
a)
The power delivered by the plant assuming constant specific heats for air.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Temperature of the air at the compressor inlet
Pressure of the air at the compressor inlet
Temperature of the air at the turbine inlet
Pressure of the air at the turbine inlet
Rate of heat transferred to air
Effectiveness for the regenerator
Calculation:
Draw the
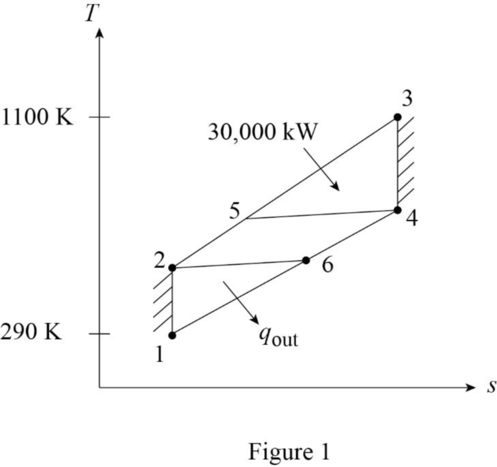
Refer Table A-2, “Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases”, obtain the properties of the nitrogen.
Calculate the pressure ratio
Calculate the temperature at state 2
Calculate the temperature at state 4
For 100% effectiveness of the regenerator, the temperatures at states 5 and 4 are equal and the temperatures at states 6 and 2 are equal.
Calculate the thermal efficiency of the cycle
Calculate the power developed by the plant
Thus, the power delivered by the plant assuming constant specific heats for air is
b)
The power delivered by the plant accounting for the variation of specific heats with temperature.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Refer table A-21, “Ideal gas properties of the air”, obtain the enthalpy and relative pressure of air at the temperature of
Calculate the relative pressure at state 2
Refer table A-21, “Ideal gas properties of the air”, obtain the enthalpy of air at the relative pressure of
Refer table A-21, “Ideal gas properties of the air”, obtain the enthalpy and relative pressure of air at the temperature of
Calculate the relative pressure at state 4
Refer table A-21, “Ideal gas properties of the air”, obtain the enthalpy of air at the relative pressure of
For 100% effectiveness of the regenerator, the enthalpies at states 5 and 4 are equal and enthalpies at states 6 and 2 are equal.
Calculate the thermal efficiency of the cycle
Calculate the power developed by the plant
Thus, the power delivered by the plant accounting for the variation of specific heats with temperature is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Thermal-fluid Sciences In Si Units
- Temperature may alternatively be defined as T = ди v Prove that this definition reduces the net entropy change of two constant-volume systems filled with simple compressible substances to zero as the two systems approach thermal equilibrium.arrow_forwardUsing the Maxwell relations, determine a relation for equation of state is (P-a/v²) (v−b) = RT. Os for a gas whose av Tarrow_forward(◉ Homework#8arrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^ 2. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A бро Barrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^2. Both boxes are 0.25 m long and 0.25 m high. The cord is attached to the bottom of Box A and the middle of box B. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A From бро Barrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardSign in PDF Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdf File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L9.pdf II! Draw | I│Alla | Ask Copilot + of 4 D Topic: Kinetics of Particles: - Forces in dynamic system, Free body diagram, newton's laws of motion, and equations of motion. TQ1. The 10-kg block is subjected to the forces shown. In each case, determine its velocity when t=2s if v 0 when t=0 500 N F = (201) N 300 N (b) TQ2. The 10-kg block is subjected to the forces shown. In each case, determine its velocity at s-8 m if v = 3 m/s at s=0. Motion occurs to the right. 40 N F = (2.5 s) N 200 N 30 N (b) TQ3. Determine the initial acceleration of the 10-kg smooth collar. The spring has an unstretched length of 1 m. 1 σ Q ☆ Q 6 ا الى ☑arrow_forwardSign in PDF Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdf File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/MMB241%20-%20Tutorial%20L9.pdf II! Draw | I│Alla | Ask Copilot + 4 of 4 | D TQ9. If motor M exerts a force of F (10t 2 + 100) N determine the velocity of the 25-kg crate when t kinetic friction between the crate and the plane are μs The crate is initially at rest. on the cable, where t is in seconds, 4s. The coefficients of static and 0.3 and μk = 0.25, respectively. M 3 TQ10. The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is unstretched when the 25-kg block is at A. Determine the acceleration of the block when s = 0.4 m. The contact surface between the block and the plane is smooth. 0.3 m F= 100 N F= 100 N k = 200 N/m σ Q Q ☆ ا الى 6 ☑arrow_forwardmy ID# is 016948724 please solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMY ID#016948724 please solve the problem step by spetarrow_forward1 8 4 For the table with 4×4 rows and columns as shown Add numbers so that the sum of any row or column equals .30 Use only these numbers: .1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY