
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The pH values after the addition of each proportion of the base to the acid is to be determined. Also, the titration curve needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Titration curve is drawn to determine the change in pH of an acid or base with respect to the added volume of base or acid to it.
The titration curve can be drawn between a strong/weak acid and strong/weak base. The change in pH shows different patterns for different combinations of acids and bases.
Explanation of Solution
Initial pH of the analyte solution can be determined as follows:
Propanoic acid is a weak acid that forms equilibrium when dissolved in water. The equilibrium is as follows.
The amount of acid at the beginning
| Reaction | Proanoic acid | Propanoate ion | OH- |
| Initial | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium | (0.1-x) | x | x |
The acid dissociation constant can be represented as follows:
Solving this quadratic equation gives the amount of hydrogen ions in the solution.
On solving the only possible value of x is
Now, pH can be calculated as follows:
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic acid | OH- | Propanoate ion | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0004 | ||
| Change | -0.0004 | -0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0021 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
Concentration of base after addition of acid
Concentration of ammonium ion
In the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the pKa is used.
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic acid | OH- | Propanoate ion | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0008 | ||
| Change | -0.0008 | -0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0017 | 0 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic acid | OH- | Propanoate ion | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00125 | ||
| Change | -0.00125 | -0.00125 | 0.00125 | 0.00125 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00125 | 0 | 0.00125 | 0.00125 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic acid | H+ | Propanoate ion | OH- |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.002 | ||
| Change | -0.002 | -0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0005 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0024 | ||
| Change | -0.0024 | -0.0024 | 0.0024 | 0.0024 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0001 | 0 | 0.0024 | 0.0024 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00245 | ||
| Change | -0.00245 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00005 | 0 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00249 | ||
| Change | -0.00249 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00001 | 0 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0025 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0000 | 0 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 |
Concentration of acid after addition of base
Concentration of propanoate ion
At this point, there is no excess acid or base. Therefore, the only possible reaction here is the dissociation of the conjugate acid of the propanoic acid (that is propanoate ion).
Thereafter, using the Kb value for propanoate ion, the amount of hydrogen ions in the solution can be determined to get the pH value at this point.
| Reaction | Propanoate ion | Propanoic acid | OH- |
| Initial | 0.05 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -X | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium | (0.05-x) | x | x |
Then the pH can be calculated as follows:
On solving the equation, the only possible value of x will be:
This is the concentration of hydroxide ion. The pOH value can be calculated as follows:
Thus, pH of the solution is
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0028 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0 |
Concentration of hydroxide ion
Addition of
Total amount of acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Propanoic | OH- | Propanoate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0030 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
Concentration of hydroxide ion
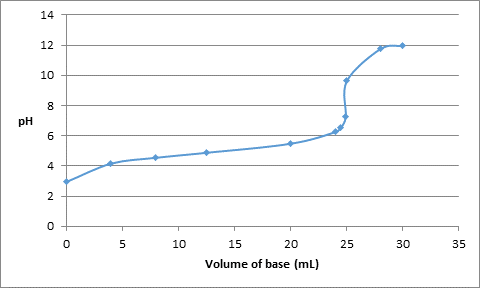
Thus, the pH values for volume of base added are as follows:
| Volume of base added (mL) | pH |
| 0.0 | 2.94 |
| 4.0 | 4.16 |
| 8.0 | 4.55 |
| 12.5 | 4.88 |
| 20.0 | 5.48 |
| 24.0 | 6.26 |
| 24.5 | 6.57 |
| 24.9 | 7.26 |
| 25.0 | 9.64 |
| 28.0 | 11.75 |
| 30.0 | 11.96 |
The titration curve can be drawn as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





