
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Structures of the major organic products formed in the reaction of
Concept introduction:
Since
According to Markovnikov’s rule. when an unsymmetrically substituted alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide, hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen and halogen adds to the carbon that has fewer hydrogen.
In hydroboration-oxidation reaction, hydrogen atom gets bonded to the carbon that has fewer hydrogen and the hydroxyl to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen. This is a rule opposite of Markovnikov’s addition.
Answer to Problem 30P
Solution:
a)
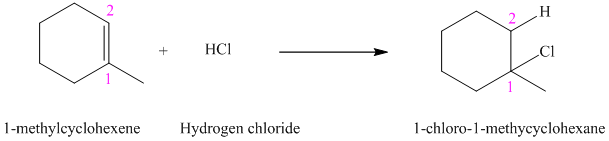
b)
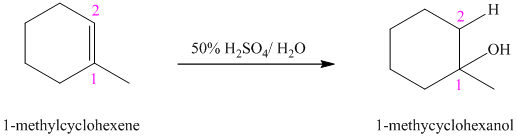
c)
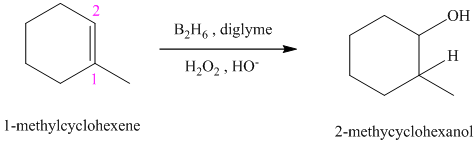
d)
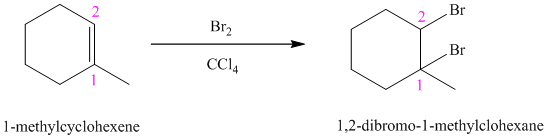
e)
f)
 g)
g)
h)
i)
Explanation of Solution
a) The reaction is as follows:
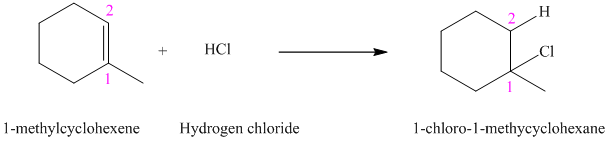
The given alkene
According to Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen chloride gets added to the double bond of
b) The reaction is as follows:
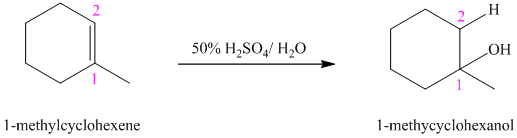
This reaction is an acid catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes. In this reaction, water molecule gets added to the double bond in
In this reaction, the addition of water molecule to alkene follows Markovnikov’s rule. The hydrogen atom in water molecule adds to the carbon
The addition mechanism for this reaction follows Markovnikov’s rule, and so the major organic product for the above acid-catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction is
c) The reaction is as follows:
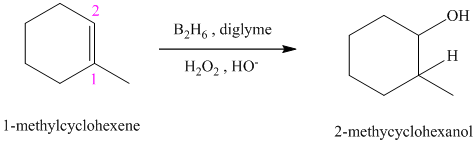
This reaction is the hydroboration-oxidation reaction of alkenes. In this reaction, water molecule gets added to the double bond in
The hydrogen atom from water molecule adds to the carbon
Thus, when
d) The reaction is as follows:
Bromine reacts rapidly with alkenes by electrophilic addition. The products are called vicinal dibromides, meaning that the bromine atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms in the double bond. It is carried out in suitable solvents such as
Bromine adds across the double bond in
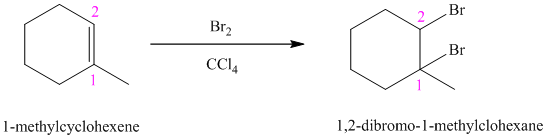
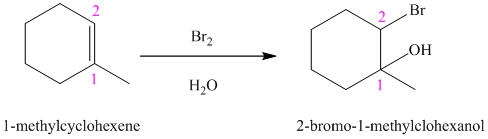
e) The reaction is as follows:
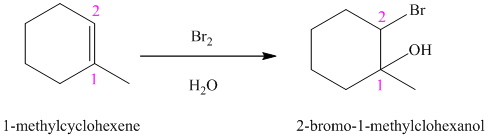
In aqueous solution, chlorine and bromine react with alkenes to give corresponding vicinal halohydrins. Halohydrin compounds have a halogen and hydroxyl group on adjacent carbon atoms. In alkene, halogen atom bonds to that carbon atom which has a larger number of hydrogen and hydroxyl group bonds to that carbon atom which has a smaller number of hydrogen.
In the reaction of
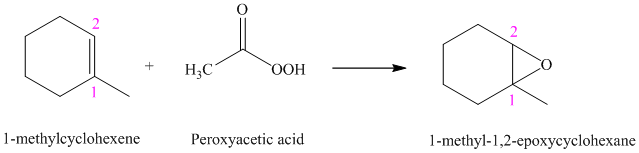
f) The reaction is as follows:
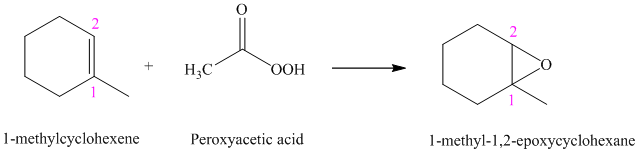
Peroxyacids transfers oxygen to the double bond of an alkene to yield epoxides. An epoxide is a three-membered oxygen-containing ring.
When
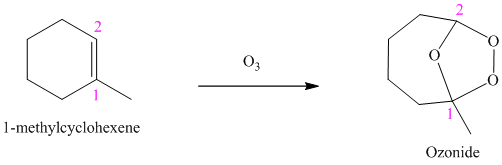
g) The reaction is as follows:
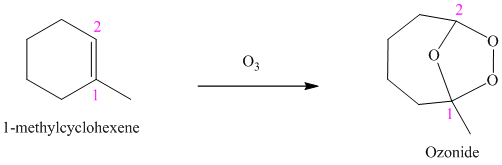
Ozone is a powerful electrophile and reacts with alkenes to cleave the double bond, forming an ozonide.
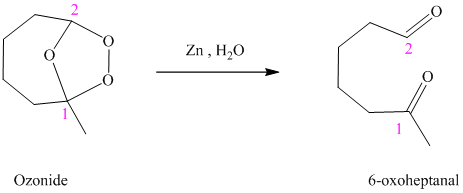
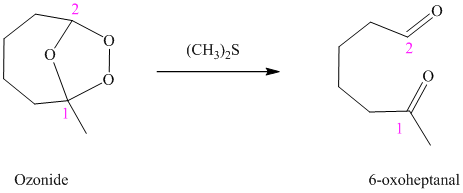
h) The reaction is as follows:
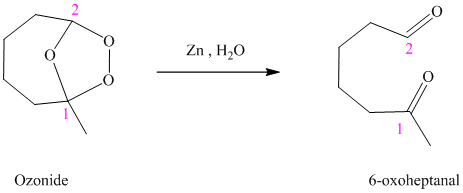
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in water, giving carbonyl compounds. According to the structure of the starting alkene, various carbonyl products are formed such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones.
When the corresponding ozonide of
i) The reaction is as follows:
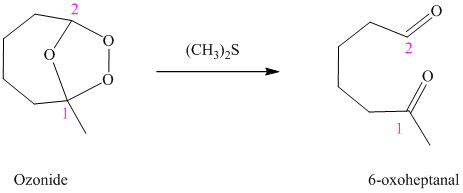
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in water, giving carbonyl compounds. According to the structure of the starting alkene, various carbonyl products are formed such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones.
When corresponding ozonide of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Draw the mechanism for the following reaction: OH A few notes: CI O • You may assume that each reagent is present in whatever amount you need to draw your mechanism. • To save you some time, one of the starting materials has been copied into the first step of the drawing area. AP Add/Remove step Cl Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3 O [0] R CH3-CH-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note: the organic equation above only shows the important organic reactant and product. Minor small-molecule reactants or products (like H₂O) are not shown. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. ×arrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: O CH3 A NH3 + HO–C—CH—CH, P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. A 5arrow_forward
- For a reaction to be spontaneous, the Gibbs Free Energy must be less than zero. True or Falsearrow_forwardWhich of the following reactions will be exothermic? a) Reaction has enthalpy less than zero. b) Reaction has enthalpy greater than zero. c) Reaction has entropy less than zero. d) Reaction has entropy equal to zero.arrow_forwardHow many valence electrons are used in predicting the Lewis Dot structure of CH4? a) 8 b) 6 c) 10 d) 2arrow_forward
- How many valence electrons are used in predicting the Lewis Dot structure of CO2? a) 32 b) 26 c) 24 d) 16arrow_forwardHow many valence electrons are used in predicting the Lewis Dot structure of NO2? a) 17 b) 12 c) 5 d) 10arrow_forwardA compound that is bonded with an ionic bond is unlikely to dissolve in water. True or Falsearrow_forward
- In VSEPR Theory, AX6 is a) linear b) tetrahedral c) octahedral d) trigonal bipyramidarrow_forwardElectronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract an electron pair needed for covalent bonding. True or Falsearrow_forwardA single bond is called a) sigma bond b) pi bond c) hybrid bond d) hydrogen bondarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





