
Using Fig. 9.43, design a problem to help other students better understand impedance.
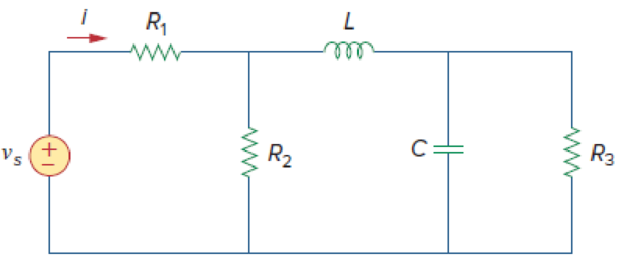
Figure 9.43
Design a problem to make better understand about the impedance using Figure 9.43.
Explanation of Solution
Problem design:
Determine the value of current
Formula used:
Write the expression to convert the time domain expression into phasor domain.
Here,
A is the magnitude,
t is the time, and
Write the expression to calculate the phasor current.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the impedance of the passive elements resistor, inductor and capacitor.
Here,
Calculation:
The Figure 9.43 is redrawn as Figure 1 by assuming the values for the passive elements.
Given voltage equation is,
Here, angular frequency
Use the equation (1) to express the above equation in phasor form.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
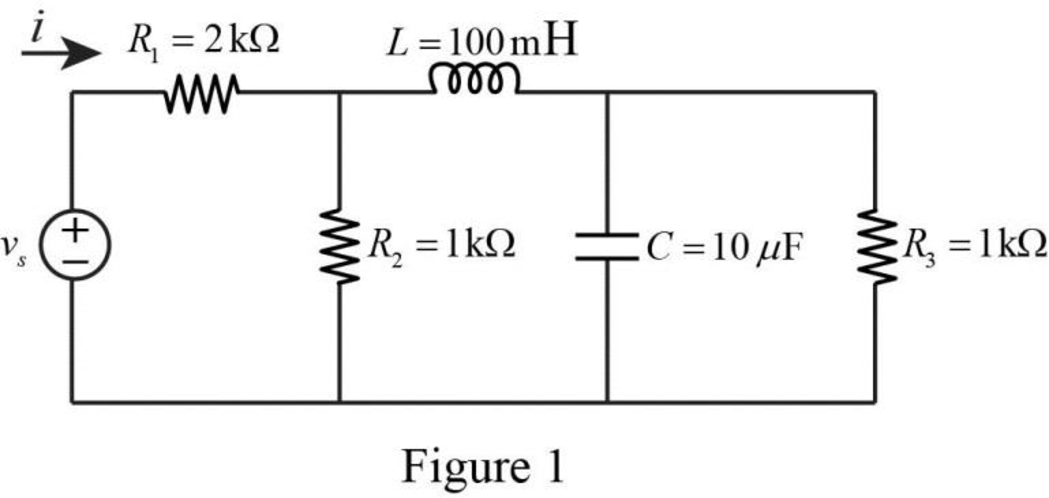
The Figure 1 is redrawn as impedance circuit in the following Figure 2.
Refer to Figure 2, the impedances
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent capacitance 1 for the parallel connected impedances
Here,
Substitute
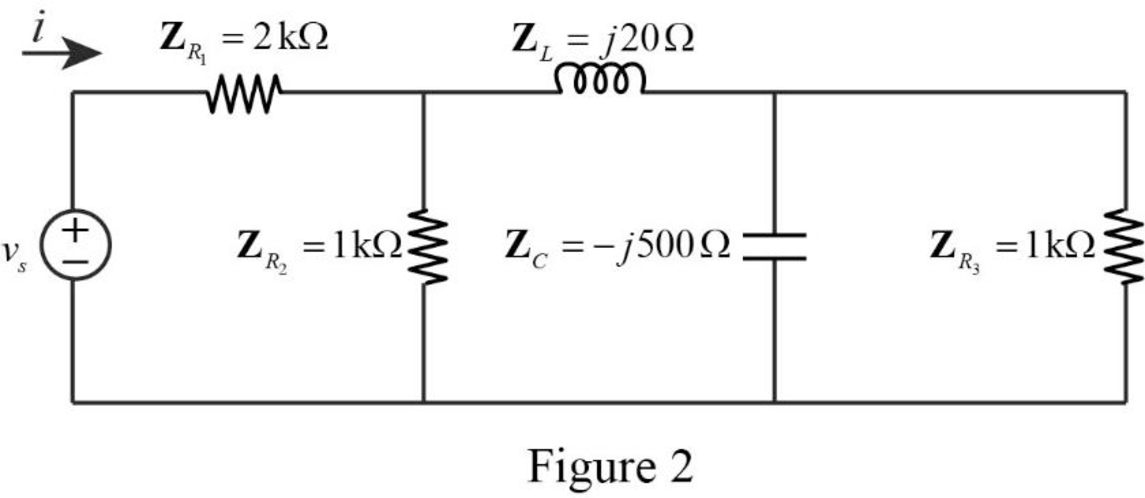
The reduced circuit of the Figure 2 is drawn as Figure 3.
Refer to Figure 3, the impedances
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent capacitance 2 for the series connected impedances
Here,
Substitute
The reduced circuit of the Figure 3 is drawn as Figure 4.
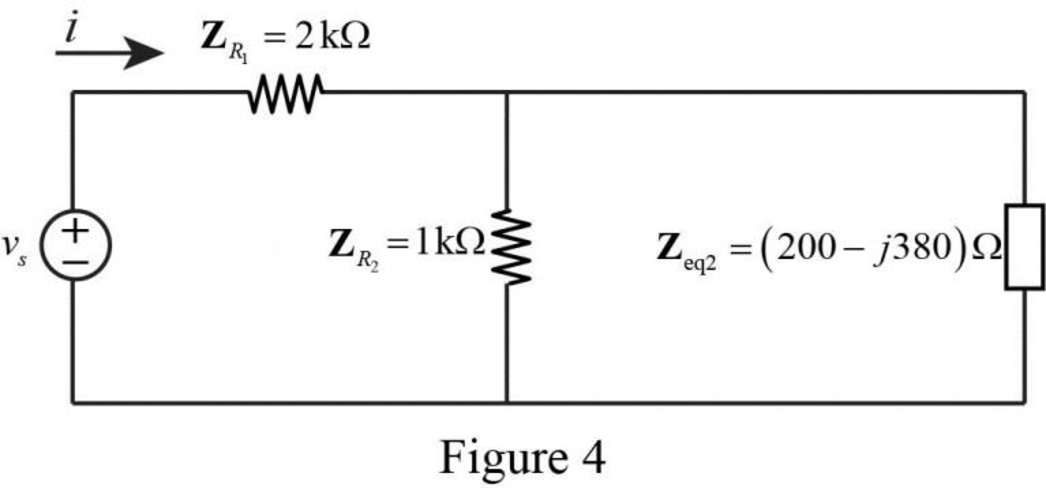
Refer to Figure 4, the impedances
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent capacitance 3 for the parallel connected impedances
Here,
Substitute
The reduced circuit of the Figure 4 is drawn as Figure 5.
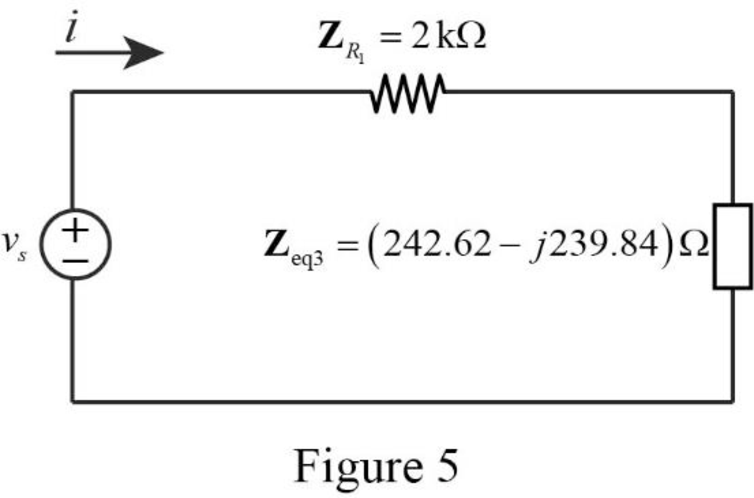
Refer to Figure 5, the impedances
Write the expression to calculate the equivalent capacitance 4 for the series connected impedances
Here,
Substitute
The reduced circuit of the Figure 5 is drawn as Figure 6.
