
(a)
Interpretation:
The element with its full and condensed electron configuration and the number of inner electrons is to be determined from the given partial orbital diagram.
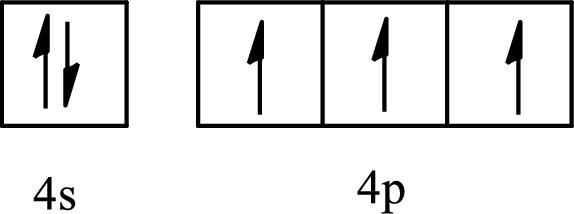
Concept introduction:
The electronic configuration tells about the distribution of electrons in various atomic orbitals.
The full electronic configuration of an atom tells about the distribution of electrons in its various atomic orbital.
The condensed electronic configuration is a way to write the electronic configuration where the inner shell configurations are compressed to the nearest noble gas configuration and only the valence shell configuration is written in the expanded form.
The partial orbital diagram is the one that shows the distribution of valence electrons only.
The inner electrons are present in the inner orbitals of the atom and the valence electrons are present in the outermost shell of the atom.
The number of inner electrons is calculated by subtracting the valence electrons from the total number of electrons
(b)
Interpretation:
The element with its full and condensed electron configuration and the number of inner electrons is to be determined from the given partial orbital diagram.
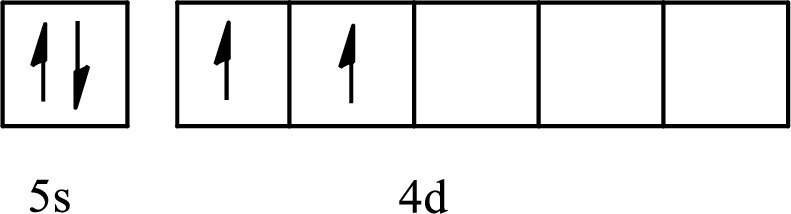
Concept introduction:
The electronic configuration tells about the distribution of electrons in various atomic orbitals.
The full electronic configuration of an atom tells about the distribution of electrons in its various atomic orbital.
The condensed electronic configuration is a way to write the electronic configuration where the inner shell configurations are compressed to the nearest noble gas configuration and only the valence shell configuration is written in the expanded form.
The partial orbital diagram is the one that shows the distribution of valence electrons only.
The inner electrons are present in the inner orbitals of the atom and the valence electrons are present in the outermost shell of the atom.
The number of inner electrons is calculated by subtracting the valence electrons from the total number of electrons
(c)
Interpretation:
The element with its full and condensed electron configuration and the number of inner electrons is to be determined from the given partial orbital diagram.
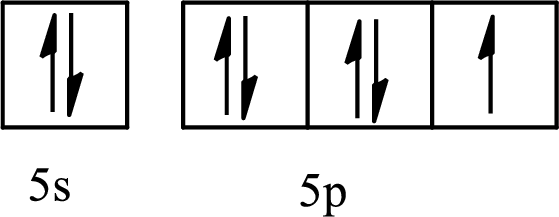
Concept introduction:
The electronic configuration tells about the distribution of electrons in various atomic orbitals.
The full electronic configuration of an atom tells about the distribution of electrons in its various atomic orbital.
The condensed electronic configuration is a way to write the electronic configuration where the inner shell configurations are compressed to the nearest noble gas configuration and only the valence shell configuration is written in the expanded form.
The partial orbital diagram is the one that shows the distribution of valence electrons only.
The inner electrons are present in the inner orbitals of the atom and the valence electrons are present in the outermost shell of the atom.
The number of inner electrons is calculated by subtracting the valence electrons from the total number of electrons
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual For Silberberg Chemistry: The Molecular Nature Of Matter And Change With Advanced Topics
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





