
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for
Concept introduction: The Lewis structures are diagrams that give information about the bonding electron pairs and the lone pairs of electrons in a molecule. Similar to electron dot structure in Lewis diagram the lone pair electrons are represented as dots and they also contain lines which represent bonding electron pairs in a bond.
To determine: If either of the chlorine atoms in the structure has an expanded valence shell and the Lewis structures for
Answer to Problem 8.105QP
Solution
The Lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The reaction of
The given compound contains two chlorine and two oxygen atoms. The chlorine atom acts as a central metal atom which is attached with two oxygen atoms. Chlorine contains seven valence electrons and oxygen has six valence electrons. The total valence electrons in
The skeleton structure is drawn in which
For oxygen atoms,
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are six and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For central chlorine
The number of valence electrons in chlorine is seven, the lone pair electrons are two and the bonding electrons are six.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For bonded chlorine atom,
The number of valence electrons in chlorine is seven, the lone pair electrons are six and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
The Lewis structure of
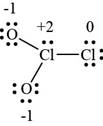
Figure 1
By assigning a formal charge over the atoms of
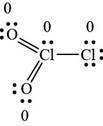
Figure 2
The formal charge over each atom is calculated by using the above formula.
For oxygen atoms,
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are four and the bonding electrons are four.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For central chlorine atom,
The number of valence electrons in chlorine is seven, the lone pair electrons are two and the bonding electrons are ten.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For bonded chlorine atom,
The number of valence electrons in chlorine is seven, the lone pair electrons are six and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
The Lewis structure shown in Figure 2 shows all the atoms carries a zero formal charge. Therefore, it is the most preferred Lewis structure of the
Conclusion
The Lewis structure for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
CHEMISTRY W/WRKBK AND SMARTWORK (LL)
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





