
Interpretation:
To show
To show the Jacobian matrix for the linearization has the form
Here, A and B are
By considering trace and determinant of matrix
To show that depending on the sizes of g and T, the determinant of matrix
By using computer, show that Hopf bifurcation can be supercritical.
Concept Introduction:
To find fixed point of the system, put
Jacobian matrix is used to check the stability of the fixed points, and it is given as:
The system which is settling down to equilibrium by exponentially damping and its decay rate depends on a control parameter
Answer to Problem 17E
Solution:
It is shown that the Jacobian matrix for the linearization has the form
It is shown that all eigenvalues of the matrix
It is shown that values of g and T determine whether the determinant of matrix
It is shown that the system goes through supercritical Hopf bifurcation.
Explanation of Solution
a)
The system equations are:
Assuming that
Here, the condition of
In above equation, L.H.S. and R.H.S. are zero and positive respectively when
Thus, the curves intersect and have unique symmetric solution.
b)
The Jacobian matrix is:
To prove determinant law,
Expanding along last column,
Again expanding along bottom row,
Therefore,
This result is used for calculation of eigenvalues of the
c)
Using determinant is product of the eigenvalues and trace is sum of eigenvalues,
But
Here,
From the above result,
The trace
Thus,
d)
For the matrix
The determinant
And trace
From the above results, the determinant is positive if
Trace can negative or positive depending upon values of b and T.
From the above conclusions of eigenvalues, pitchfork or Hopf bifurcation can occur at the point
By adjusting parameter g, if initially trace is negative, and by varying parameter g, its value is shifting towards positive value, then the pitchfork bifurcation occurs at
By adjusting parameter T, if the determinant is positive, by changing the parameter T, the trace of the matrix changes its sign, then the Hopf bifurcation occurs at a
e)
The plots of
For T being very small, the system is nearly settled down to fixed point

Increasing the value of T, the stable limit cycles just appear.
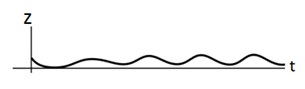
Further increasing the value of T, the size of the limit cycle increases.
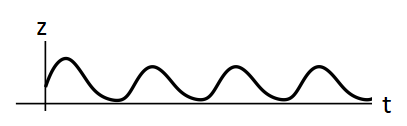
Therefore, the system goes through supercritical Hopf bifurcation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
- plate is attached to its base by 6 bolts. Each bolt is inspected before installation, and the probability of passing the inspection is 0.9. Only bolts that pass the inspection are installed. Let X denote the number of bolts that are inspected in order to attach one plate. Find the probability that less than 7 bolts need to be inspected in order to attach the plate. Round answer to four decimal places. distribution can be used here with parameters r =6 and p = The requested probability isarrow_forwardThe analysis of results from a leaf transmutation experiment (turning a leaf into a petal) is summarized by the type of transformation completed: A naturalist randomly selects three leaves from this set without replacement. Total Textural Transformation Yes No Total Yes 243 26 269 Total Color Transformation No 13 18 31 Total 256 44 300 Let X represent the number of leaves that have undergone both transformations. The appropriate probability distribution of X is a distribution. The parameters are population size N = size n = number of events K = and sample The probability that at least one leaf has undergone both transformations is probability to four decimal places.) X has a N = K= n = The requested probability is distribution. (Round thearrow_forwardThe life time of a certain battery is modeled with the Weibull distribution with shape parameter ẞ=2 and scale parameter 8-10 hours. Determine the mean time until failure of batteries. (Round the answer to one decimal place.) hoursarrow_forward
- Consider the probability distribution below. 0 1 3 f(x) 0.3 0.3 0.4 E(X)=1.5. The variance of XV (X) equals 1.65 ○ 1.28 1.56 2.33arrow_forwardConsider the probability distribution below. 10 20 30 40 f(x) 0.3 0.4 0.2 0.1 The expected value of X equals 100 ○ 25 ○ 18 ○ 21arrow_forwardThe analysis of results from a leaf transmutation experiment (turning a leaf into a petal) is summarized by the type of transformation completed: A naturalist randomly selects three leaves from this set without replacement. Total Textural Transformation Yes No Total Yes 243 26 269 Total Color Transformation No 13 18 31 Total 256 44 300 Let X represent the number of leaves that have undergone both transformations. The appropriate probability distribution of X is a distribution. The parameters are population size N = size n = number of events K = and sample The probability that at least one leaf has undergone both transformations is probability to four decimal places.) X has a N = K= n = The requested probability is distribution. (Round thearrow_forward
- The thickness of a flange on an aircraft component is uniformly distributed between 0.95 and 1.05 millimeters. Determine the mean of flange thickness. millimeters (Two decimal places.)arrow_forwardThe following table is an output from a statistical software package. The assumed standard deviation = 1.5 Variable X N 9 Mean 29.542 Σ-1 - Sum of Squares (SS): SS = Σ₁ (x − x) ² SE Mean ? StDev Variance Sum of Squares 1.218 ? ? Fill the missing information. Round answers to 3 decimal places. SE Mean = Variance = Sum of Squares =arrow_forwardFor the random variable x = 1,2,3,4, the probability mass function is f(x) = x 10 Determine the following probabilities. Round answers to one decimal place. (a) P(X = 2) = (b) P(X ≤ 2) = (c) P(X > 4) = (d) P (0 < x < 3) =arrow_forward
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,






