
(a)
The design of a three-plate moment connection of a
Answer to Problem 8.6.4P
Use a
1/8-in. fillet weld on both sides of the plate.
Use a
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Service dead-load moment = 42 ft-kips
Service live-load moment = 104 ft-kips
Service dead-load beam reaction = 8 kips
Service live-load beam reaction = 21 kips
Group A bearing type bolts
E70 electrodes
A992 steel- Beam and column
A36 steel- Plate material
Calculation:
Reaction:
Moment:
Web plate:
Neglect eccentricity.
Try 5/8-in. diameter bolts.
Assume that threads are in the plane of shear.
Shear capacity of one bolt is
Number of bolts required is
Try 4 bolts.
Determine plate thickness required for bearing. Assume that
Load resisted by each bolt =
Let
Try
Determine whether plate or beam web controls bearing. For the plate,
For the beam web,
Therefore, plate controls.
Check bearing strength assumption:
For the hole nearest the edge, minimum
Try
Therefore, use
For other bolts, minimum
Use
Therefore, use
Bearing controls over shear at each bolt location. Total strength is
Use four 5/8-in. diameter Group A bolts.
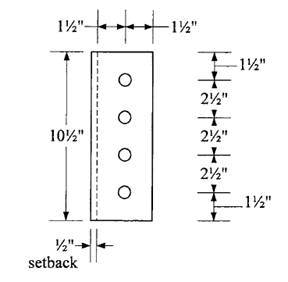
Determine plate thickness required for shear:
Shear yielding strength is
Let
Try
Check shear rupture strength:
Use hole diameter =
Check block shear:
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 64.92 kips. The design block shear strength is
Use a
Connection of shear plate to column flange:
Use E70 electrodes
Minimum weld size, based on the plate thickness, is 1/8-in. try
Weld strength =
Base metal (plate) shear strength:
Yielding:
Rupture:
Total length required =
Use a continuous 1/8-in. fillet weld, both sides of plate.
Flange plate:
From
Try 7/8-in. diameter bolts.
Assume that threads are in the plane of shear.
Number of bolts required for shear is
Try 8 bolts (4 pair)
Determine plate thickness required for bearing:
Minimum
Use
Minimum
Use
For the hole nearest the edge,
Therefore, use
For other bolts,
Therefore, use
Total connection strength =
Let
Design top flange plate as a tension connection element
Tension on gross area:
Required
Tension on net area:
Required
Try a plate width of
For gross area requirement,
For net area requirement,
Hole diameter =
Try a plate
Check compression in the bottom plate:
Assume that the plate acts as a fixed-end compression member between the end fastener and the weld. Use
For compression elements with
Therefore,
Check block shear on the plate using the dimensions and bolt layout shown.
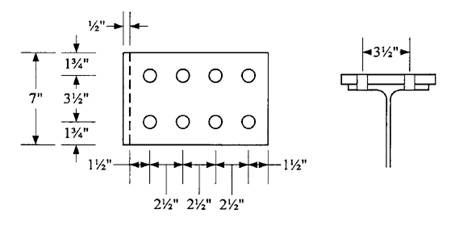
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 395.9 kips. The design block shear strength is
Check block shear strength of beam flange:
Transverse spacing = gauge distance = 3.5 in.
Transverse edge distance =
Longitudinal spacing and edge distance same as for plate.
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 199.7 kips.
The design block shear strength is
Check beam for the effect of bolt holes in the tension flange:
The gross area of one flange is
The effective hole diameter is
Since
Try a smaller diameter bolt. Try ½-in. diameter bolts.
Normal shearing strength =
Number of bolts required for shear is
Try 20 bolts (10 pair)
Bearing and block shear will be satisfactory.
