
Concept explainers
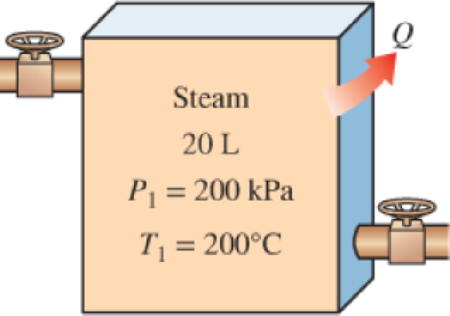
The radiator of a steam heating system has a volume of 20 L and is filled with superheated water vapor at 200 kPa and 200°C. At this moment both the inlet and the exit valves to the radiator are closed. After a while it is observed that the temperature of the steam drops to 80°C as a result of heat transfer to the room air, which is at 21°C. Assuming the surroundings to be at 0°C, determine (a) the amount of heat transfer to the room and (b) the maximum amount of heat that can be supplied to the room if this heat from the radiator is supplied to a heat engine that is driving a heat pump. Assume the heat engine operates between the radiator and the surroundings.
FIGURE P8–31
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- (read me)arrow_forward(read image)arrow_forwardQu. 13 What are the indices for the Direction 2 indicated by vector in the following sketch? Qu. 14 Determine the indices for the direction A and B shown in the following cubic unit cell. please show all work step by step from material engineeringarrow_forward
- The thin-walled open cross section shown is transmitting torque 7. The angle of twist ₁ per unit length of each leg can be determined separately using the equation 01 = 3Ti GLIC 3 where G is the shear modulus, ₁ is the angle of twist per unit length, T is torque, and L is the length of the median line. In this case, i = 1, 2, 3, and T; represents the torque in leg i. Assuming that the angle of twist per unit length for each leg is the same, show that T= Lic³ and Tmaz = G01 Cmax Consider a steel section with Tallow = 12.40 kpsi. C1 2 mm L1 20 mm C2 3 mm L2 30 mm C3 2 mm L3 25 mm Determine the torque transmitted by each leg and the torque transmitted by the entire section. The torque transmitted by the first leg is | N-m. The torque transmitted by the second leg is N-m. The torque transmitted by the third leg is N-m. The torque transmitted by the entire section is N-m.arrow_forwardPlease help, make sure it's to box out and make it clear what answers go where...arrow_forwardThe cylinder floats in the water and oil to the level shown. Determine the weight of the cylinder. (rho)o=910 kg/m^3arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





