
What are the common and systematic names of the following ethers?
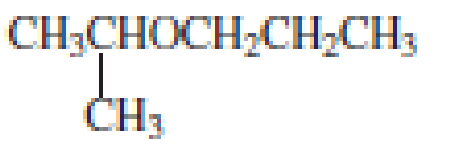
- a. CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH2CH3
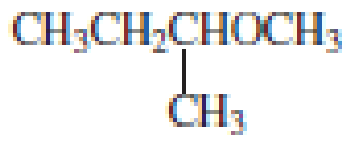
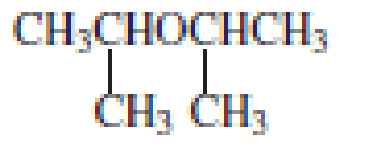
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether have to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
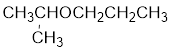
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with three carbons in the parent chain. Hence, the parent chain will be propane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
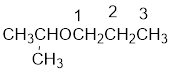
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen is the isopropyl group.
Therefore, systematic name of the compound is given below:
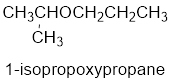
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one iso propyl group and one propyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
Propyl isopropyl ether
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
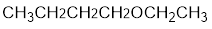
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with four carbons in the parent chain. Thus the parent chain will be butane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
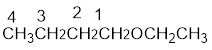
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen that is in the first carbon is the ethyl group and therefore, the prefix will be “ethoxy”.
Therefore, the systematic name of the compound is given below:
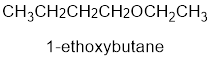
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one ethyl group and one butyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
butyl ethyl ether.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
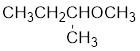
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with four carbons in the parent chain. Thus the parent chain will be butane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
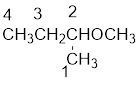
The oxygen is attached to the second carbon.
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen is the methyl group and therefore, the prefix will be “methoxy”.
Therefore, the systematic name of the compound is given below:
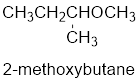
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one sec-butyl group and one methyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
Sec-butyl methyl ether.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
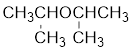
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with three carbons in the parent chain. Hence, the parent chain will be propane.
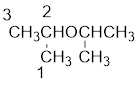
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen that is in the second carbon is the isopropyl group and therefore, the prefix of the name will be “isopropoxy”.
Therefore, systematic name of the compound is given below:
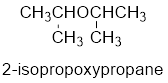
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, diisopropyl groups are attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
disopropyl ether.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