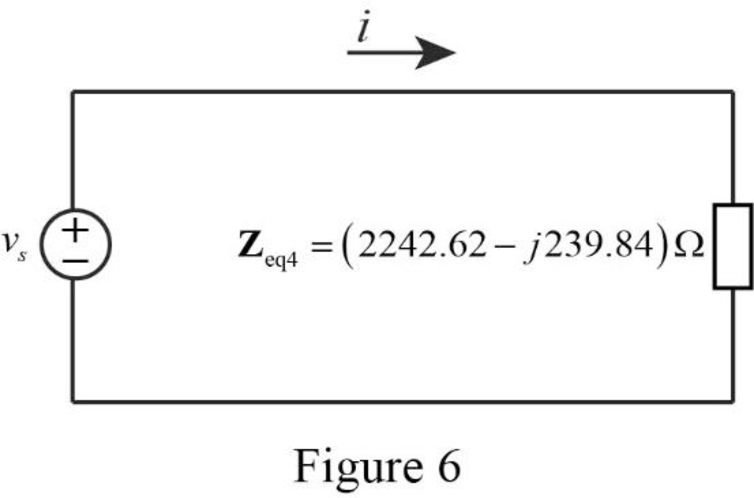
Therefore, the equivalent impedance of the circuit in Figure 1 is,
Substitute
Use the equation (1) to express the above equation in time domain form.
Substitute
Therefore, the value of current
Conclusion:
Thus, the problem to make better understand about the impedance using Figure 9.43 is designed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
- A Three-phase, 12 pole, Y-connected alternator has 108 slots and 14 conductors per slot. The windings are (5/6 th) pitched. The flux per pole is 57 mWb distributed sinusoidally over the pole. If the machine runs at 500 r.p.m., determine the following: (a) The frequency of the generated e.m.f., (b) The distribution factor, (c) The pitch factor, and (d) The phase and line values of the generated e.m.f.?arrow_forwardTwo 3-ph, 6.6 kV, Y-connected, alternators supply a load of 3000 kW at 0.8 p.f. lagging. The synchronou impedance per phase of machine A is (0.5+110) and that of machine B is (0.4 +J12) . The excitation of machine A adjusted so that it delivers 150 A. The load is shared equally between the machines. Determine the armature curre p.f., induced e.m.f., and load angle of each machine?arrow_forwardName the circuit below? The output voltage is initially zero and the pulse width is 200 μs. Find the Vout and draw the output waveform? +2.5 V V 247 -2.5 V C 0.01 F Ri W 10 ΚΩarrow_forward
- Please work outarrow_forwardFind Vfinal when Vs up and Vs V. Which LED will light in each case? Red or Green? Justify your answers. Fill the table below. Vs 8 ΚΩ Vos Χρι + 3 ΚΩ www 6 ΚΩ ww 4 ΚΩ Yo www Vo Vec-12 V Nol V final Vm w 3 ΚΩ 5 V 38 ΚΩ R= 1 kQ V -12 V Red LED Green LED Vs Vo Vfinal Which LED is ON? Varrow_forwardCircuits help please solve and explain. Question in images providedarrow_forward
- + V 6.2 A 1.2 A S R 4 Ω Find the source voltage Vs 0.8 Aarrow_forwardDetermine i(t) for t≥ 0 given that the circuit below had been in steady state for a long time prior to t = 0. Also, I₁ = 1 5 A, R₁ =22, R2 =10 Q2, R3 = 32, R4 =7 2, and L=0.15 H. Also fill the table. m L ww R2 t = 0 R₁ 29 R3 R4 Time 0 iL(t) 0 8arrow_forwardPlease help explain this problemarrow_forward
- + P = 16 W w w P = 8 W I R₁ R2 E = RT=322 1- Determine R1, R2, E ΙΩarrow_forward+ 30 V = - 20 V + R 2- Use KVL to find the voltage V - V + + 8 Varrow_forwardFind the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the portions of the networks in Figure external to the elements between points a and b. a R₁ 2002 I = 0.1 A 0° Xc : 32 Ω R2 = 6802 20 Ω фъarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





