
For the digraph shown in Fig. 8-25, find
a. the indegree and outdegree of A.
b. the indegree and outdegree of B.
c. the indegree and outdegree of D.
d. the sum of the indegrees of all the vertices.
e. the sum of the outdegrees of all the vertices.
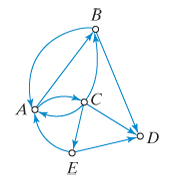
Figure 8-25
(a)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of A in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of A is 3 and out degree of A is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (1).
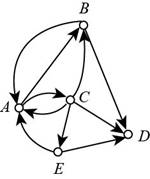
Figure (1)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (1) it can be noticed that there are 3 arcs having their ending vertex as A and 2 arcs having their starting vertex as A.
So, the indegree of A is 3 and outdegree of A is 2.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of A is 3 and outdegree of A is 2.
(b)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of B in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of B is 2 and out degree of B is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (2).
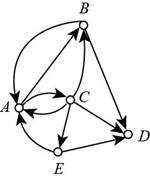
Figure (2)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (2) it can be noticed that there are 2 arcs having their ending vertex as B and 2 arcs having their starting vertex as B.
So, the indegree of B is 2 and outdegree of A is 2.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of B is 2 and outdegree of B is 2.
(c)
To find:
The in degree and out degree of D in the given digraph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The in degree of D is 3 and out degree of D is 0.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (3).
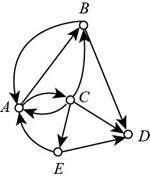
Figure (3)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (3) it can be noticed that there are 3 arcs having their ending vertex as D and no arc having their starting vertex as D.
So, the indegree of D is 3 and outdegree of D is 0.
Conclusion:
Thus, the indegree of D is 3 and outdegree of D is 0.
(d)
To find:
The sum of the in degrees of all the vertices.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The sum of all the indegrees is 10.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (4).

Figure (4)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (4) it can be noticed that there total 10 arcs, so there will be total 10 indegrees for all the vertices.
Conclusion:
Thus, the sum of all the indegrees is 10.
(e)
To find:
The sum of the out degrees of all the vertices.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The sum of all the outdegrees is 10.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given digraph is shown in figure (5).

Figure (5)
Definitions:
Arc:
An arc
Indegree:
For a vertex Y, the number of arcs having Y as their ending vertex is called indegree.
Outdegree:
For a vertex X, the number of arcs having X as their starting vertex is called outdegree.
Calculation:
From figure (5) it can be noticed that there total 10 arcs, so there will be total 10 outdegrees for all the vertices.
Conclusion:
Thus, the sum of all the outdegrees is 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics (9th Edition)
- Calculați (a-2023×b)²⁰²⁴arrow_forwardSee image for questionarrow_forwardA student completed the problem below. Identify whether the student was correct or incorrect. Explain your reasoning. (identification 1 point; explanation 1 point) 4x 3x (x+7)(x+5)(x+7)(x-3) 4x (x-3) (x+7)(x+5) (x03) 3x (x+5) (x+7) (x-3)(x+5) 4x²-12x-3x²-15x (x+7) (x+5) (x-3) 2 × - 27x (x+7)(x+5) (x-3)arrow_forward
- For this question, refer to the a1q4.py Python code that follows the assignment, as well as the dataprovided after the assignment.(a) Modify the code presented to plot the data from the two separate sets of information(from each region).(b) For each population of squirbos, let ` be the length of their front claws and s the mass ofthe skull. Determine for what value of m the s is isometric to `m. Justify it with your log − log plotsfrom (a) and suitable sketched lines.(c) What do you notice about the correlus striatus on your plot?(d) What historically might explain their situation?arrow_forwardPlease see image for question.arrow_forwardQuestion 2 Find the shortest distance between the lines [x, y, z] = [1,0,4] + t[1, 3, −1] and [x, y, z] = [0,2,0] + s[2, 1, 1]. [Do not use derivatives.]arrow_forward
- Please see image for the questions.arrow_forward2 Add the rational expressions below. Can you add them in this original form? Explain why or why not. 3x-7 5x + x² - 7x+12 4x-12 Show all steps. State your least common denominator and explain in words your process on how you determined your least common denominator. Be sure to state your claim, provide your evidence, and provide your reasoning before submitting.arrow_forwardIf xs2 + yt2 = 1, and x2s + y2t = xy − 4, find ∂x/∂s, ∂x/∂t, ∂y/∂s, ∂y/∂t at (x, y, s, t) = (1, −3, 2, −1).Hint: do the derivatives first before inserting numerical values.arrow_forward

 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285195728Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell





