
Two 8-kg blocks A and B resting on shelves are connected by a rod of negligible mass. Knowing that the magnitude of a horizontal force P applied at C is slowly increased from zero, determine the value of P for which motion occurs and what that motion is when the coefficient of static friction between all surfaces is (a) μs = 0.40, (b) μs = 0.50.
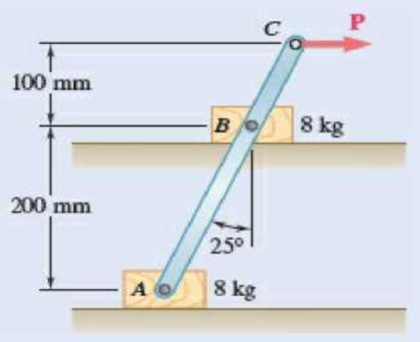
Fig. P8.43
(a)
Find the magnitude of horizontal force P applied at C for which the motion occurs.
Answer to Problem 8.43P
The magnitude of the horizontal force P is
The system
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the blocks A and B is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Consider the blocks will slide to the right.
Find the weight (W) of the blocks A and B using the relation.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Consider the acceleration due to gravity is
Substitute 8 kg for m and
Find the friction force at block A and B as follows.
Here, the normal force at block A is
Show the free-body diagram of the shelves as in Figure 1.
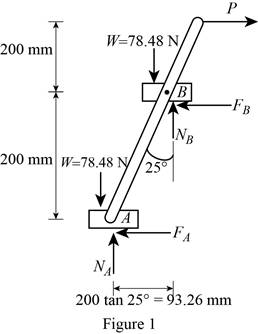
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Substitute 0.40 for
Therefore, the magnitude of the horizontal force P is
Take moment about point B.
Substitute 62.8 N for P and 0.40 for
Therefore, the system
(b)
Find the magnitude of horizontal force P applied at C for which the motion occurs.
Answer to Problem 8.43P
The
The magnitude of the horizontal force P is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the blocks A and B is
The coefficient of static friction between the surfaces is
Calculation:
Consider the blocks will slide to the right.
Find the weight (W) of the blocks A and B using the relation.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Consider the acceleration due to gravity is
Substitute 8 kg for m and
Find the friction force at block A and B as follows.
Here, the normal force at block A is
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Substitute 0.50 for
Therefore, the magnitude of the horizontal force P is
Take moment about point B.
Substitute 78.48 N for P and 0.50 for
Therefore, the
The value of
Take moment about point B.
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the magnitude of the horizontal force P is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Multiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which geometry attribute deviation(s) can be limited with a profile of a surface tolerance? A. Location B. Orientation C. Form D. All of the above 2. A true profile may be defined with: A. Basic radii B. Basic angles C. Formulas D. All of the above 3. Which modifier may be applied to the profile tolerance value? A B C. D. All of the above 4. The default tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Non-uniform B. Unilateral C. Bilateral equal distribution D. Bilateral-unequal distribution 5. An advantage of using a profile tolerance in place of a coordinate tolerance is: A. A bonus tolerance is permitted. B. A datum feature sequence may be specified C. A profile tolerance always controls size D. All of the above 6. The shape of the tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Two parallel planes B. The same as the true profile of the toleranced surface C. Equal bilateral D. Cylindrical when the diameter symbol is speci- fied…arrow_forwardOne thousand kg/h of a (50-50 wt%) acetone-in-water solution is to be extracted at 25C in a continuous, countercurrent system with pure 1,1,2-trichloroethane to obtain a raffinate containing 10 wt% acetone. Using the following equilibrium data, determine with an equilateral-triangle diagram: a- the minimum flow rate of solvent; b- the number of stages required for a solvent rate equal to 1.5 times minimum, and composition of each streamleaving each stage. c- Repeat the calculation of (a) and (b) if the solvent used has purity 93wt% (4wr% acetone, 3wt% water impurities) acetone water 1,1,2-trichloroethane Raffinate. Weight Extract. Weight 0.6 0.13 0.27 Fraction Acetone Fraction Acetone 0.5 0.04 0.46 0.44 0.56 0.4 0.03 0.57 0.29 0.40 0.3 0.02 0.68 0.12 0.18 0.2 0.015 0.785 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.01 0.89 0.55 0.35 0.1 0.5 0.43 0.07 0.4 0.57 0.03 0.3 0.68 0.02 0.2 0.79 0.01 0.1 0.895 0.005arrow_forward2500 kg/hr of (20-80) nicotine water solution is to be extracted with benzene containing 0.5% nicotine in the 1st and 2ed stages while the 3rd stage is free of nicotine. Cross- current operation is used with different amounts of solvent for each stages 2000kg/hr in the 1st stage, 2300 kg/hr in the 2nd stage, 2600 kg/hr in the 3rd, determine: - a- The final raffinate concentration and % extraction. b- b- The minimum amount of solvent required for counter-current operation if the minimum concentration will be reduced to 5% in the outlet raffinate. Equilibrium data Wt % Nicotine in water Wt % Nicotine in benzene 0 4 16 25 0 4 21 30arrow_forward
- Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1=6mm, for w2 h2 5mm, and for w3 is h3 -5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 101.15 REDMI NOTE 8 PRO AI QUAD CAMERA Farrow_forward(read image)arrow_forwardProblem 3.30 A piston-cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant- 134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the change in the volume of the refrigerant, and (c) the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a. please show Al work step by steparrow_forward
- Part 1 The storage tank contains lubricating oil of specific gravity 0.86 In one inclined side of the tank, there is a 0.48 m diameter circular inspection door, mounted on a horizontal shaft along the centre line of the gate. The oil level in the tank rests 8.8 m above the mounted shaft. (Please refer table 01 for relevant SG, D and h values). Describe the hydrostatic force and centre of pressure with the aid of a free body diagram of the inspection door. Calculate the magnitude of the hydrostatic force and locate the centre of pressure. 45° Estimate the moment that would have to be applied to the shaft to open the gate. Stop B If the oil level raised by 2 m from the current level, calculate the new moment required to open the gate. Figure 01arrow_forwardFrom thermodynamics please fill in the table show all work step by steparrow_forwardThe 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. 25 ft B = 4x A 20 ft xarrow_forward
- A virtual experiment is designed to determine the effect of friction on the timing and speed of packages being delivered to a conveyor belt and the normal force applied to the tube. A package is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped tube of radius R = 5m. The particle at the bottom will transfer to the conveyor belt, as shown below. Run the simulations for μ = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 and determine the time and speed at which the package is delivered to the conveyor belt. In addition, determine the maximum normal force and its location along the path as measured by angle 0. Submit in hardcopy form: (0) Free Body Diagram, equations underneath, derivations (a) Your MATLAB mfile (b) A table listing the values in 5 columns: μ, T (time of transfer), V (speed of transfer), 0 (angle of max N), Nmax (max N) (c) Based on your results, explain in one sentence what you think will happen to the package if the friction is increased even further, e.g. μ = 0.8. NOTE: The ODE is…arrow_forwardPatm = 1 bar Piston m = 50 kg 5 g of Air T₁ = 600 K P₁ = 3 bar Stops A 9.75 x 10-3 m² FIGURE P3.88arrow_forwardAssume a Space Launch System (Figure 1(a)) that is approximated as a cantilever undamped single degree of freedom (SDOF) system with a mass at its free end (Figure 1(b)). The cantilever is assumed to be massless. Assume a wind load that is approximated with a concentrated harmonic forcing function p(t) = posin(ωt) acting on the mass. The known properties of the SDOF and the applied forcing function are given below. • Mass of SDOF: m =120 kip/g • Acceleration of gravity: g = 386 in/sec2 • Bending sectional stiffness of SDOF: EI = 1015 lbf×in2 • Height of SDOF: h = 2000 inches • Amplitude of forcing function: po = 6 kip • Forcing frequency: f = 8 Harrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





