
Concept explainers
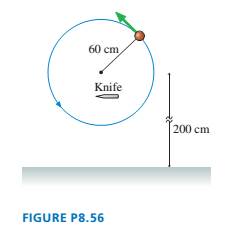
A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung in a vertical circle about a point 200 cm above the floor. The tension in the string when the ball is at the very bottom of the circle is 5.0 N. A very sharp knife is suddenly inserted, as shown in FIGURE P8.56, to cut the string directly below the point of support. How far to the right of where the string was cut does the ball hit the floor?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (Chs 1-42) Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





