
To match: The parts of a long bone with the following given terms.
Introduction: The musculoskeletal system of the body is composed of two types of systems; they are skeleton (bones and joint) and the soft tissues (skeletal muscles, ligaments, and tendons). Bones are the protective support for the tissues and organs of the body. They are the essential source of minerals in the body.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the parts of a long bone.
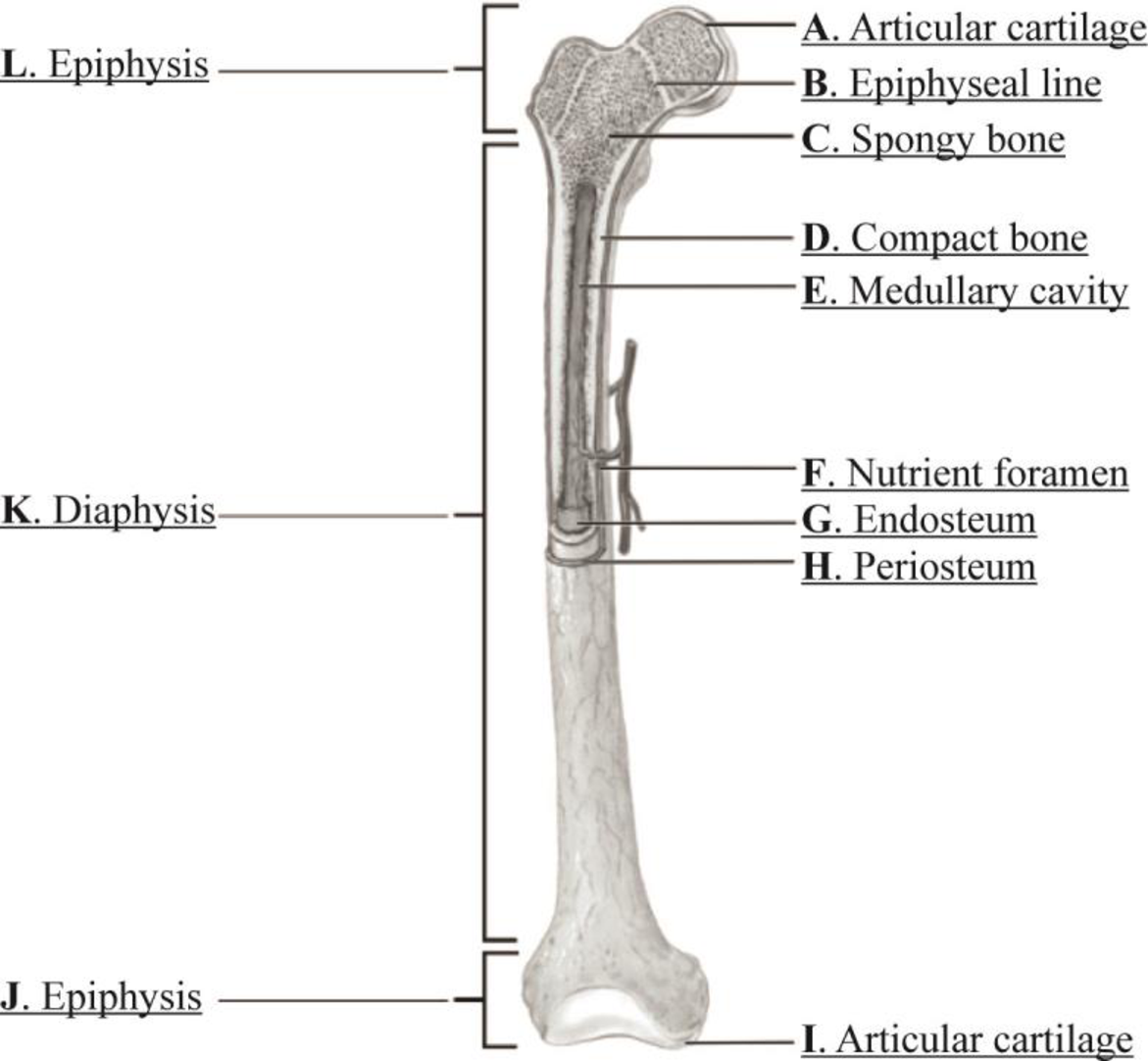
Fig.1: A long bone
Explanation of Solution
Bones are the protective support for the tissues and organs of the body. They are the essential source of minerals in the body. They are classified into four types based upon their shape – long bones, flat bones, short bones, and irregular bones.
