
Concept explainers
(a) Show that the beam of Prob. 8.41 cannot be moved if the top surface of the dolly is slightly lower than the platform. (b) Show that the beam can be moved if two 175-lb workers stand on the beam at B, and determine how far to the left the beam can be moved.
8.41 A 10-ft beam, weighing 1200 lb, is to be moved to the left onto the platform as shown. A horizontal force P is applied to the dolly, which is mounted on frictionless wheels. The coefficients of friction between all surfaces are μs = 0.30 and μs = 0.25, and initially, χ = 2 ft. Knowing that the top surface of the dolly is slightly higher than the platform, determine the force P required to start moving the beam. (Hint: The beam is supported at A and D.)
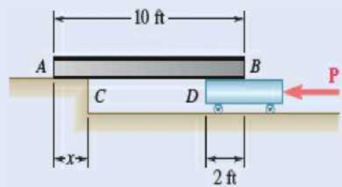
Fig. P8.41
(a)
Show that the beam cannot be moved if the top surface of the dolly is slightly lower than the platform.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is 10 ft.
The weight of the beam is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the beam AB as in Figure 1.
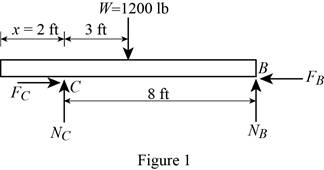
Find the normal force at point B by taking moment about end C.
Find the normal force at point C by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Find the maximum friction force at point C
Substitute 0.30 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
The maximum friction force at point B is less than the maximum friction force at point C.
The sliding is about to happen at point B.
Therefore, the beam
(b)
Show that the beam can be moved if two 175-lb workers stand on the beam at B.
Find the distance the beam moves to the left.
Answer to Problem 8.42P
The distance the beam moves to the left is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the beam is 10 ft.
The weight of the beam is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the beam AB as in Figure 2.
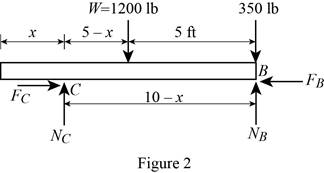
Find the normal force at point B by taking moment about end C.
Find the normal reaction at point C by taking moment about point B.
When two 175 lb workers stand on the end B:
Substitute 2 ft for x in Equation (1).
Substitute 2 ft for x in Equation (2).
Find the maximum friction force at point C
Substitute 0.30 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
The maximum friction force at point B is greater than the maximum friction force at point C.
The sliding is about to happen at point C.
Therefore, the beam
The beam will stop moving when the friction force at point C is equal to the maximum friction force at point B.
Find the friction force at point C
Substitute 0.25 for
Find the maximum friction force at point B
Substitute 0.30 for
Substitute
Therefore, the distance the beam moves to the left is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- what is an air preheater, what are formulas, and their importance, define the diagram, and give me a script on how to explain the design of an air preheater, and how did values end up in that number. based on standardsarrow_forwardQf, Qa,Qm, Qcon,Qfg, Qbd, Qref,Qloss ( meaning, formula, percentage, and importance of higher value na qf, qa etc)arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a fixed support at point C and a roller at point A. It also has an internal hinge at point B. The beam supports a point load at point D, a moment at point A and a distributed load on segment BC. a. calculate the support reactions at points A and C b. calculate the internal resultant loadings (N, V, M) at points E and F, which lies in the middle between points A and D P = 4 kip Ma = 5 kip-ft w1 = 3 kip/ft and w2 = 4 kip/ft a = 3 ftarrow_forward
- From the image of the pyramid, I want to find what s1 hat, s2 hat, and s3 hat are. I think s3 hat is just equal to e3 hat right? What about the others?arrow_forward(a) What kind of equation is it?(b) Is it linear or non-linear?(c) Is it a coupled system or uncoupled?arrow_forwardWhat kind of system is presented in Figure 2? Open loop or closed loop?arrow_forward
- What are the control hardware shown in the Figure?arrow_forwardQuestion 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forward
- If you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forwardProblem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





