
a.
To find:
The gradient between points A and B on the cinder cone using the given information. Include units in your answer.
a.
Answer to Problem 36E
The gradient between points A and B on the cinder cone is 4000 feet per mile.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A cinder cone is a type of volcano. To describe the steepness of a cinder cone from one point on cone to another, you can find the gradient between the two points.
The graph shows the cross section of a cinder cone.
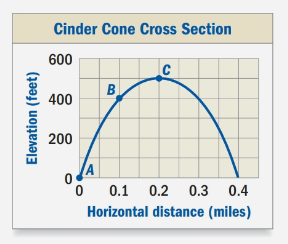
Calculation:
We can see that point A is at (0,0) and point B is at (0.1,400). Upon substituting these values in gradient formula, we will get:
Therefore, the gradient between points A and B on the cinder cone is 4000 feet per mile.
b.
To find:
The gradient between points B and Con the cinder cone using the given information. Include units in your answer.
b.
Answer to Problem 36E
The gradient between points B and C on the cinder cone is 1000 feet per mile.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A cinder cone is a type of volcano. To describe the steepness of a cinder cone from one point on cone to another, you can find the gradient between the two points.
The graph shows the cross section of a cinder cone.
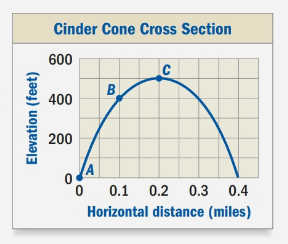
Calculation:
We can see that point B is at (0.1,400) and point C is at (0.2,500). Upon substituting these values in gradient formula, we will get:
Therefore, the gradient between points B and C on the cinder cone is 1000 feet per mile.
c.
To find:
The gradient between points A and Con the cinder cone using the given information. Include units in your answer.
c.
Answer to Problem 36E
The gradient between points A and Con the cinder cone is 2500 feet per mile.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A cinder cone is a type of volcano. To describe the steepness of a cinder cone from one point on cone to another, you can find the gradient between the two points.
The graph shows the cross section of a cinder cone.
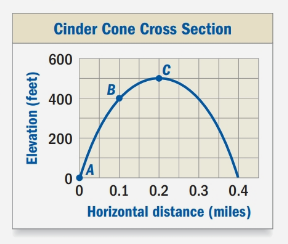
Calculation:
We can see that point A is at (0,0) and point C is (0.2,500). Upon substituting these values in gradient formula, we will get:
Therefore, the gradient between points A and Con the cinder cone is 2500 feet per mile.
Chapter 8 Solutions
ELEMENTARY+INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- Solve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5 Please type out answerarrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1 Please type out answerarrow_forwardDalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work. Dear Student If You Face any issue let me know i will solve your all doubt. I will provide solution again in more detail systematic and organized way. I would also like my last 3 questions credited to mearrow_forward
- Dalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work.arrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1arrow_forwardSolve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5arrow_forward
- Write an equation for the function shown. You may assume all intercepts and asymptotes are on integers. The blue dashed lines are the asymptotes. 10 9- 8- 7 6 5 4- 3- 2 4 5 15-14-13-12-11-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 1 1 2 3 -1 -2 -3 -4 1 -5 -6- -7 -8- -9 -10+ 60 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15arrow_forwardUse the graph of the polynomial function of degree 5 to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. -6 3 6+ 5 4 3 2 1 2 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 3 4 6 Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicityarrow_forwardUse the graph to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. 6 5 4 -6-5-4-3-2 3 21 2 1 2 4 5 ૪ 345 Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity པ་arrow_forward
- Use the graph to write the formula for a polynomial function of least degree. -5 + 4 3 ♡ 2 12 1 f(x) -1 -1 f(x) 2 3. + -3 12 -5+ + xarrow_forwardUse the graph to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. 6 -6-5-4-3-2-1 -1 -2 3 -4 4 5 6 a Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicityarrow_forwardUse the graph to write the formula for a polynomial function of least degree. 5 4 3 -5 -x 1 f(x) -5 -4 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 f(x) =arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