The parts of a long bone are given as follows:
A. Articular cartilage
The articular (hyaline) cartilage and synovial joint cavity containing synovial fluid are the two structures in a joint that help in movement. Articular cartilage is the type of hyaline cartilage present on the articular surfaces of the bones. It also lies within the synovial joint cavity. This structure reduces friction in the joints. The articular cartilage supplies the smooth, lubricated surface and a slight cushion during the movement in a joint.
B. Epiphyseal line
It is referred to as the area of cartilage tissue that is continuously being replaced by new bone tissues as the bone grows. The epiphyseal plate or line is commonly known as the growth plate. Cartilage cell at the edges of epiphyseal line forms a new bone that is responsible for lengthening of bones at childhood time and adolescence. After the bone achieves its full growth, the epiphyseal line calcifies and disappears.
C. Spongy bone
The cancellous bone is referred to be spongy or trabecular bone. These bones are much more porous and less solid than compact bone. The mineral matter present in the cancellous bone laid down in a series of separated bony fibers that are made up of a spongy latticework. The interwoven fibrous matter found in epiphysis and metaphysis of the long bone and middle part of most of the body parts. The space in between the cancellous bone contains red bone marrow that is made up of immature and mature blood cells in various stages of development.
D. Compact bone
Bones in the body are made up of compact bone tissue and spongy bone tissue. This type of bone is highly dense (tough and heavy). Compact bones are made up of osteons. They fill the outer layer of all bones. The marrow stores fats and calcium. They provide an overall support for the body.
E. Medullar cavity
The compact bones are referred to as the cortical bones which consist of a layer of hard, dense bones that lie under the periosteum in every bone and located mainly around the diaphysis of long bones. The compact bone is tunneled out in the central shaft of the long bones by a medullary cavity. It is the hollow interior of the middle portion of long bones. The endosteum lines the medullary cavities of long bones. Medullary cavity consists of both red and yellow bone marrow. Hence, it is also called as marrow cavity.
F. Nutrient foramen
All bones consist of either smaller or larger foramina (openings) for the entrance of blood-vessels. These are collectively called as nutrient foramina.
G. Endosteum
Endosteum is a thin, soft vascular connective tissue that lines the medullary cavities of long bones. It is located in bones such as humerus, femur, thoracic rib bones, hip bone, and sesamoid bones such as patella. Endosteum contains osteoblasts that mainly help in the growth of bones, bone repair, and remodeling.
H. Periosteum
Periosteum is a fibrous, strong and vascular membrane that covers the long bone surface except the end region of the epiphyses. This region contains blood vessels, osteoblasts, nerves, and lymphatics. The main function of periosteum is to act as a canal for the extensive nerve supply toward the bone. The bones other than the long bones are covered by periosteum. Pain is experienced when periosteum is either torn or stretched.
I. Articular cartilage
It is the type of hyaline cartilage present on the articular surfaces of the bones. It also lies within the synovial joint cavity. This structure reduces friction in the joints. They supply the smooth, lubricated surface and a slight cushion during joint movements.
J. Epiphysis
The long bone ends with rounded end called epiphysis. Epiphysis is present at its joint with adjacent bones. There are four types of epiphysis present in human body. The portion of long bone that forms the joint is known as pressure epiphysis (example: Hip joints with head of the femur). The non-articular region of long bone that is not involved in joint formation called epiphysis. The fused bones are called the atavistic epiphysis (coracoids process of scapula). The epiphyses that are the deviations from the norm are called aberrant epiphysis.
K. Diaphysis
It is a midsection or shaft of a long bone. It consists of cortical bone and mostly contains adipose tissue as well as bone marrow. Diaphysis is the middle tubular part which is made up of compact bone that surrounds a central marrow cavity that has both red and yellow bone marrow.
