
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305081550
Author: Braja M. Das
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.12P
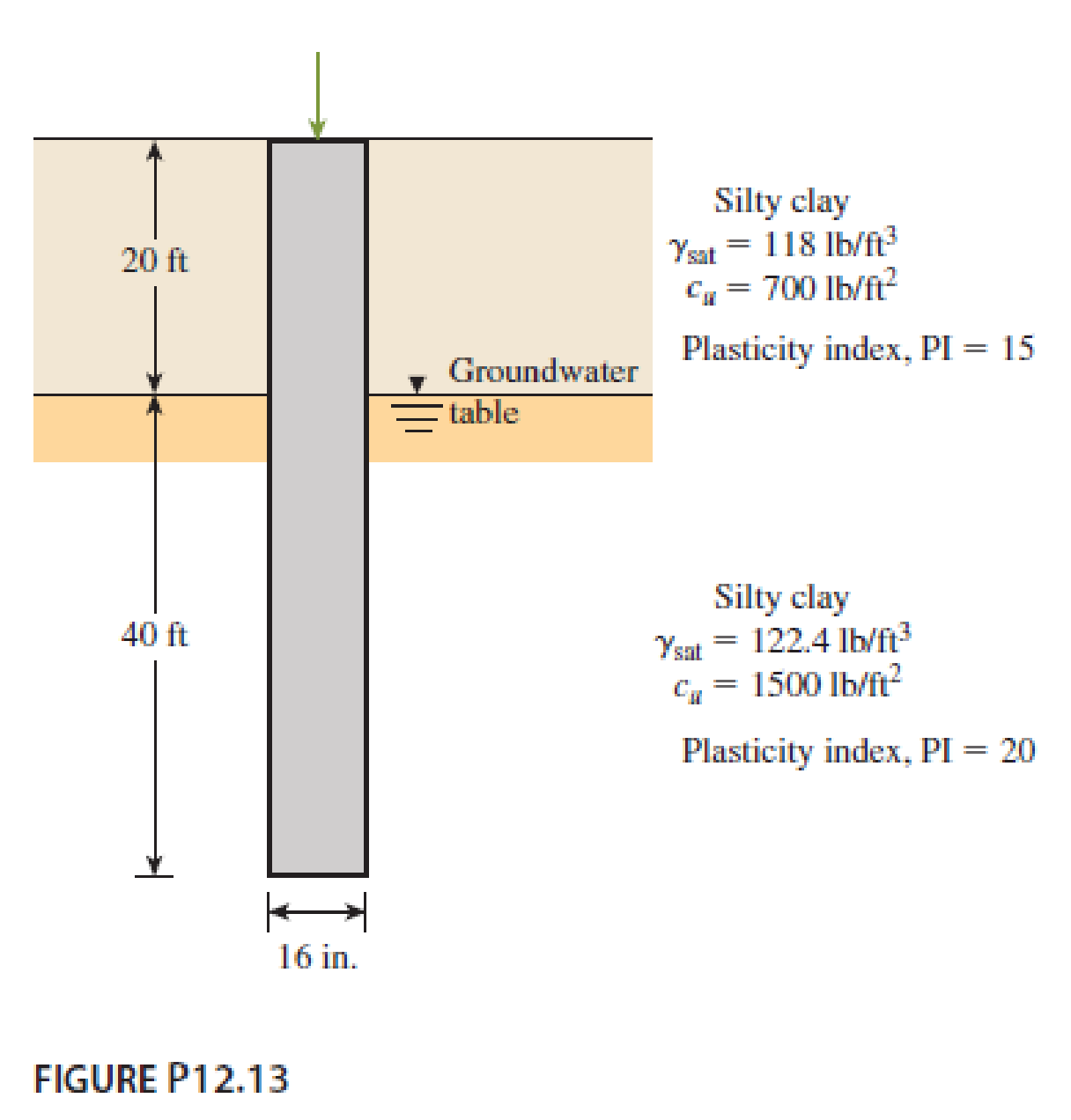
Solve Problem 12.13 using Eqs. (12.59) and (12.60).
12.13 A concrete pile 16 in. × 16 in. in cross section is shown in Figure P12.13. Calculate the ultimate skin friction resistance by using the
- a. α method [use Eq. (12.61) and Table 12.11]
- b. λ method
- c. β method
Use
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A reinforced concrete beam with b=300mm, h=670mm,and d=600 mm, having
a span of 7.3 m, can be considered as a fully fixed at the left support and simply
supported at the right end. It is reinforced for positive bending with 8-16 and for
negative bending with 4816 plus 418. Calculate the collapse load using the plastic
hinge method. (20%)
A reinforced concrete beam with b=300mm, h=670mm,and d=600 mm, having
a span of 7.3 m, can be considered as a fully fixed at the left support and simply
supported at the right end. It is reinforced for positive bending with 8-16 and for
negative bending with 4816 plus 418. Calculate the collapse load using the plastic
hinge method.
Calculate the collapse load (P) for the two fixed ended beam shown below.
Use equilibrium method
P
2 m
4 m
L=6 m
Chapter 9 Solutions
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 9 - A 20 m long concrete pile is shown in Figure...Ch. 9 - Refer to the pile shown in Figure P9.1. Estimate...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.3PCh. 9 - A driven closed-ended pile, circular in cross...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.5PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.6PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.7PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.8PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.9PCh. 9 - A concrete pile 16 in. 16 in. in cross section is...
Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.11PCh. 9 - Solve Problem 12.13 using Eqs. (12.59) and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.13PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.14PCh. 9 - A steel pile (H-section; HP 310 125; see Table...Ch. 9 - A concrete pile is 20 m long and has a cross...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.17PCh. 9 - Prob. 9.18PCh. 9 - Solve Problem 12.23 using the method of Broms....Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.20PCh. 9 - Solve Problem 12.25 using the modified EN formula....Ch. 9 - Solve Problem 12.25 using the modified Danish...Ch. 9 - Figure 12.49a shows a pile. Let L = 15 m, D (pile...Ch. 9 - Redo Problem 12.30 assuming that the water table...Ch. 9 - Refer to Figure 12.49b. Let L = 18 m, fill = 17...Ch. 9 - A concrete pile measuring 16 in. × 16 in. in cross...Ch. 9 - The plan of a group pile is shown in Figure...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.28PCh. 9 - The section of a 4 × 4 group pile in a layered...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.30P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please use virtual work/ force method as I am struggling with that particular concept.arrow_forwardThe anchor from Part A can also fail in shear in the circular head, as shown (Figure 3). What is the minimum thickness tt required for the head to support the allowed load PallowPallow = 15 kNkN if the material fails in shear at τfailτfail = 30 MPaMPa ? Use a factor of safety F.S.F.S. = 2.2.arrow_forwardFind three sites on the www related to reinforced concrete (other than thoselinked to the Syllabus). For each site, provide a written description of the sitecontent and the site’s URL.arrow_forward
- Visit the course web page on Canvas. Find the document where the advantagesand disadvantages of reinforced concrete are listed. Provide at least three additionaladvantages and three additional disadvantages. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardMax. Flow rate from catchment area=0.25 m³/s drain to road (one side road) having roof section with longitudinal slope %1, n=0.016, cross-section slope %1, 24 m width of road, 0.15 m curb stone. Gutter data: 7 cm high of water. 1-What is the capacity (or Max. flow rate) for this road? 2- With 0.5 m3 /s is it flood? 3-Whate is the clear zone in case Q=0.5 m³/s?arrow_forwardEstimate Q inlet for curb inlet in sump, If y=5 cm, L=0.5 m and %13 clogging.arrow_forward
- 3020,220 30 30m 120 Design inlet system for the road in figure below. C=0.93, i=65 mm/hr, Gutter data: y max.=9 cm, n=0.016, k=0.38, slope %1, Z=40, (space-bar-2 cm). Estimate inlet type. elevation in points (a-82.1, b=82 m), in point t rain water depth in point f>3 cm in u turn >5.5 cm. Sag point in S. Drow curbstone DATE DATE 5 100 Median strip 10 %1 d 72arrow_forwardEstimate Q inlet for grate inlet in sump, If w=0.4 m, L-0.5 m, y=5 cm and opining space 3 cm and bar width= 2.5 cm %12 clogging.arrow_forward12:39 You HD ⚫2 February, 10:33 am GE342 Physical Geodesy Quiz 1 Tuesday 30th January 2024 Duration 1 hour Ill. 68% Question 1 A spherical triangle ABC has an angle B = 90° and sides a = 50° and b = 70°. Find A, C and c (9) Question 2 Given two cities: Los Angeles (34°15′ N, 118°15' W) and Jakarta (06°20'S, 106°10'E). a. Find the length of the great circle arc connecting the two cities. (7) b. What would be the azimuth setting for an airplane flying from L.A to Jakarta? (6) c. What would be the azimuth setting for an airplane flying from Jakarta to L.A? (7) 29 ← Replyarrow_forward
- 11:49 Question 1 a. What is Geodesy? (2) b. What is physical geodesy. (2) .ill 73% c. Write short notes on the linkages physical geodesy has with each of the following: 8 marks Oceanography i. ii. Geophysics iii. iv. Geology Hydrology d. Define the following surfaces and draw a sketch showing the relationship between them. Geoid, reference ellipsoid, topography. (2+2+2) e. The following points had their ellipsoidal heights measured, compute their orthometric heights given the geoidal undulations: (2) Name TP5 ZQ135 Latitude Longitude Ellipsoid hgt. -12.61179 28.18421 1263.995 -12.80345 28.23022 1215.166 Geoidal undulations -6.715 -6.684 Question 2 (8+6+6) The following coordinates were given on a spherical earth with a radius of 6378000m, find a. The shortest distance between the points b. The azimuth from A to B c. The azimuth from B to A Latitude Longitude A 52°21'14"N 93°48'25″E B 52°24'18"N 93°42'30"E Question 3 (20) Two points lie on the same latitude as shown below: Point…arrow_forwardHome prob.: ·A Simply Supported beam, with cross section (250x60. a & Span 6.00m. It is carrying the req'd.. prestressing force for :- und.l. of 20 kN/m - Compu ic.service (a) Bottom fiber Stress equal to zero under full load with max (b1 Top fiber Stress equal to zero under D.L. plus prestressin force Cat initial stage)arrow_forwardAn oil pipeline and a 1.200 m^3 rigid air tank are connected to each other by a manometer, as shown in the figure. The tank contains 15 kg of air at 80°C. Assume the pressure in the oil pipeline to remain constant and the air volume in the manometer to be negligible relative to the volume of the tank. Determine the change in Δh when the temperature in the tank drops to 20°C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Concrete Slab Calculations 006; Author: Jerry Howard;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R19jILyBxio;License: Standard Youtube License