
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 4FP
F8–4. If the coefficient of static friction at contact points A and B is, μs = 0.3, determine the maximum force P that can be applied without causing the 100-kg spool to move.
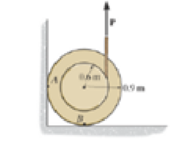
Prob. F8–4
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 3.
1.5 m
B
PROBLEM 16.121
End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the inclined surface, while end B is
attached to a collar of negligible mass which can slide along the vertical rod
shown. Knowing that the rod is released from rest when = 35° and neglecting the
effect of friction, determine immediately after release (a) the angular acceleration
of the rod, (b) the reaction at B.
25°
Problem 1. End A of the uniform 5-kg bar is pinned freely to the collar, which has an acceleration
a = 4 m/s² along the fixed horizontal shaft. If the bar has a clockwise angular velocity @ = 2 rad/s
as it swings past the vertical, determine the components of the force on the bar at A for this instant.
Answers: Ax = 5 N, Ay = 57.1 N
L
X
AO
0.8 m
@
a
=
MMB 241- Tutorial 1.pdf
1/3
80%
+ +
MMB 241 - Dynamics of Particles
Tutorial 1
Topic: Kinematics of Particles:- Displacement, velocity and acceleration of particles.
QUESTIONS
1. If v = (4t+5) m/s, where t is in seconds, determine a when t = 2 s.
2. If s = (2t³) m, where t is in seconds, determine v when t = 2 s.
3. If a = 2 m/s², determine v at s = 4 m if v = 3 m/s at s = 0.
4. If a = 4 m/s², determines when t = 3 s if v = 2 m/s and s = 2 m when t=0.
5. A particle moves along a straight line such that its position is defined by s = (t² - 6t + 5) m.
Determine the average velocity, the average speed, and the acceleration of the particle
when t = 6 s.
6. A particle is moving with a velocity of vo when s=0 and t=0. If it is subjected to a
deceleration of a = -kv³ where k is a constant, determine its velocity and position as
functions of time.
7. A particle travels along a straight-line path such that in 4s it moves from an initial position
SA = -8 m to a position SB = +3 m. Then in…
Chapter 8 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 8 - F81. Determine the friction developed between the...Ch. 8 - F82. Determine the minimum force P to prevent the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 3FPCh. 8 - F84. If the coefficient of static friction at...Ch. 8 - F85. Determine the maximum force P that can be...Ch. 8 - F86. Determine the minimum coefficient of static...Ch. 8 - F87. Blocks A, B, and C have weights of 50 N, 25...Ch. 8 - F88. If the coefficient of static friction at all...Ch. 8 - Prob. 9FPCh. 8 - Determine the maximum force P the connection can...
Ch. 8 - The mine car and its contents have a total mass of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4PCh. 8 - The automobile has a mass of 2 Mg and center of...Ch. 8 - The automobile has a mass of 2 Mg and canter of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 9PCh. 8 - Determine the angle at which the applied force P...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12PCh. 8 - The car has a mass of 1.6 Mg and center of mass at...Ch. 8 - The log has a coefficient of state friction of, s...Ch. 8 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 Ib rests...Ch. 8 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 Ib rests...Ch. 8 - Prob. 20PCh. 8 - The uniform thin pole has a weight of 30 Ib and a...Ch. 8 - The uniform pole has a weight of 30 Ib and a...Ch. 8 - The friction pawl is pinned at A and rests against...Ch. 8 - Two blocks A and B have a weight of 10 Ib and 6...Ch. 8 - Two blocks A and B have a weight of 10 Ib and 6...Ch. 8 - Determine the smallest force P that must be...Ch. 8 - The man having a weight of 200 Ib pushes...Ch. 8 - The uniform hoop of weight W is subjected to the...Ch. 8 - Determine the maximum horizontal force P that can...Ch. 8 - Determine the minimum force P needed to push the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 41PCh. 8 - Prob. 42PCh. 8 - Prob. 51PCh. 8 - Prob. 52PCh. 8 - Determine the smallest couple moment that can be...Ch. 8 - If P=250 N, determine the required minimum...Ch. 8 - Determine the minimum applied force P required to...Ch. 8 - Prob. 67PCh. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Prob. 71PCh. 8 - Prob. 72PCh. 8 - Prob. 73PCh. 8 - Prob. 74PCh. 8 - Prob. 81PCh. 8 - Determine the horizontal force P that must be...Ch. 8 - A 180-lb farmer tries to restrain the cow from...Ch. 8 - The 100-lb boy at A is suspended from the cable...Ch. 8 - Prob. 87PCh. 8 - Determine the force P that must be applied to the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 93PCh. 8 - Prob. 98PCh. 8 - Prob. 99PCh. 8 - Blocks A and B have a mass of 7 kg and 10 kg,...Ch. 8 - The uniform bar AB is supported by a rope that...Ch. 8 - Prob. 102PCh. 8 - A 10-kg cylinder D, which is attached to a small...Ch. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - The collar bearing uniformly supports an axial...Ch. 8 - The collar bearing uniformly supports an axial...Ch. 8 - The floor-polishing machine rotates at a constant...Ch. 8 - Prob. 110PCh. 8 - Prob. 111PCh. 8 - Prob. 116PCh. 8 - The collar fits loosely around a fixed shaft that...Ch. 8 - Prob. 119PCh. 8 - Prob. 120PCh. 8 - Solve Prob. 8-120 if the force P is applied...Ch. 8 - Prob. 122PCh. 8 - Prob. 123PCh. 8 - Prob. 125PCh. 8 - The bell crank fits loosely into a 0.5-in-diameter...Ch. 8 - The bell crank fits loosely into a 0.5-in-diameter...Ch. 8 - Prob. 129PCh. 8 - R81. The uniform 20-lb ladder rests on the rough...Ch. 8 - R82. The uniform 60-kg crate C rests uniformly on...Ch. 8 - R83. A 35-kg disk rests on an inclined surface for...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4RPCh. 8 - Prob. 6RPCh. 8 - Prob. 7RPCh. 8 - The hand cart has wheels with a diameter of 80 mm....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forwardQu 2 Schematically plot attractive, repulsive, and net energies versus interatomic separation for two atoms or ions. Note on this plot the equilibrium separation (distance) ro and the bonding energy Eo. Qu 3 How many atoms (or molecules) are in one mole of the substance? Qu 4 Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of gram-mole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a pound-mole of a substance? Qu 5 The atomic radii of Mg* and F ions are 0.072 and 0.133 nm, respectively. Calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another). What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?show all work step by step problems formulaarrow_forwardQu 4 Silver has FCC crystal structure at room temperature, and a lattice constant, a, of 0.407 nm. Draw a reduced sphere silver unit cell in the grids provided below, clearly label the lattice dimensions. Within the unit cell you drew, shade the (1 0 0) plane. How many atoms are contained within the (1 0 0) plane? Calculate the area of (1 0 0) plane in [nm?]. Express your answer in [nm?] to three significant figures. Calculate the planar density of the (1 0 0) plane in [atoms/nm?]. Express the answer in atoms/nm to three significant figures. show all work step by steparrow_forward
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License