
Concept explainers
a.
To observe what happens when the given function is multiplied by a constant between 0 and 1.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Let
Now multiply the given function with any value between 0 and 1, say
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of f (x) |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| -1 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| -2 | 0.25 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of g (x) |
| 0 | 0.33 |
| 1 | 0.67 |
| -1 | 0.167 |
| 2 | 1.33 |
| -2 | 0.833 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Plotting both the graphs on the same plane:
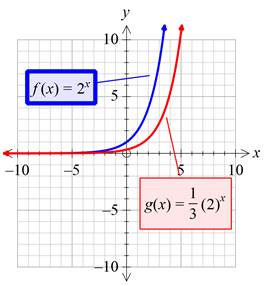
Interpretation:
By multiplying the given function with a value between 0 and 1, it is found that the new function becomes the non-rigid transform of the given function which is vertically shrink by a factor of the number multiplied to the given function, which is
b.
To describe the graph as the constant approaches 0
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Let
Now multiply the given function with any value between 0 and 1, say
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of f (x) |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| -1 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| -2 | 0.25 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of g (x) |
| 0 | 0.33 |
| 1 | 0.67 |
| -1 | 0.167 |
| 2 | 1.33 |
| -2 | 0.833 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Plotting both the graphs on the same plane:
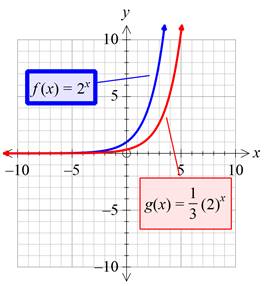
Interpretation:
By multiplying the given function with a value between 0 and 1, it is found that the new function becomes the non-rigid transform of the given function which is vertically shrink by a factor of the number multiplied to the given function, which is
So, as the value of the constant multiplied, the function decreases and approach to zero the curve and will tend to become flat and ultimately become flat as the value of constant multiplied tends to 0.
c.
To observe what happens when the given function is multiplied by a constant greater than 1.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Let
Now multiply the given function with any value greater than 1, say 3.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of f (x) |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| -1 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| -2 | 0.25 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of g (x) |
| 0 | 3 |
| 1 | 6 |
| -1 | 3 |
| 2 | 12 |
| -2 | 0.75 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Plotting both the graphs on the same plane:
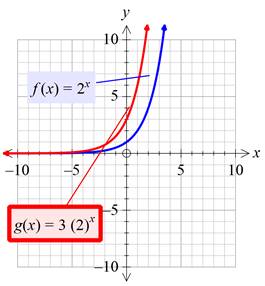
Interpretation:
By multiplying the given function with a value greater than 1, it is found that the new function becomes the non-rigid transform of the given function which is vertically stretched by a factor of the number multiplied to the given function, which is 3 in this case.
d.
To describe the graph as the constant approaches
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Let
Now multiply the given function with any value between 0 and 1, say 3.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of f (x) |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| -1 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| -2 | 0.25 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of g (x) |
| 0 | 3 |
| 1 | 6 |
| -1 | 3 |
| 2 | 12 |
| -2 | 0.75 |
From the above table the graph can be plotted.
Plotting both the graphs on the same plane:
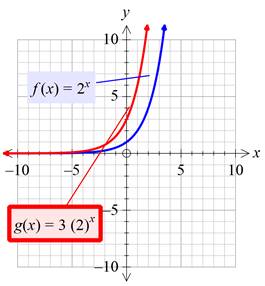
Interpretation:
By multiplying the given function with a greater value, it is found that the new function becomes the non-rigid transform of the given function which is vertically stretch by a factor of the number multiplied to the given function, which is 3 in this case.
So, as the value of the constant multiplied is increases and approach to
Chapter 7 Solutions
Algebra 1, Homework Practice Workbook (MERRILL ALGEBRA 1)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Precalculus
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