L. Epiphysis
This is the end round part of a long bone which initially grows separately from the shaft. It is composed of spongy bone which is covered by hyaline cartilage; this helps in the joint movement of articulation in between the bones.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- Anything else I should add to this slide and notes? Can you also put the notes into paragraphs with the changes?arrow_forwardAnything else I should add to this slide and notes? Can you also put the notes into paragraphs with the changes?arrow_forwardAnything else I should add to this slide and notes? Can you also put the notes into paragraphs with the changes?arrow_forward
- Anything else I should add to this slide and notes? Can you also put the notes into paragraphs with the changes?arrow_forwardAnything else I should add to this slide? Can you also put the notes into paragraphs?arrow_forwardMake a nursing care plan include cognitive goal, affective goal, psychomotor goal, cognitive, affective, psychomotor interventions, and rationale for each Cognitive (Independent Interventions) Cognitive (Dependent Interventions) Cognitive (Collaborative Interventions) Affective (Independent Interventions) Affective (Dependent Interventions) Affective (Collaborative Interventions) Psychomotor (Independent Interventions) Psychomotor (Dependent Interventions) Psychomotor (Collaborative Interventions) Nursing Diagnosis: Acute pain related to post operative surgery as evidenced by guarding and facial grimace Chief Complaints: Hypogastric pain history of present illness2 months prior to consultation the patient complained of abdominal pain associated with discomfort, she was admitted to the ER but was discharged with unrecalled medications. 1 month prior to consultation the patient had moderate to severe dysmenorrhea, a whole abdominal ultrasound was performed and the results indicated…arrow_forward
- Make a nursing care plan include Cognitive, affective, and psychomotor GOALS, cognitive, affective, psychomotor interventions, and rationale for each Cognitive (Independent Interventions) Cognitive (Dependent Interventions) Cognitive (Collaborative Interventions) Affective (Independent Interventions) Affective (Dependent Interventions) Affective (Collaborative Interventions) Psychomotor (Independent Interventions) Psychomotor (Dependent Interventions) Psychomotor (Collaborative Interventions) Nursing Diagnosis: Acute pain related to post operative surgery as evidenced by guarding and facial grimace Chief Complaints: Hypogastric pain history of present illness2 months prior to consultation the patient complained of abdominal pain associated with discomfort, she was admitted to the ER but was discharged with unrecalled medications. 1 month prior to consultation the patient had moderate to severe dysmenorrhea, a whole abdominal ultrasound was performed and the results indicated the…arrow_forwardMake a nursing care plan include cognitive, affective, psychomotor interventions, and rationale for each Cognitive (Independent Interventions) Cognitive (Dependent Interventions) Cognitive (Collaborative Interventions) Affective (Independent Interventions) Affective (Dependent Interventions) Affective (Collaborative Interventions) Psychomotor (Independent Interventions) Psychomotor (Dependent Interventions) Psychomotor (Collaborative Interventions) Nursing Diagnosis: Acute pain related to post operative surgery as evidenced by guarding and facial grimace Chief Complaints: Hypogastric pain history of present illness2 months prior to consultation the patient complained of abdominal pain associated with discomfort, she was admitted to the ER but was discharged with unrecalled medications. 1 month prior to consultation the patient had moderate to severe dysmenorrhea, a whole abdominal ultrasound was performed and the results indicated the patient to have myoma in her uterus. 2…arrow_forward3.15 Regularity: PRI: Rate: QRS: P Waves:arrow_forward
- 3.14 3.10 ha 3.11 3.12 3.13 سل سل مه سه له اسم اسم الاسهم السد 3.15 سىلىلىarrow_forward3.3 3.2 سل Regularity: Rate: P Waves: PRI: QRS: 3.4 3.5 2982 MOR MAMAORI DRSHTADTHAMarrow_forwardProblem solving process: List and identify each step within the problem-solving process. Select and summarize any recent or hypothetical health care management scenario that analyzes the responsibilities of the health care leader. In the scenario, you may wish to consider the following: Responsibilities of the health care leader Actions taken to complete the identified steps and effectiveness of the decisions made by the health care leaderarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





