
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780133942651
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 38EAP
A 2.0 kg projectile with initial velocity 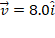
 m/s experiences the variable force
m/s experiences the variable force
a. What is the projectile’s speed at t = 2.0 s?
b. At what instant of time is the projectile moving parallel t the y-axis?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Slink, from Toy Story, is a slinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed (as shown in figure A) with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again (as shown in figure C).
The character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?
Calculate the energy needed to melt 50 g of 0°C ice
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Ch. 8 - In uniform circular motion, which of the following...Ch. 8 - A car runs out of gas while driving down a hill....Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.3 is a bird's-eye view of particles on...Ch. 8 - Tarzan swings through the jungle on a massless...Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.5 shows two balls of equal mass moving...Ch. 8 - Ramon and Sally are observing a toy car speed up...Ch. 8 - A jet plane is flying on a level course at...Ch. 8 - A small projectile is launched parallel to the...Ch. 8 - 9. You can swing a ball on a string in a vertical...Ch. 8 - A golfer starts with the club over her head and...
Ch. 8 - As a science fair project, you want to launch an...Ch. 8 - A 500 g model rocket is on a cart that is rolling...Ch. 8 - A 4.0 × 1010 kg asteroid is heading directly...Ch. 8 - A 55 kg astronaut who weighs 180 N on a distant...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car drives around a flat 200-m-diameter...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car takes a 50-m-radius unbanked curve...Ch. 8 - A 200 g block on a 50-cm-long string swings in a...Ch. 8 - In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 8 - Suppose the moon were held in its orbit not by...Ch. 8 - 10. A highway curve of radius 500 m is designed...Ch. 8 - It is proposed that future space stations create...Ch. 8 - A 5.0 g coin is placed 15 cm from the center of a...Ch. 8 - Mass m1on the frictionless table of FIGURE EX8.13...Ch. 8 - A satellite orbiting the moon very near the...Ch. 8 - What is free-fall acceleration toward the sun at...Ch. 8 - 16. A 9.4 × 1021 kg moon orbits a distant planet...Ch. 8 - Communications satellites are placed in circular...Ch. 8 - A car drives over the top of a hill that has a...Ch. 8 - The weight of passengers on a roller coaster...Ch. 8 - A roller coaster car crosses the top of a circular...Ch. 8 - The normal force equals the magnitude of the...Ch. 8 - A student has 65-cm-long arms. What is the minimum...Ch. 8 - While at the county fair, you decide to ride the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball swings in a vertical circle at the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball moves in a vertical circle on a...Ch. 8 - A heavy ball with a weight of 100 N (m = 10.2 kg)...Ch. 8 - A toy train rolls around a horizontal...Ch. 8 - 28. A new car is tested on a 200-m-diameter track....Ch. 8 - An 85,000 kg stunt plane performs a loop-the-loop,...Ch. 8 - Three cars are driving at 25 m/s along the road...Ch. 8 - Derive Equations 8.3 for the acceleration of a...Ch. 8 - 32. A 100 g bead slides along a frictionless wire...Ch. 8 - 33. Space scientists have a large test chamber...Ch. 8 - 34. A 5000 kg interceptor rocket is launched at an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 8 - 36. A rocket- powered hockey puck has a thrust of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 8 - A 2.0 kg projectile with initial velocity m/s...Ch. 8 - A 75 kg man weighs himself at the north pole and...Ch. 8 - A concrete highway curve of radius 70 m banked at...Ch. 8 - a. an object of mass m swings in horizontal circle...Ch. 8 -
42. You’ve taken your neighbor’s young child to...Ch. 8 - A 4.4-cm-diameter, 24 g plastic ball is attached...Ch. 8 - A charged particle of mass m moving with speed v...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 2.0 kg sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 300 g sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - A conical pendulum is formed by attaching a ball...Ch. 8 - The 10 mg bead in FIGURE P8.48 is free to slide on...Ch. 8 - In an old-fashioned amusement park ride,...Ch. 8 - The ultracentrifuge is an important tool for...Ch. 8 - In an amusement park ride called The Roundup,...Ch. 8 - 52. Suppose you swing a ball of mass m in a...Ch. 8 - A 30 g ball rolls around a 40-cm-diameter L-shaped...Ch. 8 - FIGURE P8.54 shows a small block of mass m sliding...Ch. 8 - The physics of circular motion sets an upper limit...Ch. 8 - A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung in a...Ch. 8 - A 60 g ball is tied to the end of a 50-cm-long...Ch. 8 - Elm Street has a pronounced dip at the bottom of a...Ch. 8 - 59. A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung...Ch. 8 - Scientists design a new particle accelerator in...Ch. 8 - 61. A 1500 kg car starts from rest and drives...Ch. 8 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 8 - 63. A 2.0 kg ball swings in a vertical circle on...