
Concept explainers
Sales and Production Budgets L08—2, L08—3
The marketing department of Jessi Corporation has submitted the following sales
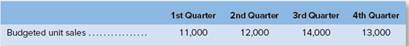
The selling price of the company’s product is S 18.00 per unit. Management expects to collect 65% of sales in the quarter in which the sales are made, 30% in the following quarter, and 50% of sales are expected to be uncollectible. The beginning balance of
The company expects to start the first quarter with 1.650 units in finished goods inventory. Management desires an ending finished goods inventory in each quarter equal to 15% of the next quarter’s budgeted sales. The desired ending finished goods inventory for the fourth quarter is 1,850 units.
Required:
1. Calculate the estimated sales for each quarter of the fiscal year and for the year as a whole. (Hints Refer to Schedule 1 for guidance.)
2. Calculate the expected cash collections for each quarter of the fiscal year and for the year as a whole. (Hint: Refer to Schedule 1 for guidance.)
3. Calculate the required production in units of finished goods for each quarter of the fiscal year and for the year as a whole. (Hint: Refer to Schedule 2 for guidance.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- If total debits exceed total credits on a trial balance, the difference is most likely:A. A net lossB. A recording errorC. A net incomeD. An overstatement of assetsarrow_forwardWhich of the following accounts would be found on the post-closing trial balance?A. Service RevenueB. Salaries ExpenseC. Retained EarningsD. Dividendsarrow_forwardNeed answer What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forward
- No chatgpt What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forwardWhat type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenueneed helparrow_forwardno ai What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forward
- What type of account is Service Revenue?A. AssetB. LiabilityC. EquityD. Revenuearrow_forwardNo chatgpt Which of the following would be found in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement?A. Cash received from issuing sharesB. Cash paid for dividendsC. Cash paid for new equipmentD. Cash received from customersarrow_forwardWhich of the following would be found in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement?A. Cash received from issuing sharesB. Cash paid for dividendsC. Cash paid for new equipmentD. Cash received from customersno aiarrow_forward
- Which of the following would be found in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement?A. Cash received from issuing sharesB. Cash paid for dividendsC. Cash paid for new equipmentD. Cash received from customerhelo mearrow_forwardHelp Which of the following would be found in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement?A. Cash received from issuing sharesB. Cash paid for dividendsC. Cash paid for new equipmentD. Cash received from customersarrow_forwardWhich of the following would be found in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement?A. Cash received from issuing sharesB. Cash paid for dividendsC. Cash paid for new equipmentD. Cash received from customersarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning



