
Solve Prob. 8.13 assuming that package B is placed to the right of both packages A and C.
8.13 Three 4-kg packages A, B, and C are placed on a conveyor belt that is at rest. Between the belt and both packages A and C, the coefficients of friction are μs = 0.30 and μk = 0.20; between package B and the belt, the coefficients are μs = 0.10 and μk = 0.08. The packages are placed on the belt so that they are in contact with each other and at rest. Determine which, if any, of the packages will move and the friction force acting on each package.
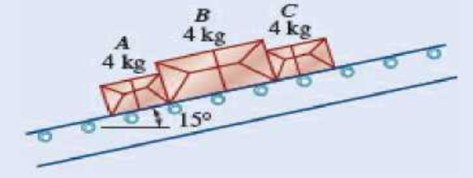
Fig. P8.13
Find whether any of the package moves and the friction force acting on each package.
Answer to Problem 8.14P
The packages A, C, and B will
The friction force in the package C is
The friction force in the package A is
The friction force in the package B is
Therefore,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the package A, B, and C is
The static coefficient of friction between packages A and C and the belt is
The static coefficient of friction between package B and belt is
The kinetic coefficient of friction between packages A and C and belt is
The kinetic coefficient of friction between package B and belt is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Consider Block B:
Show the free body diagram of the block B as in Figure 1.
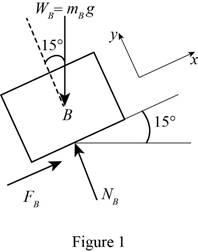
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.10 for
The maximum friction force is less than the friction force.
Therefore, the package C will move.
Consider Block A, B, and C together:
Show the free body diagram of the block A, B, and B as in Figure 2.
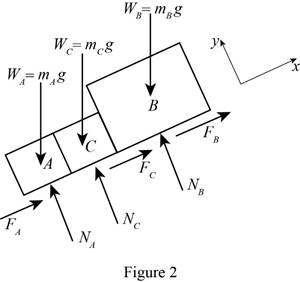
The normal force in package A is
The normal force in package C is
The normal force in package B is
The friction force in package A is
The friction force in package C is
The friction force in package B is
Find the total normal force in package A, B, and C as follows;
Find the total friction force in package A, B, and C as follows;
The maximum friction force in package A is
The maximum friction force in package C is
Find the maximum friction force
Substitute 0.10 for
The maximum friction force in package B is
Find the maximum friction force
The maximum friction force is less than the friction force.
Therefore, the packages A, C, and B will
Find the friction force in the package A using the kinetic relation.
Substitute 0.20 for
Find the friction force in the package B using the kinetic relation.
Substitute 0.08 for
Find the friction force in the package C using the kinetic relation.
Substitute 0.20 for
Therefore, the friction force in the package A is
Therefore, the friction force in the package B is
Therefore, the friction force in the package C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
VECTOR MECH....F/ENGNRS-STATICS -CONNECT
- A 16-lb spool is at rest on an inclined surface. Around its center a cable is wound which travels with the same inclination of the ramp, passes through a frictionless pulley, and is attached to a block B at its other end.The coefficient of static friction between block B and the floor is 0.25. For the position shown, with the given value of α, determine: R (in) = 11,1 in r (in) = 7 in α (°) = 16° 1. The minimum coefficient of static friction that must exist between the reel and the floor of the ramp, so that the reel does NOT slide on the ramp (does not slip). 2.The minimum weight that block B must have for the reel to NOT roll down the ramp dragging block B. Do not allow for the possibility of the block turning or tipping over.arrow_forward2. A 10-1b block B rests as shown on a 20-1b bracket A. The coefficients of friction are µg= 0.30 between block B and bracket A, and there is no friction in the pulley or between the bracket and the horizontal surface. (a) Determine the maximum weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A. A B. Carrow_forward9. Knowing that the coefficient of friction between the 15-kg block and the incline is us 0.25, determine (a) the smallest value of P required to maintain the block in equilibrium, (b) the corresponding value of ß. (P=108.8 N, ß=46º) 15 kg 60°arrow_forward
- A rope having a weight per unit length of 0.4 lb/ft is wound 2 1/2 Times around a horizontal rod. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction between the rope and the rod is 0.30, determine the minimum length x of rope that should be left hanging if a 100-lb load is to be supported.arrow_forwardTwo blocks A and B weighing 3 kN and 15 kN, respectively, are held in position against an inclined plane by applying a horizontal force P as shown in Fig. Find the least value of P which will induce motion of the block A upwards. Angle of friction for all contact surfaces is 12°.7.arrow_forwardThe coefficient of static friction µs between the 111-lb body and the 18° wedge is 0.17. Determine the magnitude of the force P required to begin raising the 111-lb body if (a) rollers of negligible friction are present under the wedge, as illustrated, and (b) the rollers are removed and the coefficient of static friction μs = 0.17 applies at this surface as well. Answers: (a) P = (b) P = M. 18° 111 lb lb lbarrow_forward
- A 40-kg packing crate is pulled by a rope as shown. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.35. If α =40°,determine (a) the magnitude of the force P required to move the crate, (b) whether the crate will slide or tip.arrow_forwardParvinbhaiarrow_forwardTwo 8-kg blocks A and B resting on shelves are connected by a rod of negligible mass. Knowing that the magnitude of a horizontal force P applied at C is slowly increased from zero, determine the value of P for which motion occurs and what that motion is when the coefficient of static friction between all surfaces is (a) μs= 0.40, (b) μs= 0.50.arrow_forward
- Determine the maximum value of weight at restarrow_forwardKnowing that the coefficient of friction between the 25-kg block and the incline is μs= 0.25, draw the free-body diagram needed to determine both the smallest value of P required to start the block moving up the incline and the corresponding value of β.arrow_forwardA block weighing 200 N is just moved on a rough horizontal plane by a pull of 90 Newton acting at an angle of 30 degree with the horizontal. Determine: (i) the coefficient of friction . (ii) Push that should be applied to the block at the same angle to attain the condition of limiting equilibrium.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