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - Sam (75 kg) takes off up a 50-m-high, 10°...Ch. 8 - In the absence of air resistance, a projectile...Ch. 8 - The father of Example 8.2 stands at the summit of...Ch. 8 - A small bead slides around a horizontal circle at...Ch. 8 - A 500 g steel block rotates on a steel table while...Ch. 8 - If a vertical cylinder of water (or any other...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two very long line charges are set up along lines that areparallel to the z-axis, so they set up Electric fields strictly in the xy plane. One goes throughthe x-axis at x = −0.40 m and has charge a density λ1 = +12.0 μC/m, the other goesthrough the x-axis at x = +0.40 m has charge density λ2 = −8.0 μC/m.A. Find the Electric field at point A: (0.40, 0.80) (distances in meters). Give answersin unit vector notation and draw a graph of the x-y plane with the E-fields you justfound.B. Find a point on the x-axis at which the total E-field is 0.arrow_forwardIn order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight. (a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car? ] (b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb? ] (c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system? Eburned Δυarrow_forwardA 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact? Narrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.) a m ha 3.20 m 2.00 m i (a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and point B ©. m/s m/s point (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J A to pointarrow_forwardA 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forwardReport on the percentage errors (with uncertainty) between the value of 'k' from the F vs displacement plot and each of the values of 'k' from the period measurements. Please comment on the goodness of the results. Value of k = Spring constant k = 50.00 N/m Each of the values of k from period measurements: Six Measurements of time for 5 osccilations: t1 = 7.76s, t2=8.00s, t3=7.40s, t4=7.00s, t5=6.90s, t6=7.10s (t1-tavg)^2 = (7.76-7.36)^2 = 0.16%(t2-tavg)^2 =(8.00-7.36)^2 = 0.4096%(t3-tavg)^2 =(7.40-7.36)^2 = 0.0016%(t4-tavg)^2 =(7.00-7.36)^2 = 0.1296%(t5-tavg)^2 =(6.90-7.36)^2 = 0.2116%(t6-tavg)^2 =(7.10-7.36)^2 = 0.0676arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardBased on the two periods (from hand timed and ultrasonic sensor), find the value of 'k' they suggest from the physics and from the value of the hanging mass. hand time period is 1.472s and ultrasonic sensor time period is 1.44sarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Experimental Research Report Template Title: Paper Airplane Flight. Materials: Paper, ruler, tape Procedure: Fold paper into different airplane designs, such as dart, glider, or classic. Measure and record the distances each design flies when thrown with the same force. Discuss aerodynamics and the factors that affect flight distance. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the…arrow_forwardTitle: Studying the Relationship Between Drop Height and Bouncing Height of a Ball: You can drop balls of different materials (e.g., rubber, plastic, ping pong) from various heights onto a flat surface and measure the height of their bounce using a ruler. Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.) Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.) Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.) Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.) Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the lab: tables, charts, graphs, sketches, etc.) Data Analysis: (Explain you…arrow_forwardA traveler at an airport takes an escalator up one floor as in the figure below. The moving staircase would itself carry him upward with vertical velocity component v between entry and exit points separated by height h. However, while the escalator is moving, the hurried traveler climbs the steps of the escalator at a rate of n steps/s. Assume that the height of each step is hs. (a) Determine the amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy by the traveler's leg muscles during his escalator ride given that his mass is m. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) energy = (b) Determine the work the escalator motor does on this person. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.) work =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams With Examples; Author: The Physics Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3rZR7FSSidc;License: Standard Youtube License