
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.2, Problem 3P
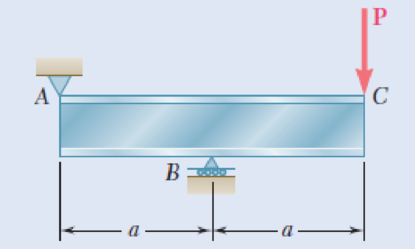
An overhanging W920 × 449 rolled-steel beam supports a load P as shown. Knowing that P = 700 kN, a = 2.5 m, and σall = 100 MPa, determine (a) the maximum value of the normal stress σm in the beam, (b) the maximum value of the principal stress σmax at the junction of the flange and web, (c) whether the specified shape is acceptable as far as these two stresses are concerned.
Fig. P8.3
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
My answers are incorrect
Picture
What is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf?
The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05
N.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is
KN.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05
kg-m/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023
lbf.
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 8.2 - A W10 = 39 rolled-steel beam supports a load P as...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.1, assuming that P = 22.5 kips and a...Ch. 8.2 - An overhanging W920 449 rolled-steel beam...Ch. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.3, assuming that P = 850 kN and a =...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.5 and 8.6 (a) Knowing that all = 160 MPa and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.7 and 8.8 (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...
Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 12PCh. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - 8.9 through 8.14 Each of the following problems...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 8.2 - Using the notation of Sec. 8.2 and neglecting the...Ch. 8.2 - The 4-kN force is parallel to the x axis, and the...Ch. 8.2 - The vertical force P1 and the horizontal force P2...Ch. 8.2 - The two 500-lb forces are vertical and the force P...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shafts ABC and DEF and the gears shown...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 28PCh. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.2 - The solid shaft AE rotates at 600 rpm and...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - Two 1.2-kip forces are applied to an L-shaped...Ch. 8.3 - The cantilever beam AB has a rectangular cross...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - 8.34 through 8.36 Member AB has a uniform...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the pipe AB as shown....Ch. 8.3 - Several forces are applied to the pipe assembly...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pile AB has a 100-mm outer diameter and...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to a 4-in.-diameter plate...Ch. 8.3 - The steel pipe AB has a 72-mm outer diameter and a...Ch. 8.3 - A 13-kN force is applied as shown to the...Ch. 8.3 - A vertical force P of magnitude 60 lb is applied...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the bar shown....Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces are applied to the small post BD as...Ch. 8.3 - Three forces are applied to the machine component...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 52PCh. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Three steel plates, each 13 mm thick, are welded...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Two forces P1 and P2 are applied as shown in...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 57PCh. 8.3 - Four forces are applied to a W8 28 rolled-steel...Ch. 8.3 - A force P is applied to a cantilever beam by means...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 60PCh. 8.3 - A 5-kN force P is applied to a wire that is...Ch. 8.3 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8.3 - The structural tube shown has a uniform wall...Ch. 8 - (a) Knowing that all = 24 ksi and all = 14.5 ksi,...Ch. 8 - Neglecting the effect of fillets and of stress...Ch. 8 - Knowing that rods BC and CD are of diameter 24 mm...Ch. 8 - The solid shaft AB rotates at 450 rpm and...Ch. 8 - A 6-kip force is applied to the machine element AB...Ch. 8 - A thin strap is wrapped around a solid rod of...Ch. 8 - A close-coiled spring is made of a circular wire...Ch. 8 - Forces are applied at points A and B of the solid...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the bracket AB has a uniform...Ch. 8 - For the post and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 8 - Knowing that the structural tube shown has a...Ch. 8 - The cantilever beam AB will be installed so that...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward
- 12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forwardGiven: = refueling Powertran SOURCE EMISSIONS vehide eff eff gasoline 266g co₂/kwh- HEV 0.90 0.285 FLgrid 411ilg Co₂/kWh 41111gCo₂/kWh EV 0.85 0.80 Production 11x10% og CO₂ 13.7 x 10°g CO₂ A) Calculate the breakeven pont (in km driven) for a EV against on HEV in Florida of 0.1kWh/kM Use a drive cycle conversion 5) How efficient would the powertrain of the HEV in this example have to be to break even with an EV in Florida after 150,000 Miles of service (240,000) km Is it plausible to achieve the answer from pert b Consideans the HaXINERY theoretical efficiency of the Carnot cycle is 5020 and there are additional losses of the transMISSION :- 90% efficiency ? c A what do you conclude is the leading factor in why EVs are less emissive than ICE,arrow_forwardsolve autocontrolsarrow_forward
- Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.arrow_forwardPUNTO 4. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 5. Groundarrow_forwardPUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. III IAarrow_forward
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license