
In Problems 8-12, please use the following steps (i)-(v) for all hypothesis tests:
(i) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses.
(ii) Check Requirements What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making? What is the value of the sample test statistic?
(iii) Find (or estimate) the P-value. Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
(iv) Based on your answers in parts (i)-(iii), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level a?
(v) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student’s t table, use the closet d.f. that is smaller. In some situation, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value a small amount and thereby produce a slightly more "conservative” answer.
Testing and Estimating µ with σ Known Let x be a random variable that represents micrograms of lead per liter of water (µg/L). An industrial plant discharges water into a creek. The Environmental Protection Agency has studied the discharged water and found x to have a
(a) The industrial plant says that the population
(b) Find a 95% confidence interval for µ using the sample data and the EPA value for σ.
(e) How large a sample should be taken to be 95% confident that the sample mean
(a)
(i)
The level of significance, null and alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution: The level of significance is
Explanation of Solution
The level of significance is defined as the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, it is denoted by
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis
(ii)
To find: The sampling distribution that should be used and compute the value of the sample test statistic.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution: The normal distributionshould be used. The sample test statisticis 2.53.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We will use the normal distribution because the original distribution x is normal and also
Using
The sample test statistic z is
(iii)
To find: The P-value of the test statistic and sketch the sampling distribution showing the area corresponding to the P-value.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution: The P-value of the test statistic is 0.0057.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We have z = 2.53
Graph:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
Step 1: Go to the Minitab software.
Step 2: Go to Graph > Probability distribution plot > View probability.
Step 3: Select ‘Normal’ and Mean = 0, Standard deviation = 1.
Step 4: Click on the Shaded area > X value.
Step 5: Enter X-value as 2.53 and select ‘Right Tail’.
Step 6: Click on OK.
The obtained distribution graph is:
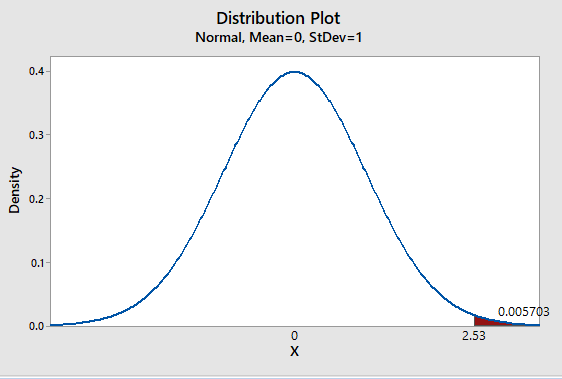
(iv)
Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesisand whether the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution: The P-value < α, hence we will reject the
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0057 is less than the level of significance (α) of 0.01. Therefore we have to reject the null hypothesis
(v)
The interpretation for the conclusion.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution: There is enough evidence to conclude that lead concentration population average is higher than the industrial plant claims.
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0057 is less than the level of significance (
(b)
To find: A 95% confidence interval for the mean using the sample data.
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution:
The 95% confidence interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We have to find 95% confidence interval
95% confidence interval is
The 95% confidence interval for
(c)
To find: The minimum sample size so that the margin of error is not more than 0.2
Answer to Problem 8CRP
Solution:
The sample size is 48 so that the margin of error is not more than 0.2
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We have the sample size formula as follows
Therefore n = 48 is the minimum sample size to ensure that the margin of error E is not more than 0.2
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Brase/Brase's Understanding Basic Statistics, 7th
- Show all workarrow_forwardplease find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture belowarrow_forwardA marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forward
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forwardThe following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



