
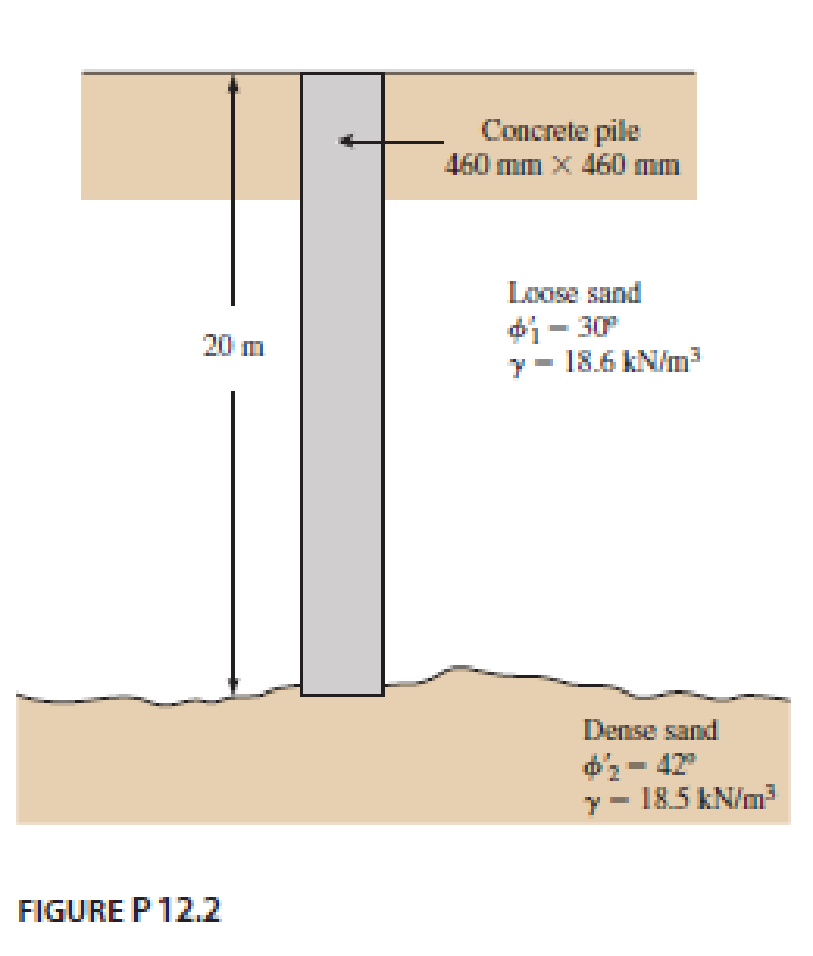
A 20 m long concrete pile is shown in Figure P12.2. Estimate the ultimate point load Qp by
- a. Meyerhof’s method
- b. Vesic’s method
- c. Coyle and Castello’s method
Use m = 600 in Eq. (12.28).
a.
Find the ultimate point load using Meyerhof’s method.
Answer to Problem 9.1P
The ultimate point load using Meyerhof’s method is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the concrete pile is 20 m.
Area of the concrete pile
Soil friction angle
Unit weight of sand
Depth
Calculation:
Find the bearing capacity
Substitute 20 m for D and
Refer Table 12.6. “Interpolated values of
The value of
Take the atmospheric pressure
Find the value of ultimate point load
Here,
Find the value of
Substitute
Find the value of
Substitute
Substitute
The ultimate load should satisfy,
Substitute
So take the value of
Therefore, the ultimate point load using Meyerhof’s method is
b.
Find the ultimate point load using Vesic’s method.
Answer to Problem 9.1P
The ultimate point load using Vesic’s method is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the modulus of elasticity
Substitute 600 for m and
Find the Poisson’s ratio of the soil using the relation:
Substitute 42 for
Find the value of average volumetric strain in the plastic zone below the pile point
Substitute 42 for
Find the value of rigidity index
Substitute
Find the value of reduced rigidity index
Substitute 66.1 for
Find the mean effective normal ground stress
Substitute
Refer Table 12.8. “Bearing capacity factors
The value of
Find the value of ultimate point load
Substitute
Therefore, the ultimate point load using Vesic’s method is
c.
Find the ultimate point load using Coyle and Castello’s method.
Answer to Problem 9.1P
The ultimate point load using Coyle and Castello’s is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the value of
Substitute 20 m for L and 460 mm for D.
Refer Figure 12.20, “Variation of
The value of
Find the value of ultimate point load
Substitute
Therefore, the ultimate point load using Coyle and Castello’s method is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- Send me the solution to the following question based on the source and I do not want the solution from artificial intelligencearrow_forwardSend me the solution to the following question based on the source and I do not want the solution from artificial intelligencearrow_forwardSend me the solution to the following question based on the source and I do not want the solution from artificial intelligencearrow_forward
- STRUCTURES I Homework #1: Force Systems Name: TA: PROBLEM 1 Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force in the cable shown. PROBLEM 2 The horizontal component of force F is 30 lb. What is the magnitude of force F? 6 10 4 4 F = 600lbs F = ?arrow_forward18:02 28% 50 同 こ 【Recommend】 Easily add text in PDF 3 m 35 kN 4m 84 kN +3m EA = constant E = 200 GPa A T5 4m Add 1,200 mm² Find Horizontal and vertical displacement at B 4 kN m m- B Determine Vertical displacement at C Determine the displacement or point B of the steel beam shown in Take E200 GPa, I = 500(106) mm4. 5 m 2/ 40 kN B 12 kN/m 4 m. 12 kN/m 3 m B 10 m- E constant = 70 GPa I 554 (10) mm Determine Displacement at C ΙΣΤ Edit Annotate Fill & Sign Convert Allarrow_forwardIn a floor of an industrial building, boilers are supported symmetrically on secondary beams A and B, which have a centre-to-centre distance of 5 m and which are in turn supported by the main beam, which has a span of 9 m (see Fig. 10.62). Design the main beam given the following data:arrow_forward
- S₂ S S,-40 S,-100 P S,=40 40 80 80 40arrow_forwardThe bolted connection shown is connected with M20 bolts in standard holes. The plate material is A36 steel. Find the allowable (ASD) tensile strength of each plate. 50 65 65 65 13 40 65 40 13arrow_forwardA 3.048 m long column (Fy = 483 MPa) carries an axial compression load of 5000 kN dead load. The column is braced at mid-height to strengthen the column in the weak direction. Use LRFD. Which of the following most nearly gives the nominal compressive strength? Show solution and drawingsarrow_forward
- When an open-ended square tube is placed vertically into a pool of water, the water rises 4 mm up inside of the tube. A) Determine the inner length of the square tube. A solid cylindrical rod is then placed vertically down the center of the open-ended square tube and the water rises an additional 4 mm up the tube. B) Determine the diameter of the solid rod that was inserted. 0.073 @ 20N m T C s = = o .arrow_forwardPlease use the following labels in the image such as Va, Vbr, Vbl and etc. Show step by step solution for each. Thanks!arrow_forwardThe single story building shown in Fig. 2 has an applied uniform load of 300 psf (0.3ksf) including the self weight of the beams and the girders. The roof has a 16 ft x 15 ft opening as shown. 1. Determine the axial loads on Columns C1 and C2 using reactions from the beams supported on the columns. 2. Determine the axial loads on Columns C1 and C2 using the concept of tributary areas.arrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning