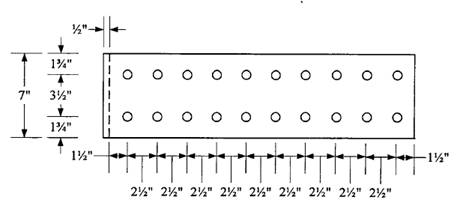
Check reduction in beam flange area:
Use a hole diameter =
Since
Plate length =
Conclusion:
Use a
(b)
The design of a three-plate moment connection of a
Answer to Problem 8.6.4P
Use a
1/8-in. fillet weld on both sides of the plate.
Use a
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Service dead-load moment = 42 ft-kips
Service live-load moment = 104 ft-kips
Service dead-load beam reaction = 8 kips
Service live-load beam reaction = 21 kips
Group A bearing type bolts
E70 electrodes
A992 steel- Beam and column
A36 steel- Plate material
Calculation:
Reaction:
Moment:
Web plate:
Neglect eccentricity.
Try 5/8-in. diameter bolts.
Assume that threads are in the plane of shear.
Shear capacity of one bolt is
Number of bolts required is
Try 4 bolts.
Determine plate thickness required for bearing. Assume that
Load resisted by each bolt =
Let
Try
Determine whether plate or beam web controls bearing. For the plate,
For the beam web,
Therefore, plate controls.
Check bearing strength assumption:
For the hole nearest the edge, minimum
Try
Therefore, use
For other bolts, minimum
Use
Therefore, use
Bearing controls over shear at each bolt location.
Total strength is
Use four 5/8-in. diameter Group A bolts.
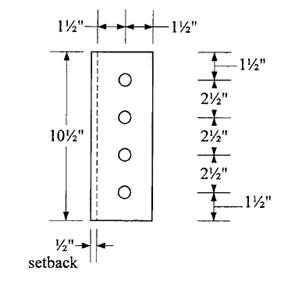
Determine plate thickness required for shear:
Shear yielding strength is
Let
Try
Check shear rupture strength:
Use hole diameter =
Check block shear:
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 64.92 kips. The design block shear strength is
Use a
Connection of shear plate to column flange:
Use E70 electrodes.
Minimum weld size, based on the plate thickness, is 1/8-in. try
Weld strength =
Base metal (plate) shear strength:
The allowable shear yield strength per unit length is
The base metal allowable shear rupture strength per unit length is
Total length required =
Use a continuous 1/8-in. fillet weld, both sides of plate.
Flange plate:
From
Try 7/8-in. diameter bolts.
Assume that threads are in the plane of shear.
Number of bolts required for shear is
Try 8 bolts (4 pair)
Determine plate thickness required for bearing:
Minimum
Use
Minimum
Use
For the hole nearest the edge,
Therefore, use
For other bolts,
Therefore, use
Total connection strength =
Let
Design top flange plate as a tension connection element
Tension on gross area:
Required
Tension on net area:
Required
Try a plate width of
For gross area requirement,
For net area requirement,
Hole diameter =
Try a plate
Check compression in the bottom plate:
Assume that the plate acts as a fixed-end compression member between the end fastener and the weld. Use
For compression elements with
Therefore,
Check block shear on the plate using the dimensions and bolt layout shown.
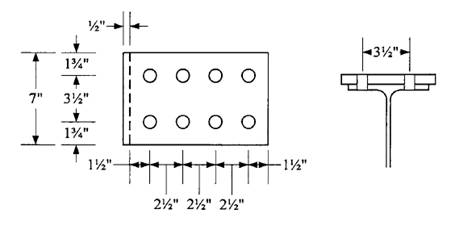
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 395.9 kips. The design block shear strength is
Check block shear strength of beam flange:
Transverse spacing = gauge distance = 3.5 in.
Transverse edge distance =
Longitudinal spacing and edge distance same as for plate.
Shear areas:
Tension area:
with an upper limit of
The nominal block shear strength is therefore 199.7 kips.
The design block shear strength is
Check beam for the effect of bolt holes in the tension flange:
The gross area of one flange is
The effective hole diameter is
Since
Try a smaller diameter bolt. Try ½-in. diameter bolts.
Normal shearing strength =
Number of bolts required for shear is
Try 20 bolts (10 pair)
Bearing and block shear will be satisfactory.
Check reduction in beam flange area:
Use a hole diameter =
Since
Plate length =
Conclusion:
Use a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Bundle: Steel Design, Loose-leaf Version, 6th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- Consider a pool of saturated water at atmospheric pressure. The base of the pool is made of thick polished copper square plate of length 1 m. To generate steam, exhaust gas is flowing underneath and parallel to the base plate with velocity 3 m/s and average temperate of 1090°C. The bottom surface the plate is at constant temperature of 110°. Use the properties of air for exhaust gas. a) Determine the boiling heat transfer rate. b) Determine the temperature of the top surface of the plate. Comment on the results. c) Examine the impact of your assumptions on your solutions. (what will change if any of the assumptions is not valid?)arrow_forward-The axial deflection pipe in inches. -The lateral deflection of the beam in inches -The total deflection of the beam like structure in inches ? all to 4 sig figs AI did not help. as i input what i get im not sure if its a rounding error or what.arrow_forward1. For the foundation shown below: Qapp = 60 kips (Load obtained from structural engineer) 1.5 ft G.W.T. 3 ft Poorly Graded Sand (SP): Ym 115 pcf (above G.W.T.) Ysat 125 pcf (below G.W.T.) c' = 0, ' = 35° K Square footing, 4' x 4' Foundation Dimension Information: 1-ft x 1-ft square concrete column. 1-ft thick "foot" flanges. Yconc=150 pcf *Assume weight of reinforcing steel included in unit weight of concrete. *Assume compacted backfill weighs the same as in-situ soil. Assume this foundation is being designed for a warehouse that had a thorough preliminary soil exploration. Using the general bearing capacity equation: a. Calculate the gross applied bearing pressure, the gross ultimate bearing pressure, and determine if the foundation system is safe using a gross bearing capacity ASD approach. Please include the weight of the foundation, the weight of the backfill soil, and the effect of the uplift pressure caused by the presence of the water table in your bearing capacity…arrow_forward
- ٢٥ ٠٥:٤٠١٠ 2025 ChatGPT VivaCut Onet Puzzle مسلم X Excel JPG I❤> PDF Copilot Chat Bot PDF2IMG iLovePDF NokoPrint O.O StudyX ☑ W CapCut Candy Crush DeepSeek Word ☐ Saga 啡 AcadAl ل TikTokarrow_forwardRefer to the figure below. Given: L = 7 m, y = 16.7 kN/m², and ø' = 30°. L L3 ση Sand γ $' D T LA L σε σε IN P Sand 1. Calculate the theoretical depth of penetration, D. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) D= m 2. Calculate the maximum moment. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Mmax kN-m/marrow_forwardWhy is it important for construction project managers to be flexible when dealing with the many variable factors that pop up in a project?arrow_forward
- What are some reasons for why a company would accelerate a construction project?arrow_forwardFor the design of a shallow foundation, given the following: Soil: ' = 20° c' = 52 kN/m² Unit weight, y = 15 kN/m³ Modulus of elasticity, E, = 1400 kN/m² Poisson's ratio, μs = 0.35 Foundation: L=2m B=1m Df = 1 m Calculate the ultimate bearing capacity. Use the equation: 1 - qu = c' NcFcs Fcd Fcc +qNqFqsFqdFqc + ½√BN√Fãs F√dƑxc 2 For '=20°, Nc = 14.83, N₁ = 6.4, and N₁ = 5.39. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) qu = kN/m²arrow_forwardA 2.0 m wide strip foundation carries a wall load of 350 kN/m in a clayey soil where y = 15 kN/m³, c' = 5.0 kN/m² and ' = 23°. The foundation depth is 1.5 m. For ' = 23°: Nc = 18.05; N₁ = 8.66; Ny = = = 8.20. Determine the factor of safety using the equation below. qu= c' NcFcs FcdFci+qNqFqsFq 1 F + gd. 'qi 2 ·BN√· FF γί Ysyd F (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) FS =arrow_forward
 Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
