
Paloma Co. has four employees. FICA Social Security taxes are 6.2% of the first $127,200 paid to each Problem employee, and FICA Medicare taxes are1.45% of gross pay. Also, for the first $7,000 paid to each employee, the Company’s FUTA taxes are 3.5% and SUTA taxes are 2.5%. The company is preparing its payroll calculations for the week ended August 25. Payroll records show the following information for the company's four employees.
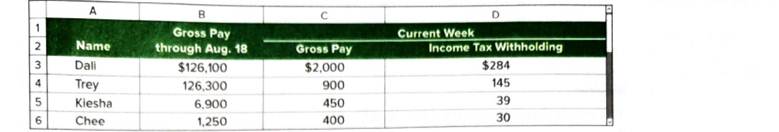
In addition to gross pay, the company must pay two-thirds of the $60 per employee weekly health insurance; each employee pays the remaining one-third. The company also contributes an extra 8% of each employee’s gross pay (at no cost to employees) to a pension fund.
Required
Compute the following for the week ended August 25 (Round amounts to the nearest cent):
- Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Social Security.
- Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
- Employer’s FICA taxes for Social Security.
- Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
- Employer’s FUTA taxes.
- Employer’s SUTA taxes.
- Each employee’s net (take-home) pay.
- Employer’s total payroll-related expenses for each employee.
1.
Introduction: FICA stands for Federal insurance contribution act. FICA withholding for social security taxes means deductions done from salary to cover the retirement, disability and survivorship after retirement from employment.
To compute: Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Social Security.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s FICA withholdings for social security.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person D | |
| Maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,100 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $1,100 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $1,100 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.2% |
| FICA social security tax | $68.20 |
| Person T | |
| Maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,300 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $900 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $900 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $900 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.2% |
| FICA social security tax | $55.80 |
| Person K | |
| Maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $6,900 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $120,300 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $450 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $450 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.2% |
| FICA social security tax | $27.90 |
| Person C | |
| Maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $1,250 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $125,950 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $400 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $400 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.2% |
| FICA social security tax | $24.80 |
2.
Introduction: FICA stands for Federal insurance contribution act. FICA withholding for Medicare refer to the amount deducted from the salary of the employee to cover the medical emergencies that will arise after retirement.
To compute: Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person D | |
| Gross pay of current week | $2,000 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $29 |
| PersonT | |
| Gross pay of current week | $900 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $13.05 |
| PersonK | |
| Gross pay of current week | $450 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $6.52 |
| PersonC | |
| Gross pay of current week | $400 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $5.80 |
3.
Introduction: Employer’s FICA taxes for social security refer to the total amount of contribution made by the employer for the survivorship and retirement of the employee.
To compute: Employer’s FICA taxes for Social Security.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FICA taxes for social security.
| Particular | Amount |
| FICA social security tax of person D | $68.20 |
| FICA social security tax of personT | $55.80 |
| FICA social security tax of personK | $27.90 |
| FICA social security tax of personC | $24.80 |
| Total employer’s FICA taxes for social security | $176.70 |
4.
Introduction: Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare refer to the total amount of contribution made by the employer for employee regarding medical emergencies that will arise after retirement.
To compute: Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
| Particular | Amount |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of personD | $29 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of personT | $13.05 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of personK | $6.52 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of personC | $5.80 |
| Total employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare | $54.37 |
5.
Introduction: FUTA stands for Federal unemployment tax act. It is a law applicable on employers. Main aim of this act is to remove unemployment. For removing unemployment specific amount of fund is collected from the employer.
To compute: Employer’s FUTA taxes.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FUTA taxes.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person D | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,100 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| FUTA tax rate | 3.5% |
| FUTA tax | $0 |
| PersonT | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,300 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $900 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| FUTA tax rate | 3.5% |
| FUTA tax | $0 |
| PersonK | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $6,900 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $100 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $450 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $100 |
| FUTA tax rate | 3.5% |
| FUTA tax | $3.50 |
| PersonC | |
| Maximum limit of Gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August18 | $1,250 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $5,750 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $400 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $400 |
| FUTA tax rate | 3.5% |
| FUTA tax | $14 |
| Total FUTA tax of Employer | $17.50 |
6.
Introduction: SUTA stands for State unemployment tax act. It is a law applicable on employers. The main aim of this act is to remove unemployment from the state. For removing unemployment specific amount of fund is collected from the employer.
To compute: Employer’s SUTA taxes.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FUTA taxes.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person D | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for SUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,100 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| SUTA tax rate | 2.5% |
| SUTA tax | $0 |
| PersonT | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $126,300 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $900 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| SUTA tax rate | 2.5% |
| SUTA tax | $0 |
| PersonK | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $6,900 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $100 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $450 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $100 |
| SUTA tax rate | 2.5% |
| SUTA tax | $2.50 |
| PersonC | |
| Maximum limit of Gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till August 18 | $1,250 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $5,750 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $400 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $400 |
| SUTA tax rate | 2.5% |
| SUTA tax | $10 |
| Total SUTA tax of Employer | $12.50 |
7.
Introduction: Net (take-home) pay refer to the amount that a person has in hand after making deductions regarding the expenses and contribution made by individual towards various withholdings.
To compute: Each employee’s net (take-home) pay.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s net (take home) pay.
| Particular | Person D | PersonT | PersonK | PersonC |
| Gross Pay | $2,000 | $900 | $450 | $400 |
| Less: Income Tax Withholding | ($284) | ($145) | ($39) | ($30) |
| Less: FICA social security tax | ($68.20) | ($55.80) | ($27.90) | ($24.80) |
| Less: FICA taxes for Medicare | ($29) | ($13.05) | ($6.52) | ($5.80) |
| Less: Weekly health insurance | ($20) | ($20) | ($20) | ($20) |
| Net (take home) pay | $1598.8 | $666.15 | $356.58 | $319.4 |
8.
Introduction: Payroll-related expenses refer to those expenses which are done by the employer towards employee for their well-being and all other payment made to government in respect of employee.
To compute: Employer’s total payroll-related expense for each employee.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of employer’s total payroll-related expense for each employee.
| Particular | PersonD | PersonT | PersonK | PersonC |
| Gross pay | $2,000 | $900 | $450 | $400 |
| Employer’s FICA taxes for social security | $68.20 | $55.80 | $27.90 | $24.80 |
| Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare | $29 | $13.05 | $6.52 | $5.80 |
| Employer’s FUTA taxes | $0 | $0 | $3.5 | $14 |
| Employer’s SUTA taxes | $0 | $0 | $2.50 | $10 |
| Employee weekly health insurance | $40 | $40 | $40 | $40 |
| Total payroll-related expense | $2137.20 | $1008.85 | $530.42 | $494.60 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Financial Accounting: Information for Decisions
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





