 - Write a program that will compute stress, strain,...Ch. 9 - The Viking Bin Company manufactures suspended bins...Ch. 9 - Write a computer program that will calculate the...Ch. 9 - The joint between a diagonal and a chord in a...Ch. 9 - In Problem 9.26, find the required length of the...Ch. 9 - A column is supported by a base plate, pedestal,...Ch. 9 - If the soil pressure under the footing of Problem...Ch. 9 - A hopper weighing 75 kN is supported by three...Ch. 9 - A steel bar has a rectangular cross section 25 mm...Ch. 9 - A steel wire is suspended vertically from its...Ch. 9 - A W1240 shape is subjected to a tensile load of...Ch. 9 - Calculate the required diameter of steel tie rods...Ch. 9 - A 30-ft-long steel rod of circular cross section...Ch. 9 - Consider the bolted lap joint shown in Figure...Ch. 9 - An inclined member is braced with a glued block,...Ch. 9 - Calculate the force a punch press must exert if it...Ch. 9 - A 34 - in. - diameter punch is used to punch a...Ch. 9 - A control arm is keyed to a 1-in. -diameter shaft...Ch. 9 - Calculate the required width b for the key of...Ch. 9 - A 25-mm-diameter aluminum rod, 3 m long, is...Ch. 9 - A short timber post of Douglas fir is subjected to...Ch. 9 - A 1 00-ft surveyor’s steel tape with a...Ch. 9 - An 18-in-long steel rod is subjected to a tensile...Ch. 9 - Compute the magnitude of the tensile load that...Ch. 9 - A 5-mm-diameter steel wire, 18 m in length, is...Ch. 9 - A structural steel rod 112 in. in diameter and 20...Ch. 9 - A rectangular structural steel eyebar 34 in. thick...Ch. 9 - 9.50 A
in. — diameter steel rod, 100 ft long, is...Ch. 9 - For the truss shown, compute the total deformation...Ch. 9 - A steel bar with a cross section of 12 in. by 12...Ch. 9 - Rework Problem 9.52 , changing the second load...Ch. 9 - In the structure shown, the tie-back BC is a round...Ch. 9 - A hook is suspended by two steel wires, as shown....Ch. 9 - The trolley of a small hoist is supported on a...Ch. 9 - The steel piston rod to the master cylinder has a...Ch. 9 - A stranded steel brake cable is composed of 7...Ch. 9 - The piston of a steam engine is 400 mm in diameter...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
What will the following program display? def main (): x = 1 y = 3.4 print(x, y) change_us(x, y) print(x, y) def...
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Describe two properties that each candidate key must satisfy.
Modern Database Management
Simplify the following program segment Y = 5 if (Y == 7): Z = 8 else: Z = 9
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Explain the term foreign key, and give an example.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forwardProblem 1 8 in. in. PROBLEM 15.109 Knowing that at the instant shown crank BC has a constant angular velocity of 45 rpm clockwise, determine the acceleration (a) of Point A, (b) of Point D. 8 in. Answer: convert rpm to rad/sec first. (a). -51.2j in/s²; (b). 176.6 i + 50.8 j in/s²arrow_forward
- Problem 4 The semicircular disk has a radius of 0.4 m. At one instant, when 0-60°, it is rotating counterclockwise at 0-4 rad/s, which is increasing in the same direction at 1 rad/s². Find the velocity and acceleration of point B at this instant. (Suggestion: Set up relative velocity and relative acceleration that way you would for a no-slip disk; remember what I told you to memorize on the first day of class.) (Answer: B = −2.98î - 0.8ĵ m/s, ãB = 2.45î - 5.74ĵ m/s²) B 0.4 m y Xarrow_forwardA C C 2r A 2r B B (a) (b) Problem 3 Refer to (b) of the figure shown above. The disk OA is now rolling with no slip at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = 2wk, AB = w²k)arrow_forwardProblem 2 Refer to (a) of the figure shown below, where the disk OA rotates at a constant angular velocity of w. Find the angular velocity and angular acceleration of link AB and link BC. (Partial Answers: WBC = wk, AB = w²k) A 2r C B (a) A 2r B (b)arrow_forward
- Example Two rotating rods are connected by slider block P. The rod attached at A rotates with a constant clockwise angular velocity WA. For the given data, determine for the position shown (a) the angular velocity of the rod attached at B, (b) the relative velocity of slider block P with respect to the rod on which it slides. b = 8 in., w₁ = 6 rad/s. Given: b = 8 in., WA = 6 rad/s CW constant Find: (a). WBE (b). Vp/Frame E 60° 20° Barrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin + N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f (t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: • Analytically (hand calculations) Creating Simulink Model Plot solutions for first two, three and four non-zero terms as well as the Simulink solution on the same graph for the first 15 sec. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward
- Two springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m² = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. (y₁ = 0) www k₁ = 3 Jm₁ = 1 k2=2 www (Net change in spring length =32-31) (y₂ = 0) m₂ = 1 32 32 System in static equilibrium System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁ (t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Produce an animation of the system for all solutions for the first minute.arrow_forwardTwo large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min 1 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t≥ 0: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Plot all solutions on the same graph for the first 15 min. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward5. Estimate the friction pressure gradient in a 10.15 cm bore unheated horizontal pipe for the following conditions: Fluid-propylene Pressure 8.175 bar Temperature-7°C Mass flow of liquid-2.42 kg/s. Density of liquid-530 kg/m³ Mass flow of vapour-0.605 kg/s. Density of vapour-1.48 kg/m³arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About TRANSVERSE SHEAR in 10 Minutes!! - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4x0E9yvzfCM;License: Standard Youtube License