
Concept explainers
The equation for unknown flow rates or diameters for each pipe section in the pipe networks and branching pipes.
The analogy between the electric current in electric circuits and fluid flow in pipe networks.
Answer to Problem 186P
The total discharge in the branched pipe is
The analogy of network pipe is
Explanation of Solution
The following figure represents the branched pipes.
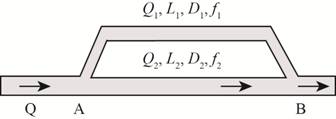
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the area of pipe.
Here, the diameter of pipe is
Write the expression for the discharge rate in the pipe.
Here, the discharge in the pipe is
Write the expression for head loss in the pipe.
Here, the loss head is
Write the expression for total discharge in branched pipes.
Here, the total discharge in pipe is
Write the expression for head loss in the pipe 1.
Here, the velocity in pipe 1 is
Write the expression for head loss in the pipe 2.
Here, the velocity in pipe 2 is
The following figure represents the T-pipe network.
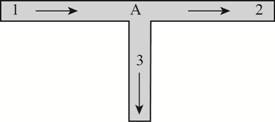
Figure (2)
Write the expressions for head loss in pipe 1.
Write the expressions for head loss in pipe 2.
Write the expressions for head loss in pipe 3.
Here, the discharge in pipe 3 is
Write the expression for loop method.
Here, the analogy of network pipe is
Calculation:
Substitute
Here, the area of pipe 1 is
Substitute
Here, the area of pipe 2 is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The total discharge in the branched pipe is
Substitute
The analogy of network pipe is
Conclusion:
The analogy of network pipe is
The total discharge in the branched pipe is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Let Hill frame H = {i-hat_r, i-hat_θ, i-hat_h} be the orbit frame of the LMO satellite. These base vectors are generally defined as:i-hat_r = r_LM / |r_LM|, i-hat_theta = i-hat_h X i-hat_r, i-hat_h = r_LM X r-dot_LMO /( | r_LM X r-dot_LMO | ) How would you: • Determine an analytic expressions for [HN]arrow_forwardDe Moivre’s Theoremarrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forward
- Determine the shear flow qqq for the given profile when the shear forces acting at the torsional center are Qy=30Q_y = 30Qy=30 kN and Qz=20Q_z = 20Qz=20 kN. Also, calculate qmaxq_{\max}qmax and τmax\tau_{\max}τmax. Given:Iy=10.5×106I_y = 10.5 \times 10^6Iy=10.5×106 mm4^44,Iz=20.8×106I_z = 20.8 \times 10^6Iz=20.8×106 mm4^44,Iyz=6×106I_{yz} = 6 \times 10^6Iyz=6×106 mm4^44. Additional parameters:αy=0.5714\alpha_y = 0.5714αy=0.5714,αz=0.2885\alpha_z = 0.2885αz=0.2885,γ=1.1974\gamma = 1.1974γ=1.1974. (Check hint: τmax\tau_{\max}τmax should be approximately 30 MPa.)arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forwardIn the bending of a U-profile beam, the load path passes through the torsional center C, causing a moment of 25 kNm at the cross-section under consideration. Additionally, the beam is subjected to an axial tensile force of 100 kN at the centroid. Determine the maximum absolute normal stress.(Check hint: approximately 350 MPa, but where?)arrow_forward
- ### Make an introduction to a report of a rocket study project, in the OpenRocket software, where the project consists of the simulation of single-stage and two-stage rockets, estimating the values of the exhaust velocities of the engines used, as well as obtaining the graphs of "altitude", "mass ratio x t", "thrust x t" and "ψ × t".arrow_forwardA 6305 ball bearing is subjected to a steady 5000-N radial load and a 2000-N thrust load and uses a very clean lubricant throughout its life. If the inner race angular velocity is 500 rpm find The equivalent radial load the L10 life and the L50 lifearrow_forwardWhere on the below beam is the Maxiumum Slope likely to occur? C A; Атят Barrow_forward
- What is the moment of Inertia of this body? What is Ixx, Iyy, and Izzarrow_forwardi need the The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing at AA and a smooth journal bearing at BB. Draw the shear diagram for the shaft. Follow the sign convention.arrow_forward4- In the system shown in the figure, the water velocity in the 12 in. diameter pipe is 8 ft/s. Determine the gage reading at position 1. Elevation 170 ft 1 Elevation 200 ft | 8 ft, 6-in.-diameter, 150 ft, 12-in.-diameter, f = 0.020 f = 0.020 A B Hints: the minor losses should consider the contraction loss at A and the expansion loss at B.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





