
Differential Equations: An Introduction to Modern Methods and Applications
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781118531778
Author: James R. Brannan, William E. Boyce
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.3, Problem 13P
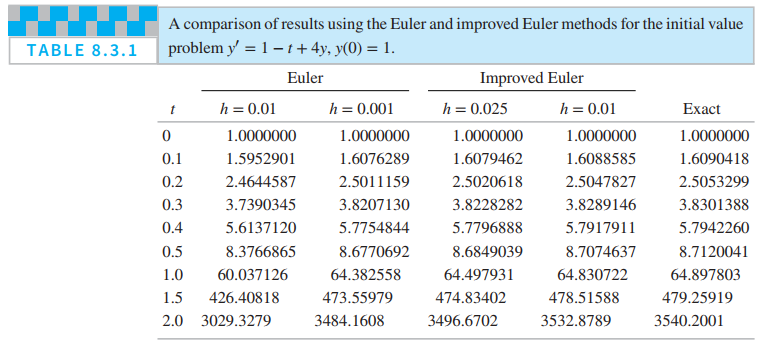
Complete the calculation leading to the entries in columns four and five of Table 8.3.1.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Suppose an experiment was conducted to compare the mileage(km) per litre
obtained by competing brands of petrol I,II,III. Three new Mazda, three new
Toyota and three new Nissan cars were available for experimentation. During the
experiment the cars would operate under same conditions in order to eliminate
the effect of external variables on the distance travelled per litre on the assigned
brand of petrol. The data is given as below:
Brands of Petrol Mazda Toyota Nissan
I 10.6 12.0 11.0
II 9.0 15.0 12.0
III 12.0 17.4 13.0
(a) Test at the 5% level of significance whether there are signi
cant differences among the brands of fuels and also among the cars. [10]
(b) Compute the standard error for comparing any two fuel brands means. Hence
compare, at the 5% level of significance, each of fuel brands II, and III with
the standard fuel brand I. [10] �
Business discuss
Use the method of undetermined coefficients to solve the given nonhomogeneous system.X' =
−1 33 −1
X +
−4t2t + 2
X(t) =
Chapter 8 Solutions
Differential Equations: An Introduction to Modern Methods and Applications
Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 1 through 4 :
Find approximate...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 1 through 4 :
Find approximate...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 1 through 4: a) Find...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 1 through 4 :
Find approximate...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10 , draw a...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10, draw a direction...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10, draw a direction...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10, draw a direction...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10 , draw a...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 5 through 10, draw a direction...
Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 11 through 14 , use Eular’s...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 11 through 14 , use Eular’s...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 11 through 14 , use Eular’s...Ch. 8.1 - In each of Problems 11 through 14 , use Eular’s...Ch. 8.1 - Consider the initial value problem...Ch. 8.1 - Consider the initial value problem
Use Euler’s...Ch. 8.1 - Consider the initial value problem...Ch. 8.1 - Consider the initial value problem
Where is a...Ch. 8.1 - Consider the initial value problem y=y2t2,y(0)=,...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.2 - Complete the calculations leading to the entries...Ch. 8.2 - Using three terms in the Taylor series given in...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 15 and 16, estimate the local...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 15 and 16, estimate the local...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 17 and 20, obtain a formula...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 17 and 20, obtain a formula...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 17 and 20, obtain a formula...Ch. 8.2 - In each of Problems 17 and 20, obtain a formula...Ch. 8.2 - Consider the initial value problem y=cos5t,y(0)=1....Ch. 8.2 - Using a step size h=0.05 and the Euler method,...Ch. 8.2 - The following problem illustrates a danger that...Ch. 8.2 - The distributive law a(bc)=abac does not hold, in...Ch. 8.2 - In this section we stated that the global...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 1 through 6, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problem 7 through 12, find approximate...Ch. 8.3 - Complete the calculation leading to the entries in...Ch. 8.3 - Confirm the results in Table 8.3.2 by executing...Ch. 8.3 - Consider the initial value problem y=t2+y2,y(0)=1....Ch. 8.3 - Consider the initial value problem
Draw a...Ch. 8.3 - In this problem, we establish that the local...Ch. 8.3 - Consider the improved Euler method for solving the...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 19 and 20, use the actual...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 19 and 20, use the actual...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 21 through 24, carry out one...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 21 through 24, carry out one...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 21 through 24, carry out one...Ch. 8.3 - In each of Problems 21 through 24, carry out one...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - In each of Problems 1 through 6, determine...Ch. 8.4 - Consider the example problemwith the initial...Ch. 8.4 - Consider the initial value problem...Ch. 8.P1 - Assume that the shape of the dispensers are...Ch. 8.P1 - After viewing the results of her computer...Ch. 8.P2 - Show that Euler’s method applied to the...Ch. 8.P2 - Simulate five sample trajectories of Eq. (1) for...Ch. 8.P2 - Use the differential equation (4) to generate an...Ch. 8.P2 - Variance Reduction by Antithetic Variates. A...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Whether the ‘Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine’ has the potential to create a bias in a statistical...
Elementary Statistics
Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true. An equation that expresses a relationship between t...
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Length of a Guy Wire A communications tower is located at the top of a steep hill, as shown. The angle of incli...
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
True or False? In Exercises 5–8, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it a...
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Fill in each blanks so that the resulting statement is true. Any set of ordered pairs is called a/an _______. T...
College Algebra (7th Edition)
The salaries of physicians in a certain speciality are approximately normally distributed. If 25 percent of the...
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5) You are purchasing a game for $30. You have a 5% off coupon and sales tax is 5%. What will your final price be? Does it matter if you take off the coupon first or add in the tax first? 6) You have ten coupons that allow you to take 10% off the sales price of a jacket, and for some strange reason, the store is going to allow you to use all ten coupons! Does this mean you get the jacket for free? Let's really think about what would happen at the checkout. First, the teller would scan the price tag on the jacket, and the computer would show the price is $100. After the teller scans the first coupon, the computer will take 10% off of $100, and show the price is $90. (Right? Think about why this is.) Then after the teller scans the second coupon, the computer will take 10% off of $90. (a) Continue this reasoning to fill in the table below showing the price of the jacket (y) after you apply x coupons. (b) Make a graph showing the price of the jacket from x = 0 to x = 10 coupons applied.…arrow_forwardDetailed report without CHATGPT, accept if you can give with code and plots, previous reported . Do not waste my question.arrow_forwardPlease do not give inappropriate solutions, previous question reported, i need correct report solution for this, NO CHATGPTarrow_forward
- Need detailed report without CHATGPT, accept if you can give with code and plots, previous reported Plots are required.arrow_forwardNeed detailed report without CHATGPT, accept if you can give with code and plots, previous reportedarrow_forwardWhat would you say about a set of quantitative bivariate data whose linear correlation is -1? What would a scatter diagram of the data look like? (5 points)arrow_forward
- 1. Which set of parametric equations is shown in the graph below? Explain your reasoning. a) x = t; y = t² b) x = = t²; y = t -3-2-1 5 4 3 2 1 12 3 2. Using the graph of f, a. determine whether dy/dt is positive or negative given that dx/dt is negative and b. determine whether dx/dt is positive or negative given that dy/dt is positive. Explain your reasoning. 2 f x 1 2 3 4arrow_forwardFind the perimeter of the triangle. Express the perimeter using the same unit of measure that appears on the given sides. 9 ft 13 ft 6 ft The perimeter isarrow_forwardUse the formula for Pr to evaluate the following expression. 9P5 9P5 =☐arrow_forward
- Find the volume of the figure. The volume of the figure is 3 m 3 m 3 marrow_forwardFind the circumference and area of the circle. Express answers in terms of and then round to the nearest tenth. Find the circumference in terms of C= (Type an exact answer in terms of x.) Find the circumference rounded to the nearest tenth. C= Find the area in terms of A= (Type an exact answer in terms of x.) Find the area rounded to the nearest tenth. A= 10 cmarrow_forwardSox & Sin (px) dx 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:9781285195780
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Write the Complex Number in Trigonometric (Polar) Form; Author: The Math Sorcerer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9kZOHHRjfIQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY