
(a)
Interpretation:- The products formed by assigning the appropriate mass spectrum to each compound needs to be confirmed. The parent and the base peaks needs to be specified.
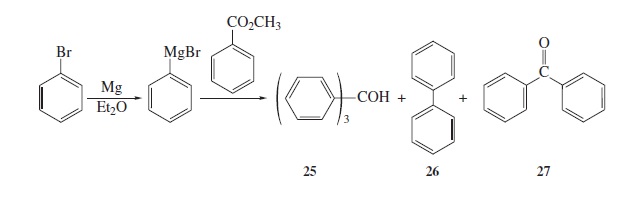
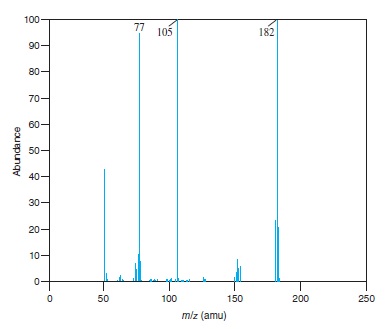
Fig − 8.61
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
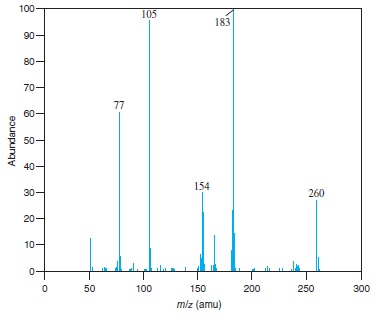
Fig − 8.62
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
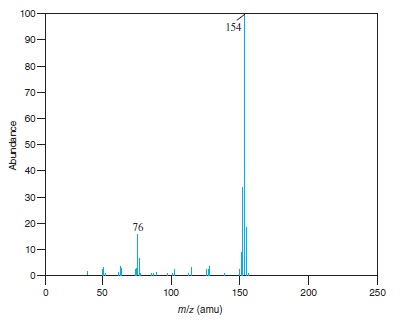
Fig − 8.63
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
Concept Introduction: Fragmentation is the process in which energetically unstable molecular ions gets dissociated, when these molecules are passed through the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer.
(b)
Interpretation:- The compound represented by the mass spectrum needs to be identified.
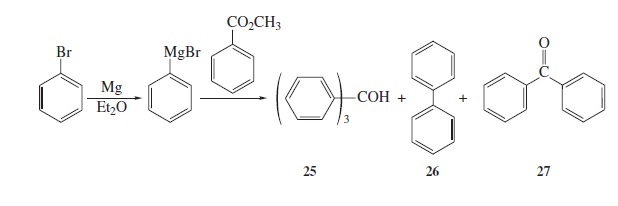
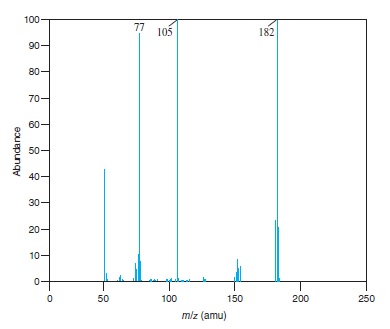
Fig − 8.61
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
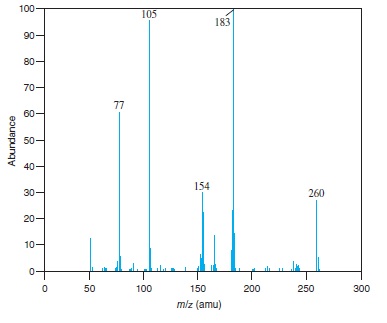
Fig − 8.62
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
Fig − 8.63
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
Concept Introduction: Fragmentation is the process in which energetically unstable molecular ions gets dissociated, when these molecules are passed through the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of the ion for each of the peaks for which value of
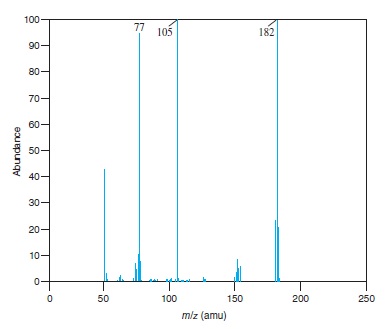
Fig − 8.61
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
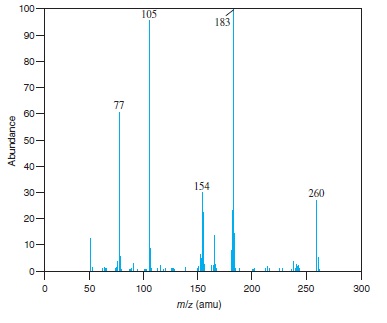
Fig − 8.62
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
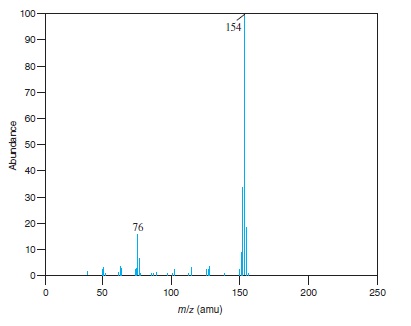
Fig − 8.63
Mass spectrum of component of reaction mixture
Concept Introduction: Fragmentation is the process in which energetically unstable molecular ions gets dissociated, when these molecules are passed through the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Miniscale & Microscale Approach (Cengage Learning Laboratory Series for Organic Chemistry)
- how to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forwardAssign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forward
- Assign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
