
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and IUPAC name of each group substituent in the given molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
For
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkyne molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(a)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
The systematic names for the given molecules (a-c) are shown below.
(a). 2,2,5-Trimethyl-3-hexene
Explanation of Solution
The systematic name for the given molecule (a).
Draw the given molecule (a) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents for naming the compound.
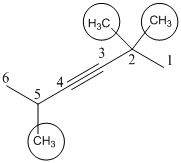
(a). 2,2,5-Trimethyl-3-hexene
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is the chain which contains 6 carbons. Hence the root name of the molecule is hexa. Since it is an alkyne with 6 carbons then hexane will be the parent carbon chain name.
The substituents present in the molecule are methyl, bromo (Br) groups on 2 and 5. Therefore on numbering the three methyl groups are present at 2 and 5. Positions is 2,2,5-Trimethyl.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (a) is 2,2,5-Trimethyl-3-hexene
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and IUPAC name of each group substituent in the given molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkyne molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
The systematic names for the given molecules (a-c) are shown below.
(b). 4,4-Dichloro-2-hexene
Explanation of Solution
The systematic name for the given structure (b).
Draw the given molecule (b) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
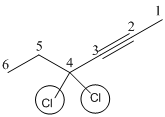
4,4-Dichloro-2-hexyne
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain six carbon atoms.
In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is linear in nature which consistes of 6 carbons so the root word for the molecule is 4,4- Dichloro-2-hexyne. The suffix ‘yne’ is used since it is an alkyne.
The substituent present in the molecule are 2-chloro atoms in C4 carbon.
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (b) is 4,4-Dichloro-2-hexyne.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and IUPAC name of each group substituent in the given molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkyne molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
The systematic names for the given molecules (a-c) are shown below.
(c). 1-Hexyne
Explanation of Solution
The systematic name for the given structure (c).
Draw the given molecule (d) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents.
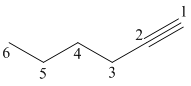
1-Hexyne
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the longest continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is linear in nature which consists of 6 carbons so that root word for the molecule is 1-Hexyne. The suffix ‘yne’ is used since it is an alkyne.
The parent chain is numbered so that the triple bond is assigned the lowest possible locate (1 indicates that the the triple bond is located between C1 and C2).
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (c) is 1-Hexyne.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and IUPAC name of each group substituent in the given molecules should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
For alkynes molecules, suffix will be ‘yne’.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Two stereoisomers are there for an alkyne molecule. It depends upon the location of bulky group (or high molecular weight) on the triple bonded carbon atoms. If the bulky groups are in same side then it is cis-isomer. If the bulky groups are in opposite side then it is trans-isomer.
(d)
Answer to Problem 32PP
Answer
The systematic names for the given molecules (a-c) are shown below.
(d). 3-Bromo-3-methyl-1-butyne
Explanation of Solution
The systematic name for the given structure (d).
Draw the given molecule (d) and find the longest parent carbon chain or carbon skeleton and the substituents for naming the compound.
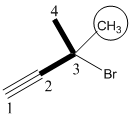
3-Bromo-3-methyl-1-butyne
The given molecule is drawn. The parent carbon skeleton is the continuous carbon chain that should contain more number of carbons. In the given molecule the parent carbon skeleton is the chain which contains 4 carbons. Hence the root name of the molecule is butane. Since it is an alkene with 4 carbons then butyne will be the parent carbon chain name.
In the given molecule parent chain is numbered so that the triple bond assigned the lowest possible locate (1 indicates that the triple bond is located between C1 and C2). The one methyl group, one bromo groups are present at C3 positions is 3-Bromo-3-methyl (The alphabetized in the name, Br and CH3).
Hence the systematic name for the molecule (a) is 3-Bromo-3-methyl-1-butyne.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, WITH SOL. MAN/ STUDY
- Draw structures corresponding to the following names and give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (8 Point) a) b) c) CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CH CH3 C=C H3C H H2C=C=CHCH3 d) CI e) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene f) (Z)-4-bromo-3-methyl-3-penten-1-yne g) cis-1-Bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane h) (5R)-4,4,5-trichloro-3,3-dimethyldecanearrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardReview: Design a total total synthesis synthesis of the following compound using methyloxacyclopropane and any other necessary reagents.arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection from carbon 3 to carbon 2 in the highest energy conformation for the following molecule. What is this conformation called? What kind of strain is present? Brarrow_forwardWhich of the following dienophiles is most reactive in a Diels-Alder reaction: Please explain why the correct answer to this question is option 5. Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forward
- Which of the following would you expect to be aromatic? Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forwardDraw the enantiomer and diastereomers of the following molecule. Label each type of stereoisomers. Label each chiral center as R or S. HOarrow_forwardWhich diene and dienophile would you choose to synthesize the following compound? Please provide a detailed explanation. Please include a drawing showing the mechanism of the synthesis. Please also explain why it is the correct diene and dienophile.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





