
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553278
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 45AP
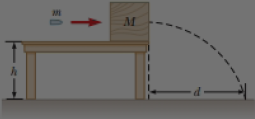
Review. A bullet of mass m = 8.00 g is fired into a block of mass M = 250 g that is initially at rest at the edge of a frictionless table of height h = 1.00 m (Fig. P9.45). The bullet remains in the block, and after the impact the block lands d = 2.00 m from the bottom of the table. Determine the initial speed of the bullet.
Figure P9.45 Problems 45 and 46.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A 0.500 kg sphere moving with a velocity given by (2.00î – 2.60ĵ + 1.00k) m/s strikes another sphere of mass 1.50 kg moving with an initial velocity of (−1.00î + 2.00ĵ – 3.20k) m/s.
(a) The velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.90î + 3.00ĵ − 8.00k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere.
R =
m/s
Identify the kind of collision (elastic, inelastic, or perfectly inelastic).
○ elastic
O inelastic
O perfectly inelastic
(b) Now assume the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.250 + 0.850ĵ - 2.15k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere.
✓ =
m/s
Identify the kind of collision.
O elastic
O inelastic
O perfectly inelastic
(c) Take the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision as (−1.00ỉ + 3.40] + ak) m/s. Find the value of a and the velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere after an elastic collision. (Two values of a are possible, a positive value and a negative value. Report each with their
corresponding final velocities.)
a…
A cannon is rigidly attached to a carriage, which can move along horizontal rails, but is connected to a post by a large spring, initially unstretched and with force constant k = 1.31 x 104 N/m, as in the figure below. The cannon fires a 200-kg projectile at a velocity of 136 m/s directed 45.0°
above the horizontal.
45.0°
(a) If the mass of the cannon and its carriage is 5000 kg, find the recoil speed of the cannon.
m/s
(b) Determine the maximum extension of the spring.
m
(c) Find the maximum force the spring exerts on the carriage. (Enter the magnitude of the force.)
N
launch angle.
Passage Problems
Alice (A), Bob (B), and Carrie (C) all start from their dorm and head
for the library for an evening study session. Alice takes a straight path,
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Ch. 9.1 - Two objects have equal kinetic energies. How do...Ch. 9.1 - Your physical education teacher throws a baseball...Ch. 9.3 - Two objects are at rest on a frictionless surface....Ch. 9.3 - Rank an automobile dashboard, seat belt, and air...Ch. 9.4 - In a perfectly inelastic one-dimensional collision...Ch. 9.4 - A table-tennis ball is thrown at a stationary...Ch. 9.6 - A baseball bat of uniform density is cut at the...Ch. 9.7 - A cruise ship is moving at constant speed through...Ch. 9 - A particle of mass m moves with momentum of...Ch. 9 - A 3.00-kg particle has a velocity of...
Ch. 9 - A baseball approaches home plate at a speed of...Ch. 9 - A 65.0-kg boy and his 40.0-kg sister, both wearing...Ch. 9 - Two blocks of masses m and 3m are placed on a...Ch. 9 - When you jump straight up as high as you can, what...Ch. 9 - A glider of mass m is free to slide along a...Ch. 9 - You and your brother argue often about how to...Ch. 9 - The front 1.20 m of a 1 400-kg car Ls designed as...Ch. 9 - The magnitude of the net force exerted in the x...Ch. 9 - Water falls without splashing at a rate of 0.250...Ch. 9 - A 1 200-kg car traveling initially at vCi = 25.0...Ch. 9 - A railroad car of mass 2.50 104 kg is moving with...Ch. 9 - Four railroad cars, each of mass 2.50 104 kg, are...Ch. 9 - A car of mass m moving at a speed v1 collides and...Ch. 9 - A 7.00-g bullet, when fired from a gun into a...Ch. 9 - A tennis ball of mass 57.0 g is held just above a...Ch. 9 - (a) Three carts of masses m1 = 4.00 kg, m2 = 10.0...Ch. 9 - You have been hired as an expert witness by an...Ch. 9 - Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange...Ch. 9 - Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange...Ch. 9 - A 90.0-kg fullback running east with a speed of...Ch. 9 - A proton, moving with a velocity of vii, collides...Ch. 9 - A uniform piece of sheet metal is shaped as shown...Ch. 9 - Explorers in the jungle find an ancient monument...Ch. 9 - A rod of length 30.0 cm has linear density (mass...Ch. 9 - Consider a system of two particles in the xy...Ch. 9 - The vector position of a 3.50-g particle moving in...Ch. 9 - You have been hired as an expert witness in an...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - A 60.0-kg person bends his knees and then jumps...Ch. 9 - A garden hose is held as shown in Figure P9.32....Ch. 9 - A rocket for use in deep space is to be capable of...Ch. 9 - A rocket has total mass Mi = 360 kg, including...Ch. 9 - An amateur skater of mass M is trapped in the...Ch. 9 - (a) Figure P9.36 shows three points in the...Ch. 9 - Review. A 60.0-kg person running at an initial...Ch. 9 - A cannon is rigidly attached to a carriage, which...Ch. 9 - A 1.25-kg wooden block rests on a table over a...Ch. 9 - A wooden block of mass M rests on a table over a...Ch. 9 - Two gliders are set in motion on a horizontal air...Ch. 9 - Pursued by ferocious wolves, you are in a sleigh...Ch. 9 - Review. A student performs a ballistic pendulum...Ch. 9 - Why is the following situation impossible? An...Ch. 9 - Review. A bullet of mass m = 8.00 g is fired into...Ch. 9 - Review. A bullet of mass m is fired into a block...Ch. 9 - A 0.500-kg sphere moving with a velocity expressed...Ch. 9 - Prob. 48APCh. 9 - Review. A light spring of force constant 3.85 N/m...Ch. 9 - Prob. 50APCh. 9 - Review. There are (one can say) three coequal...Ch. 9 - Sand from a stationary hopper falls onto a moving...Ch. 9 - Two particles with masses m and 3m are moving...Ch. 9 - On a horizontal air track, a glider of mass m...