
Concept explainers
Simple electric motor
Obtain the equipment illustrated at right assemble it as shown.
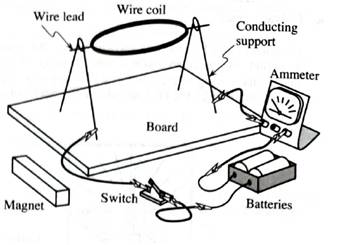
You should have:
•a magnet, a battery, a switch, some connecting, and an ammeter.
• a copper wire coil. The ends of the wire leads to the coil have been stripped of the insulating enamel coating so that half the wire is bare.
• twoconducting supports for the leads to the coil
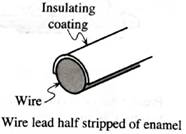
1. Examine the leads to the wire coil closely, so that you understand which portion of the wire has been stripped of the insulating coating.
For what orientations of the coil will there be a current through it due to the battery?
Check your answer by losing the switch and observing the deflection of the ammeter as you rotate the coil manually through one complete revolution.
2. Hold one pole of the magnet near the coil. Close the switch. If the coil does not begin to spin, adjust the location of the magnet or gently rotate the coil to Stan it spinning.
Use the ideas that we have developed in this and previous tutorials to explain the motion of the wire coil. (The questions that follow may serve as a guide to help you develop an understanding of the operation of the motor.)
When the coil is in the position shown, there is a current, I, through it.
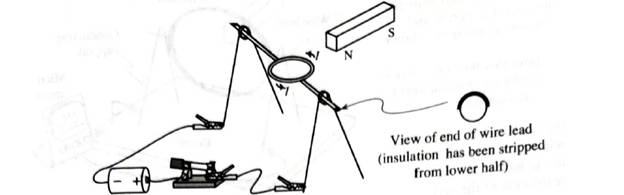
a. The coil is manually started spinning so that it rotates clockwise.
During which portions of the cycle does the coil from a complete circuit with the battery such that there is a current through the wire of the coil?
The current results in a magnetic moment that interacts with the magnetic field of the magnet. Will the interaction tend to increase or to decrease the angular speed of the coil? Explain.
b. The coil is manually started spinning so that it rotates counterclockwise:
During which portions of the cycle does the coil form a complete circuit with the battery so that there is a current through the wire of the coil?
The current results in a magnetic moment that interacts with the magnetic field of the magnet. Will the interaction tend to increase or to decrease the angular speed of the coil? Explain.
Check that the behavior of your motor is consistent with your answers.
4. Consider the following questions about the motor:
• Why was insulated wire used for the coil? Would bare wire also work? Explain.
• Would you expect the motor to work if the leads to the coil were stripped completely? Explain.
5. Predict the effect on the motor of (i) reversing the leads to the battery and (ii) reversing the orientation of the magnet
Check your predictions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





