
Concept explainers
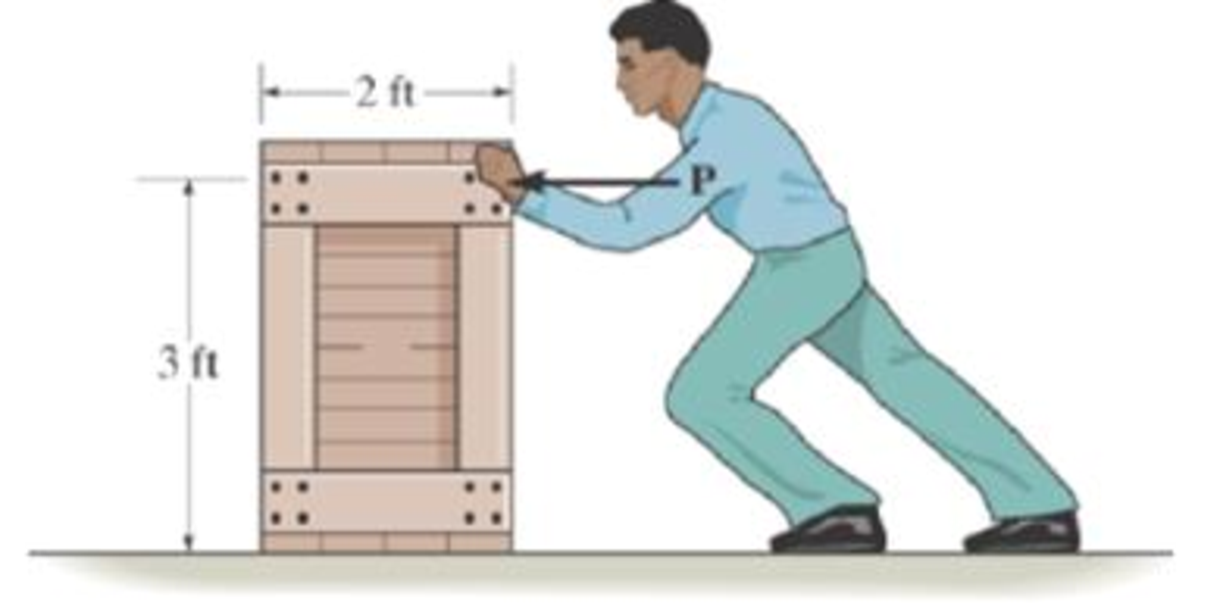
The man having a weight of 200 Ib pushes horizontally on the crate. If the coefficient of static friction between the 450-Ib crate and the floor is, μs = 0.3 and between his shoes and the floor is, μ’s = 0.6, determine if he can move the crate.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 8 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics, Student Value Edition; Modified Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Engineering Mechanics: Statics (14th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
- reading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forward
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