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- below the horizontal, and land 55 m horizontally from the end of the jump. Your job is to specify the slope of the ground so skiers' trajectories make an angle of only 3.0° with the ground on land- ing, ensuring their safety. What slope do you specify? T 9.5° -55 marrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch and a free body diagram. DO NOT give me examples but ONLY the solutionarrow_forwardMake sure to draw a sketch AND draw a Free body diagramarrow_forward
- P -3 ft 3 ft. O A B 1.5 ft Do 1.5 ft ✓ For the frame and loading shown, determine the magnitude of the reaction at C (in lb) if P = 55 lb. (Hint: Use the special cases: Two-force body and Three-force body.)arrow_forwardA convex mirror (f.=-6.20cm) and a concave minor (f2=8.10 cm) distance of 15.5cm are facing each other and are separated by a An object is placed between the mirrors and is 7.8cm from each mirror. Consider the light from the object that reflects first from the convex mirror and then from the concave mirror. What is the distance of the image (dia) produced by the concave mirror? cm.arrow_forwardAn amusement park spherical mirror shows park spherical mirror shows anyone who stands 2.80m in front of it an upright image one and a half times the person's height. What is the focal length of the minor? m.arrow_forward
- An m = 69.0-kg person running at an initial speed of v = 4.50 m/s jumps onto an M = 138-kg cart initially at rest (figure below). The person slides on the cart's top surface and finally comes to rest relative to the cart. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the person and the cart is 0.440. Friction between the cart and ground can be ignored. (Let the positive direction be to the right.) m M (a) Find the final velocity of the person and cart relative to the ground. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s (b) Find the friction force acting on the person while he is sliding across the top surface of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N (c) How long does the friction force act on the person? S (d) Find the change in momentum of the person. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N.S Find the change in momentum of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) N.S (e) Determine the displacement of the…arrow_forwardSmall ice cubes, each of mass 5.60 g, slide down a frictionless track in a steady stream, as shown in the figure below. Starting from rest, each cube moves down through a net vertical distance of h = 1.50 m and leaves the bottom end of the track at an angle of 40.0° above the horizontal. At the highest point of its subsequent trajectory, the cube strikes a vertical wall and rebounds with half the speed it had upon impact. If 10 cubes strike the wall per second, what average force is exerted upon the wall? N ---direction--- ▾ ---direction--- to the top to the bottom to the left to the right 1.50 m 40.0°arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the net force exerted in the x direction on a 3.00-kg particle varies in time as shown in the figure below. F(N) 4 3 A 2 t(s) 1 2 3 45 (a) Find the impulse of the force over the 5.00-s time interval. == N⚫s (b) Find the final velocity the particle attains if it is originally at rest. m/s (c) Find its final velocity if its original velocity is -3.50 î m/s. V₁ m/s (d) Find the average force exerted on the particle for the time interval between 0 and 5.00 s. = avg Narrow_forward
- ••63 SSM www In the circuit of Fig. 27-65, 8 = 1.2 kV, C = 6.5 µF, R₁ S R₂ R3 800 C H R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 0.73 MQ. With C completely uncharged, switch S is suddenly closed (at t = 0). At t = 0, what are (a) current i̟ in resistor 1, (b) current 2 in resistor 2, and (c) current i3 in resistor 3? At t = ∞o (that is, after many time constants), what are (d) i₁, (e) i₂, and (f) iz? What is the potential difference V2 across resistor 2 at (g) t = 0 and (h) t = ∞o? (i) Sketch V2 versus t between these two extreme times. Figure 27-65 Problem 63.arrow_forwardThor flies by spinning his hammer really fast from a leather strap at the end of the handle, letting go, then grabbing it and having it pull him. If Thor wants to reach escape velocity (velocity needed to leave Earth’s atmosphere), he will need the linear velocity of the center of mass of the hammer to be 11,200 m/s. Thor's escape velocity is 33532.9 rad/s, the angular velocity is 8055.5 rad/s^2. While the hammer is spinning at its maximum speed what impossibly large tension does the leather strap, which the hammer is spinning by, exert when the hammer is at its lowest point? the hammer has a total mass of 20.0kg.arrow_forwardIf the room’s radius is 16.2 m, at what minimum linear speed does Quicksilver need to run to stay on the walls without sliding down? Assume the coefficient of friction between Quicksilver and the wall is 0.236.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Impulse Derivation and Demonstration; Author: Flipping Physics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9rwkTnTOB0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY