
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118233764
Author: David Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 133P
Conservative force F(x) acts on a particle that moves along an x axis. Figure 8-72 shows how the potential energy U(x) associated with force F(x) varies with the position of the particle, (a) Plot F(x) for the range 0 < x < 6 m. (b) The mechanical energy E of the system is 4.0 J. Plot the kinetic energy K(x) of the particle directly on Fig. 8-72
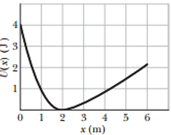
Figure 8-72 Problem 133.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The figure gives the acceleration a versus time t for a particle moving along an x axis. The a-axis scale is set by as = 12.0 m/s². At t = -2.0
s, the particle's velocity is 11.0 m/s. What is its velocity at t = 6.0 s?
a (m/s²)
as
-2
0
2
t(s)
4
Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that the average normal stress must not
exceed 150 MPa in either rod, determine the smallest allowable values of the diameters d₁ and d2. Take P= 85 kN.
P
125 kN
B
125 kN
C
0.9 m
1.2 m
The smallest allowable value of the diameter d₁ is
The smallest allowable value of the diameter d₂ is
mm.
mm.
Westros, from Game of Thrones, has an area of approximately 6.73⋅106 miles26.73⋅106miles2. Convert the area of Westros to km2 where 1.00 mile = 1.609 km.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-18, a horizontally moving block can take...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-19 gives the potential energy function of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-20 shows one direct path and four...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-21, a small, initially stationary block...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-22, a block slides from A to C along a...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-23a, you pull upward on a rope that is...Ch. 8 - The arrangement shown in Fig. 8-24 is similar to...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-25, a block slides along a track that...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-26 shows three situations involving a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-27 shows three plums that are launched...
Ch. 8 - When a particle moves from f to i and from j to i...Ch. 8 - SSM What is the spring constant of a spring that...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-29, a single frictionless roller-coaster...Ch. 8 - You drop a 2.00 kg book to a friend who stands on...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-31 shows a ball with mass m = 0.341 kg...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-32, a 2.00 g ice flake is released...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-33, a small block of mass m = 0.032 kg...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a thin rod, of length L = 2.00 m...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg snowball is fired from a cliff 12.5 m...Ch. 8 - GO In Problem 2, what is the speed of the car at a...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 3, what is the speed of the book when...Ch. 8 - SSM WWW a In Problem 5, what is the speed of the...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 8, using energy techniques rather...Ch. 8 - SSM A 5.0 g marble is fired vertically upward...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 4, what initial speed must be given...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-35, a runaway truck with failed...Ch. 8 - A 700 g block is released from rest at height h0...Ch. 8 - In Problem 6, what are the magnitudes of a the...Ch. 8 - a In Problem 7, what is the speed of the ball at...Ch. 8 - GO Figure 8-36 shows an 8.00 kg stone at rest on a...Ch. 8 - GO A pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg stone swinging...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a pendulum of length L = 1.25 m....Ch. 8 - A 60 kg skier starts from rest at height H = 20 m...Ch. 8 - ILW The string in Fig. 8-38 is L = 120 cm long,...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 2.0 kg is dropped from height...Ch. 8 - At t = 0 a 1.0 kg ball is thrown from a tall tower...Ch. 8 - A conservative force F=(6.0x12)i N, where x is in...Ch. 8 - Tarzan, who weighs 688 N, swings from a cliff at...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-41a applies to the spring in a cork gun...Ch. 8 - SSM WWW In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 12 kg is...Ch. 8 - GO A 2.0 kg breadbox on a frictionless incline of...Ch. 8 - ILW A block with mass m = 2.00 kg is placed...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-45, a chain is held on a frictionless...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-46, a spring with k = 170 N/m is at...Ch. 8 - GO A boy is initially seated on the top of a...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-42, a block of mass m = 3.20 kg...Ch. 8 - GO Two children are playing a game in which they...Ch. 8 - A uniform cord of length 25 cm and mass 15 g is...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-49 shows a plot of potential energy U...Ch. 8 - GO Figure 8-50 shows a plot of potential energy U...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a diatomic molecule a...Ch. 8 - A single conservative force Fx acts on a 1.0 kg...Ch. 8 - A worker pushed a 27 kg block 9.2 m along a level...Ch. 8 - A collie drags its bed box across a floor by...Ch. 8 - A horizontal force of magnitude 35.0 N pushes a...Ch. 8 - SSM A rope is used to pull a 3.57 kg block at...Ch. 8 - An outfielder throws a baseball with an initial...Ch. 8 - A 75 g Frisbee is thrown from a point 1.1 m above...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-51, a block slides down an incline. As...Ch. 8 - SSM ILW A 25 kg bear slides, from rest, 12 m down...Ch. 8 - A 60 kg skier leaves the end of a ski-jump ramp...Ch. 8 - During a rockslide, a 520 kg rock slides from rest...Ch. 8 - A large fake cookie sliding on a horizontal...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-52, a 3.5 kg block is accelerated...Ch. 8 - A child whose weight is 267 N slides down a 6.1 m...Ch. 8 - ILW In Fig. 8-53, a block of mass m = 2.5 kg...Ch. 8 - You push a 2.0 kg block against a horizontal...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-54, a block slides along a track from...Ch. 8 - A cookie jar is moving up a 40 incline. At a point...Ch. 8 - A stone with a weight of 5.29 N is launched...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - When a click beetle is upside down on its back, it...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-55, a block slides along a path that...Ch. 8 - The cable of the 1800 kg elevator cab in Fig. 8-56...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-57, a block is released from rest at...Ch. 8 - GO A particle can slide along a track with...Ch. 8 - A 3.2 kg sloth hangs 3.0 m above the ground. a...Ch. 8 - SSM A spring k = 200 N/m is fixed at the top of a...Ch. 8 - From the edge of a cliff, a 0.55 kg projectile is...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-60, the pulley has negligible mass,...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-38, the string is L = 120 cm long,...Ch. 8 - SSM In Fig. 8-51, a block is sent sliding down a...Ch. 8 - Two snowy peaks are at heights H = 850 m and h =...Ch. 8 - SSM The temperature of a plastic cube is monitored...Ch. 8 - A skier weighing 600 N goes over a frictionless...Ch. 8 - SSM To form a pendulum, a 0.092 kg ball is...Ch. 8 - We move a particle along an x axis, first outward...Ch. 8 - SSM A conservative force Fx acts on a 2.00 kg...Ch. 8 - At a certain factory, 300 kg crates are dropped...Ch. 8 - SSM A 1500 kg car begins sliding down a 5.0...Ch. 8 - In Fig. 8-65, a 1400 kg block of granite is pulled...Ch. 8 - A particle can move along only an x axis, where...Ch. 8 - For the arrangement of forces in Problem 81, a...Ch. 8 - SSM A 15 kg block is accelerated at 2.0 m/s2 along...Ch. 8 - A certain spring is found not to conform to Hookes...Ch. 8 - SSM Each second, 1200 m3 of water passes over a...Ch. 8 - GO In Fig. 8-67, a small block is sent through...Ch. 8 - SSM A massless rigid rod of length L has a ball of...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg water balloon is shot straight up with...Ch. 8 - A 2.50 kg beverage can is thrown directly downward...Ch. 8 - A constant horizontal force moves a 50 kg trunk...Ch. 8 - GO Two blocks, of masses M = 2.0 kg and 2M, are...Ch. 8 - A volcanic ash flow is moving across horizontal...Ch. 8 - A playground slide is in the form of an arc of a...Ch. 8 - The luxury liner Queen Elizabeth 2 has a...Ch. 8 - A factory worker accidentally releases a 180 kg...Ch. 8 - If a 70 kg baseball player steals home by sliding...Ch. 8 - A 0.50 kg banana is thrown directly upward with an...Ch. 8 - A metal tool is sharpened by being held against...Ch. 8 - A swimmer moves through the water at an average...Ch. 8 - An automobile with passengers has weight 16 400 N...Ch. 8 - A 0.63 kg ball thrown directly upward with an...Ch. 8 - The summit of Mount Everest is 8850 m above sea...Ch. 8 - A sprinter who weighs 670 N runs the first 7.0 m...Ch. 8 - A 20 kg object is acted on by a conservative force...Ch. 8 - A machine pulls a 40 kg trunk 2.0 m up a 40 ramp...Ch. 8 - Prob. 106PCh. 8 - The only force acting on a particle is...Ch. 8 - In 1981, Daniel Goodwin climbed 443 m up the...Ch. 8 - A 60.0 kg circus performer slides 4.00 m down a...Ch. 8 - A 5.0 kg block is projected at 5.0 m/s up a plane...Ch. 8 - A 9.40 kg projectile is fired vertically upward....Ch. 8 - A 70.0 kg man jumping from a window lands in an...Ch. 8 - A 30 g bullet moving a horizontal velocity of 500...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car starts from rest on a horizontal...Ch. 8 - A 1.50 kg snowball is shot upward at an angle of...Ch. 8 - A 68 kg sky diver falls at a constant terminal...Ch. 8 - A 20 kg block on a horizontal surface is attached...Ch. 8 - Resistance to the motion of an automobile consists...Ch. 8 - SSM A 50 g ball is thrown from a window with an...Ch. 8 - A spring with a spring constant of 3200 N/m is...Ch. 8 - A locomotive with a power capability of 1.5 MW can...Ch. 8 - SSM A 0.42 kg shuffleboard disk is initially at...Ch. 8 - A river descends 15 m through rapids. The speed of...Ch. 8 - The magnitude of the gravitational force between a...Ch. 8 - Approximately 5.5 106 kg of water falls 50 m over...Ch. 8 - To make a pendulum, a 300 g ball is attached to...Ch. 8 - In a circus act, a 60 kg clown is shot from a...Ch. 8 - A 70 kg firefighter slides, from rest, 4.3 m down...Ch. 8 - The surface of the continental United States has...Ch. 8 - A spring with spring constant k = 200 N/m is...Ch. 8 - Fasten one end of a vertical spring to a ceiling,...Ch. 8 - The maximum force you can exert on an object with...Ch. 8 - Conservative force Fx acts on a particle that...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-73a shows a molecule consisting of two...Ch. 8 - Repeat Problem 83, but now with the block...Ch. 8 - A spring with spring constant k = 620 N/m is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
11.57 Draw the cis and trans isomers for each of the following: (11.6)
a. 2-pentene
b. 3-hexene
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Modified True/False 6. __________ Halophiles inhabit extremely saline habitats, such as the Great Salt Lake.
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Correct any incorrect equations. If no reaction occurs, write NO REACTION. a. Ba(NO3)2(aq)+(NH4)2SO4(aq)BaSO4(s...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
The pHactivity profile for glucose-6-phosphate isomerase indicates the participation of a group with a pKa = 6....
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) What is the lenght of x? b) Findθ c) Find ϕarrow_forwardA surveyor measures the distance across a straight river by the following method: Starting directly across from a tree on the opposite bank, he walks x = 97.7 m along the riverbank to establish a baseline. Then he sights across to the tree. The angle from his baseline to the tree is θ = 33.0 °. How wide is the river?arrow_forwardA small turtle moves at a speed of 697. furlong/fortnight. Find the speed of the turtle in centimeters per second. Note that 1.00 furlong = 220. yards, 1.00 yard = 3.00 feet, 1.00 foot = 12.0 inches, 1.00 inch = 2.54 cm, and 1.00 fortnight = 14.0 days.arrow_forward
- The landmass of Sokovia lifted in the air in Avengers: Age of Ultron had a volume of about 1.98 km3. What volume is that in m3?arrow_forwardA fathom is a unit of length, usually reserved for measuring the depth of water. A fathom is exactly 6.00 ft in length. Take the distance from Earth to the Moon to be 252,000 miles, and use the given approximation to find the distance in fathoms. 1 mile = 5280 ft. (Answer in sig fig.)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- One of the earliest video games to have a plot, Zork, measured distances in “Bloits” where 1 Bloit was defined as the distance the king’s favorite pet could run in one hour, 1,090 m. In the same game the king has a statue made that is 9.00 Bloits high. What is this in meters?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Defination of voltagearrow_forwardAt point A, 3.20 m from a small source of sound that is emitting uniformly in all directions, the intensity level is 58.0 dB. What is the intensity of the sound at A? How far from the source must you go so that the intensity is one-fourth of what it was at A? How far must you go so that the sound level is one-fourth of what it was at A?arrow_forwardMake a plot of the acceleration of a ball that is thrown upward at 20 m/s subject to gravitation alone (no drag). Assume upward is the +y direction (and downward negative y).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7u6pIfUVy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY