
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9798214171104
Author: Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Custom
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 8, Problem 2E
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The reason the below product are not formed in addition reactions should be explained.
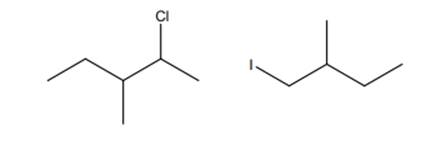
Concept introduction: Alkenes are regarded electron-rich and often undergo addition reaction in presence of electrophilic halo acids or nucleophilic sodium cyanide. The intermediate formed in former is tertiary carbocation and finally nucleophilic part of halo acid attacks in a rapid step to give addition product.
The product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw both of the chair flips for both the cis and trans isomers for the following
compounds:
1,4-diethylcyclohexane
1-methyl-3-secbutylcyclohexane
Ppplllleeeaaasssseeee hellppp wiithhh thisss physical chemistryyyyy
I talked like this because AI is very annoying
For this question, if the product is racemic, input both enantiomers in the same Marvin editor.
A) Input the number that corresponds to the reagent which when added to (E)-but-2-ene will result in a
racemic product.
Input 1 for Cl, in the cold and dark
Input 2 for Oy followed by H₂O, Zn
Input 3 for D₂ with metal catalyst
Input 4 for H₂ with metal catalyst
B) Draw the skeletal structure of the major organic product made from the reagent in part A
Marvin JS
Help
Edit drawing
C) Draw the skeletal structure of the major organic product formed when (2)-but-2-ene is treated with
peroxyacetic acid.
Marvin 35
Help
Chapter 8 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 2CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 8 - Draw the products that result from the electron...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 8 - Draw the products that would result if the arrow...Ch. 8 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 8 - What information (if any) from the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 8 - The reactants, intermediates, final products, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 22CTQCh. 8 - Explain how you can tell from the energy diagram...Ch. 8 - Explain why the following mechanism for hydration...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 26CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 27CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 28CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 29CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 30CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 31CTQCh. 8 - The hydration above is one of a family of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33CTQCh. 8 - Which statement is false? a. A mechanistic step...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 36CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 37CTQCh. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism including the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - Explain why ethene does not react with HX ( X=Cl ,...Ch. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism of each pair of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Prob. 6ECh. 8 - Prob. 7ECh. 8 - Prob. 8ECh. 8 - Prob. 9ECh. 8 - Prob. 10ECh. 8 - Prob. 11ECh. 8 - Prob. 12ECh. 8 - Prob. 15ECh. 8 - A student proposes the following reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17ECh. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Prob. 19E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Michael Reactions 19.52 Draw the products from the following Michael addition reactions. 1. H&C CH (a) i 2. H₂O* (b) OEt (c) EtO H₂NEt (d) ΕΙΟ + 1. NaOEt 2. H₂O' H H 1. NaOEt 2. H₂O*arrow_forwardRank the labeled protons (Ha-Hd) in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic. НОН НЬ OHd Онсarrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? ? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C :0 T Add/Remove step Garrow_forward
- The following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forwardA covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forward
- Which one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning